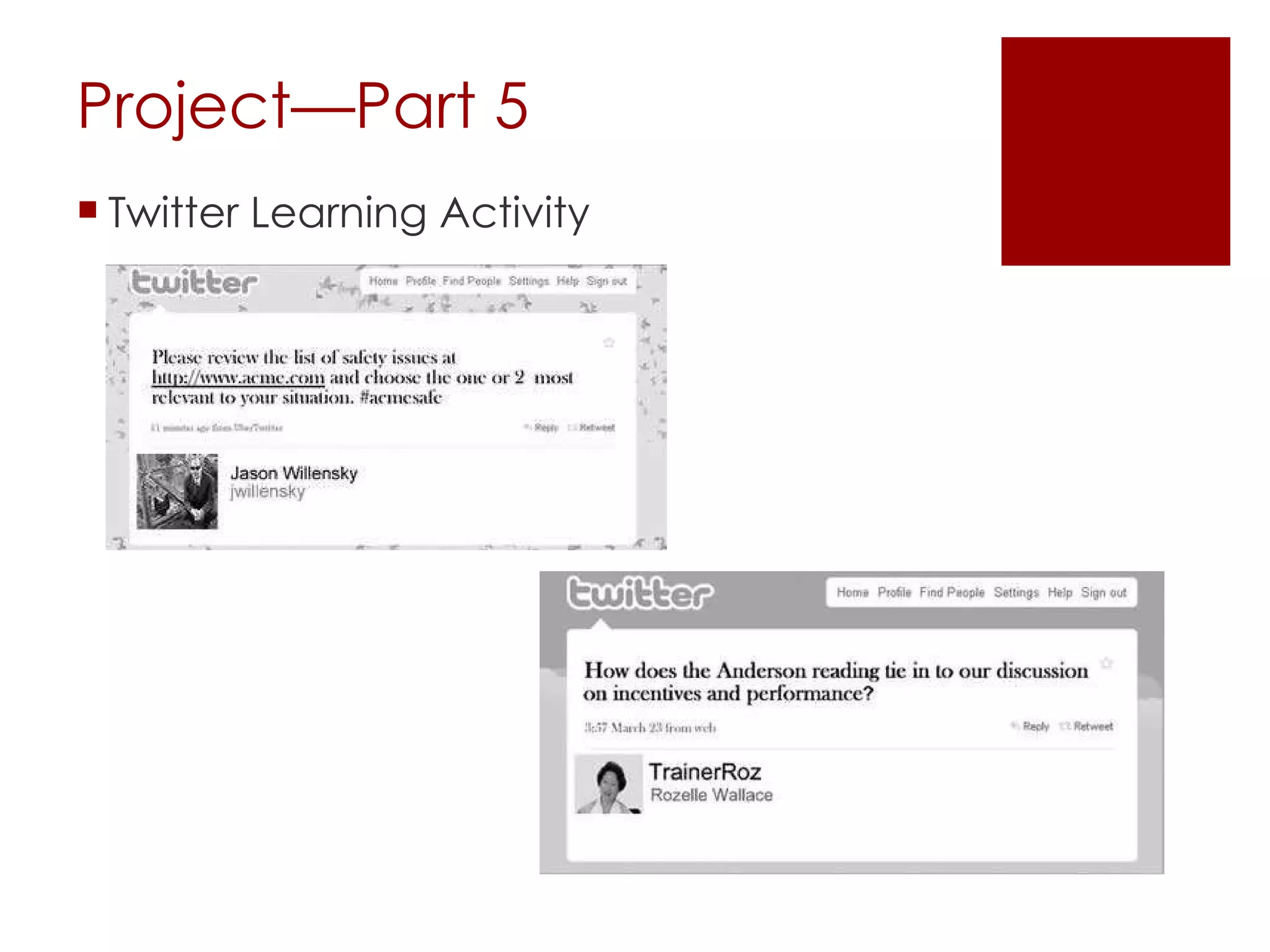
This document provides an overview of the syllabus for an online course on integrating technology across the curriculum. It outlines required and recommended texts, as well as a multi-part educational internet portfolio project. This project involves creating instructional elements like a webquest, learning objects, an online video, blog, Twitter activity, bookmarks, wiki, educational game, and activities using productivity apps. It also provides a timeline of key internet developments and discusses tools for effective internet research and use of online resources.