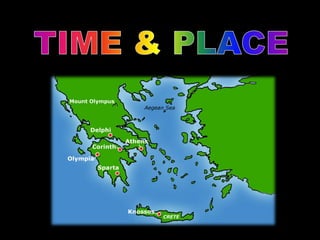
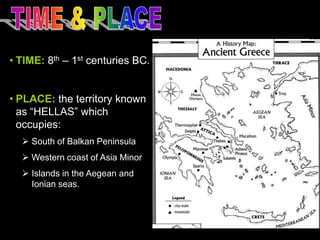
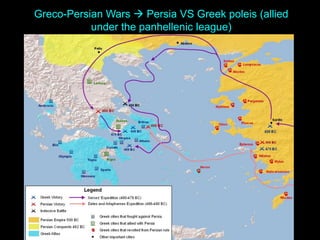
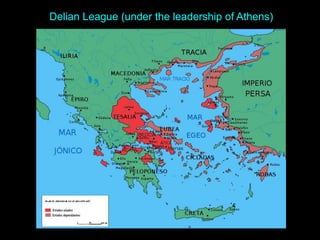
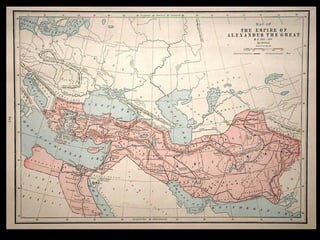
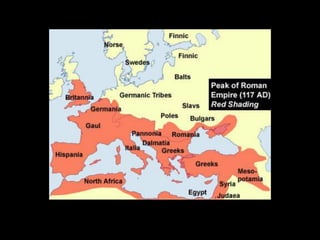
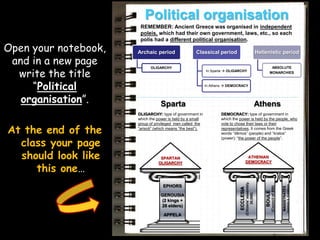
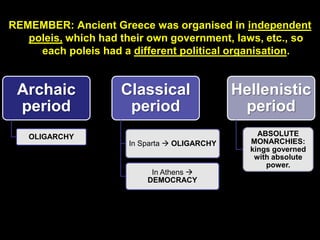
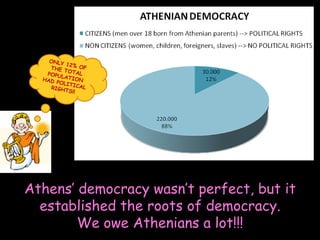
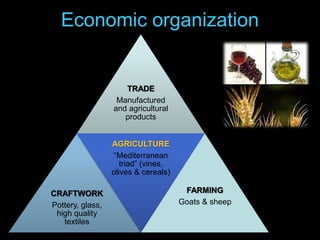
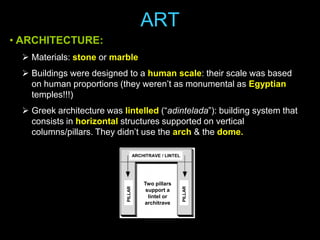
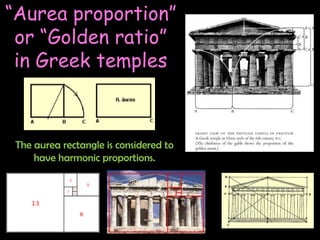
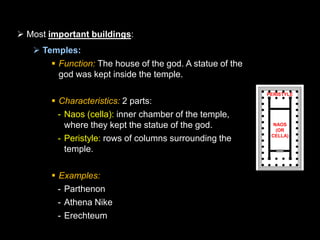
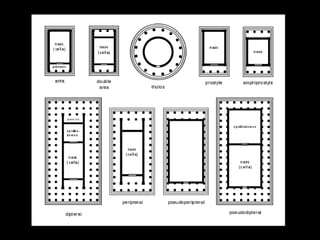
Ancient Greek civilization developed between the 8th-1st centuries BC in the territory of Hellas, which included the southern Balkan Peninsula, western coast of Asia Minor, and Aegean and Ionian islands. The geography of Hellas, characterized by mountains and islands, made unification difficult and led to the development of independent city-states called poleis such as Athens and Sparta. During this period, the Greeks also began colonizing the coasts of the Black and Mediterranean Seas. Ancient Greek civilization is typically divided into the Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic periods, during which time democracy was invented in Athens and the territory was later conquered by Macedon and incorporated into Hellenistic empires before