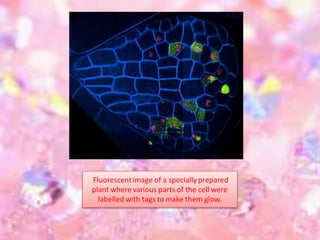
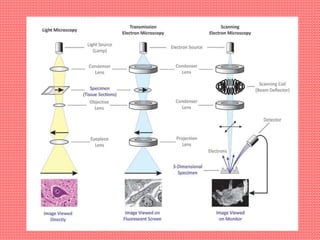
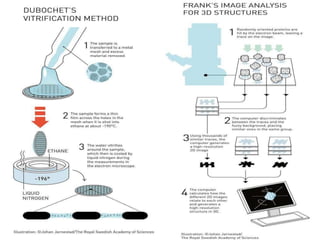
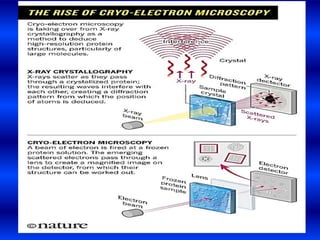
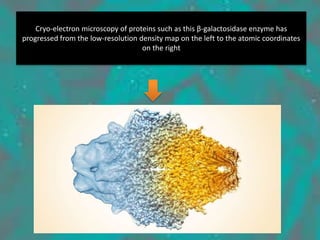
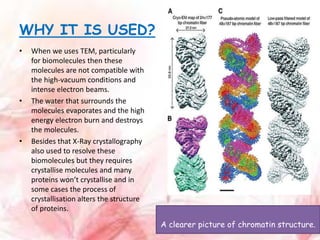
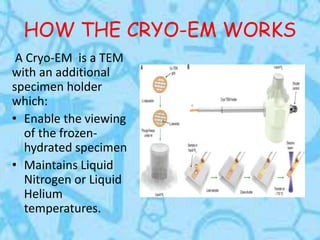
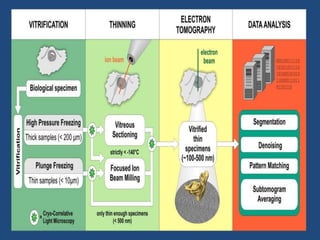
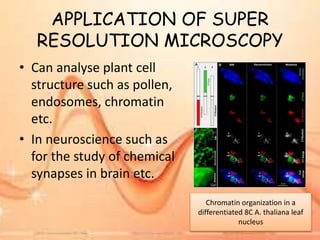
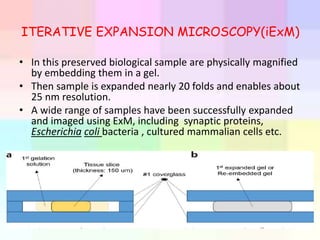
Cryo-electron microscopy is an emerging technique that uses electron microscopes to image biomolecules such as proteins that have been rapidly frozen to preserve their structure. It overcomes limitations of other techniques by not requiring crystallization and allowing study of molecules in their natural state. In cryo-EM, a sample is frozen at liquid nitrogen temperatures to vitrify it before being imaged with an electron microscope. This technique has helped determine structures of important proteins and revealed new details about their function. Recent advances in direct electron detectors, image processing, and specimen preparation have led to remarkable improvements in resolution with cryo-EM.