This document provides an overview of computers including:
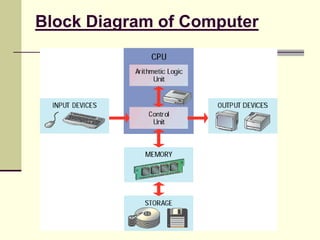
- A computer is an electronic device that processes data into useful information. It includes hardware, software, data, and users.
- Computers can be classified based on their processing capabilities as supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, microcomputers, and wearables. They can also be classified as analog, digital, or hybrid based on their input/output signals.
- General purpose computers can solve many types of problems, while special purpose computers are designed to solve specific problems through dedicated programming. Servers are computers designed to share resources over a network.