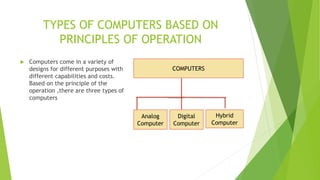
Computers can be classified based on their operation principles into three types: analog, digital, and hybrid. Digital computers, which operate using binary digits, have become increasingly prevalent due to their speed and accuracy, while hybrid computers combine features of both analog and digital systems. Additionally, computers are categorized by configuration into micro, mini, mainframe, and supercomputers, each serving specific uses and capabilities.