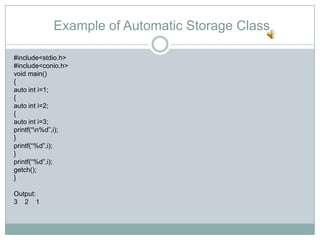
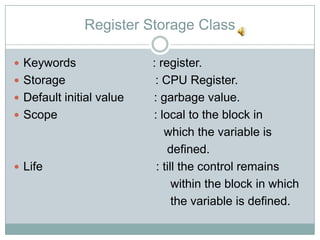
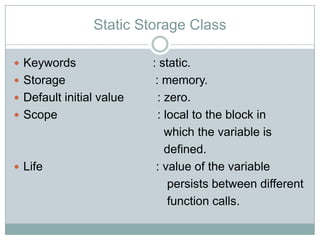
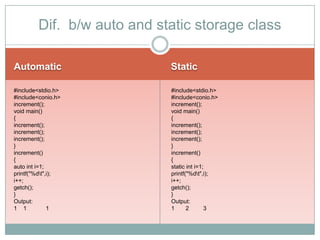
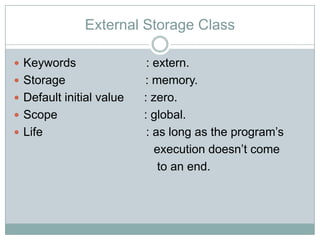
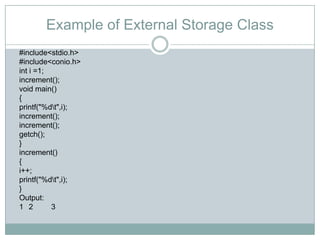
The storage class determines where a variable is stored in memory (CPU registers or RAM) and its scope and lifetime. There are four storage classes in C: automatic, register, static, and external. Automatic variables are stored in memory, have block scope, and are reinitialized each time the block is entered. Register variables try to store in CPU registers for faster access but may be stored in memory. Static variables are also stored in memory but retain their value between function calls. External variables have global scope and lifetime across the entire program.