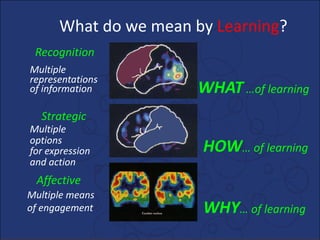
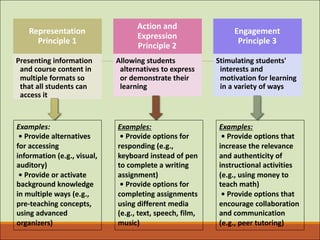
Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an educational framework that provides flexibility in how information is presented, how students respond or demonstrate knowledge, and how students are engaged to meet the needs of all learners. UDL is designed from the beginning to be inclusive rather than adding accommodations later. It aims to reduce barriers in instruction and increase access for all students through multiple means of representation, action and expression, and engagement. Key aspects of UDL implementation include flexible learning environments, assignment options, regular feedback, and accessible digital materials. UDL benefits all students by considering individual differences.