The document discusses different types of probability events:
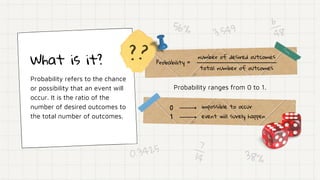
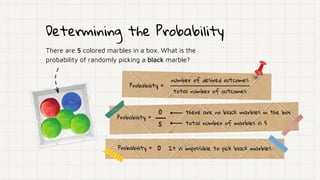
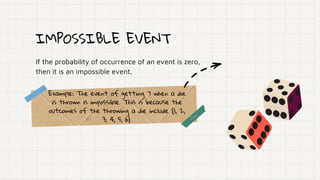
- Sure events have a probability of 1 and will always occur. Impossible events have a probability of 0.
- Complementary events cover all possible outcomes such that one event must occur.
- Mutually exclusive events cannot occur together, while mutually inclusive events can occur simultaneously.
- Exhaustive events together cover all possible outcomes such that one is sure to occur. Equally likely events have outcomes that are equally possible.
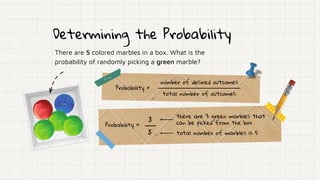
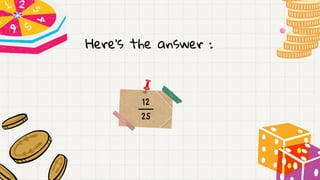
- An example calculates the probability of randomly selecting a number greater than 13 from numbers 1 to 25. The probability is 12/25.