The document discusses the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) in the Indian Constitution. It provides 3 key points:
1. Part IV of the Indian Constitution outlines the DPSP, which prescribe the fundamental obligations of the state to its citizens and establish a welfare state through socio-economic justice.
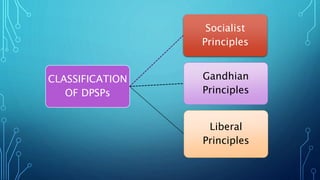
2. The DPSP are classified into socialist principles, Gandhian principles, and liberal principles based on their ideological influences.
3. Several amendments have been made to the DPSP over time to strengthen them and make basic education a fundamental right. However, the DPSP remain non-justiciable and establish the economic and social aims of governance in India.