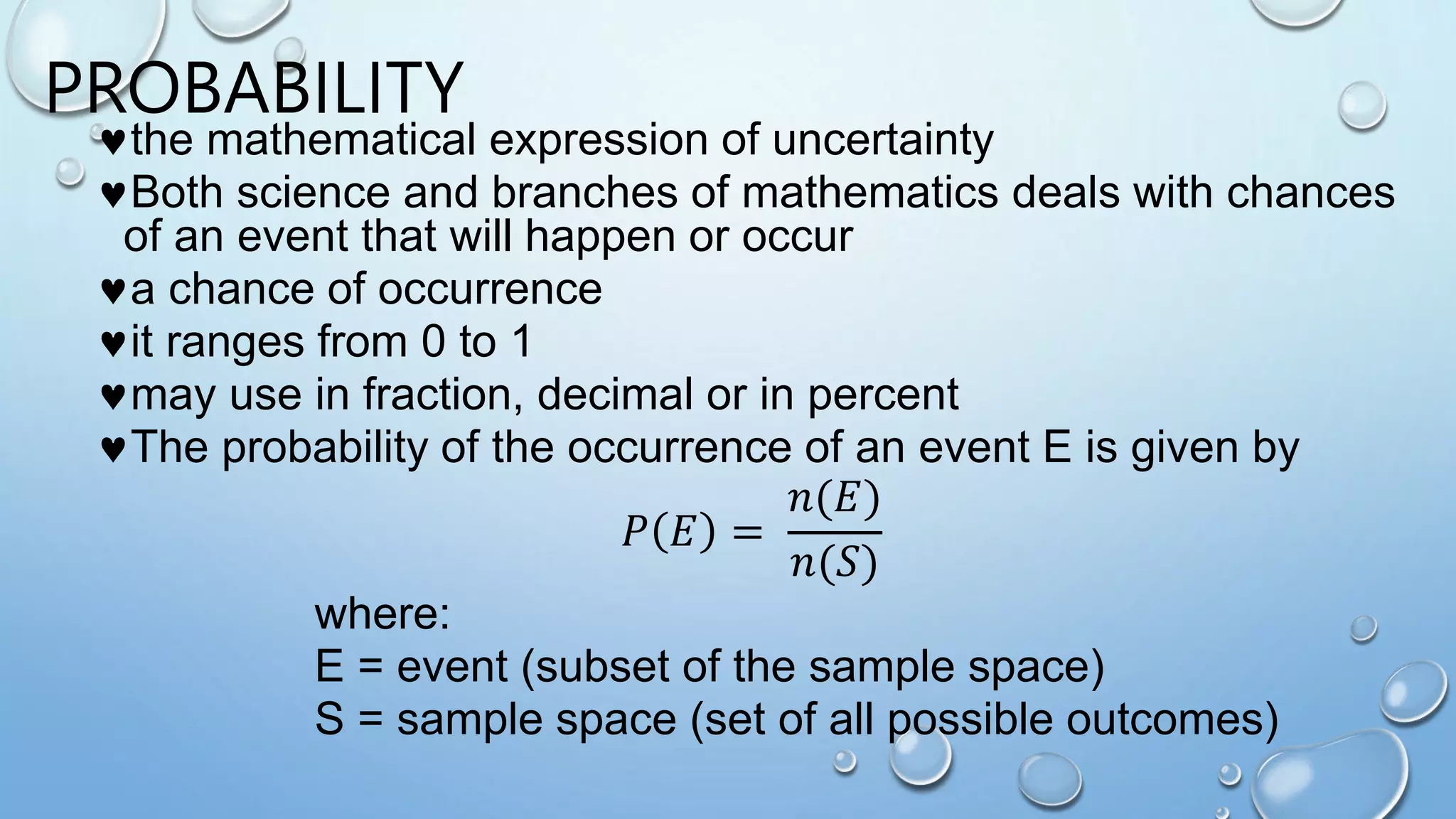
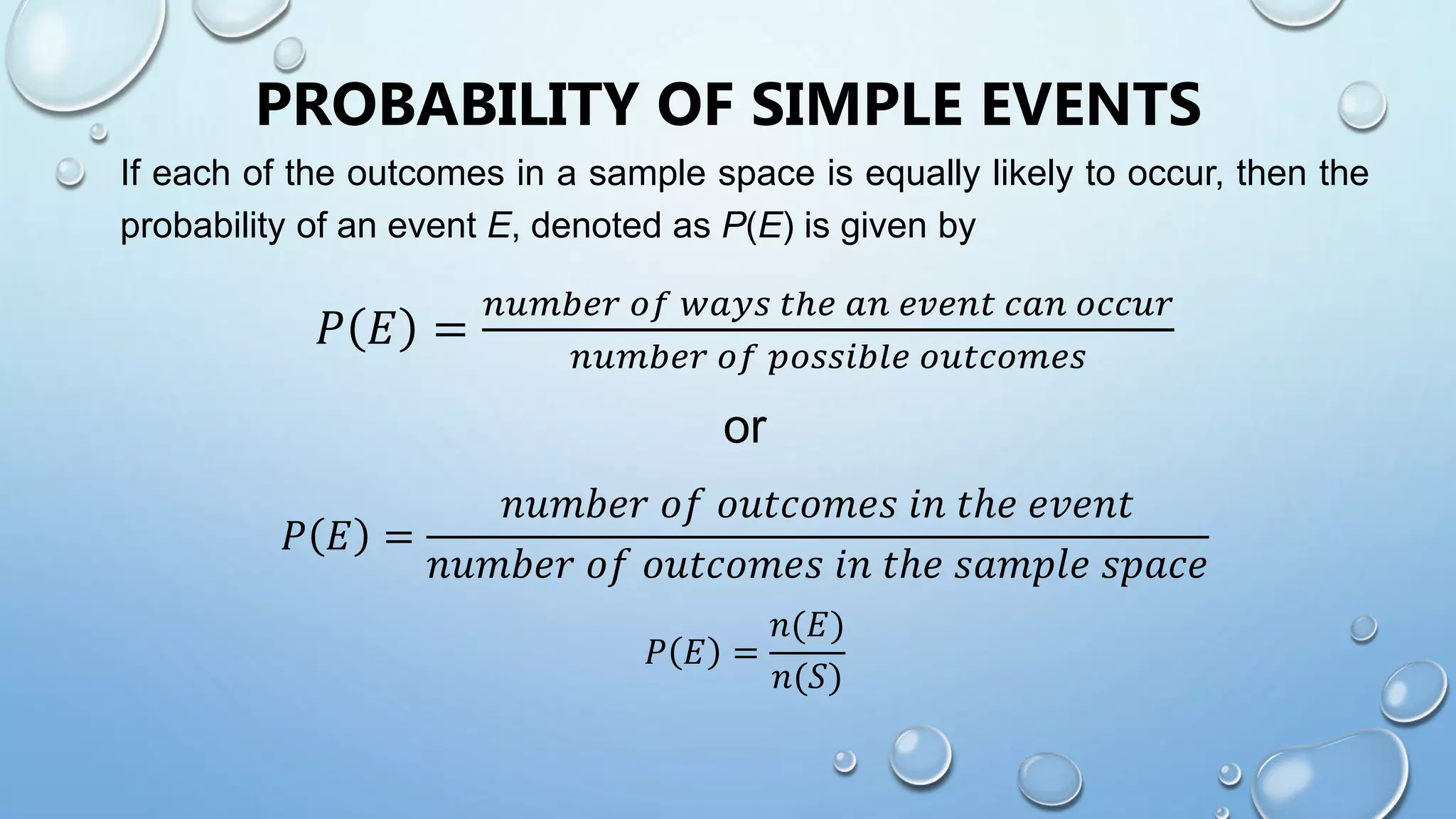
Here are the probabilities of the compound events in the assignment:
1a) The probability of drawing an 8 or 16 is 2/20 = 0.1
1b) The probability of drawing a 5 or a number divisible by 3 is 11/20
1c) The probability of drawing an odd number or a number divisible by 3 is 17/20
1d) The probability of drawing a number divisible by 3 or divisible by 4 is 19/20
2) The probability of drawing a violet marble or a pink marble is 40/52
3) The probability that a randomly selected household has a rabbit or a dog is 1824/4820 + 720/4820 - 252/48