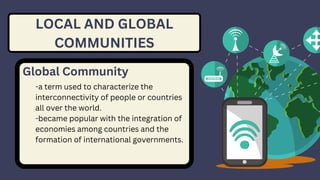
The document discusses various typologies of communities, introducing concepts such as Gemeinschaft and Gesellschaft, defined by sociologist Ferdinand Tonnies. It categorizes communities into urban, rural, suburban, and rurban, highlighting their different characteristics. Additionally, it details local and global communities along with various community sectors, including public, private, voluntary, and for-benefit sectors, as well as the concept of social spaces.