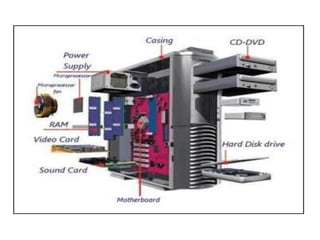
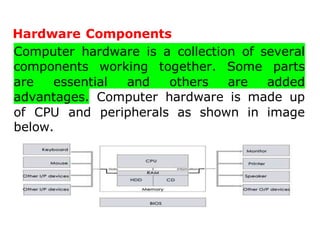
The document discusses different types of computers and their components. It defines hardware as the physical parts of a computer like the CPU, keyboard, and hard drive. Software is defined as a set of instructions that allows computers to perform tasks and is divided into system software and application software. Computers are classified based on their capacity as mainframe, mini, super, or micro computers and based on the type of data they process as analog, digital, or hybrid computers. Each type is designed for specific uses.