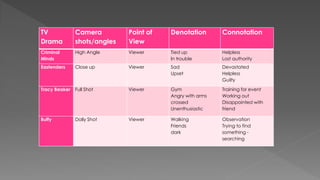
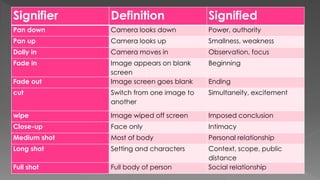
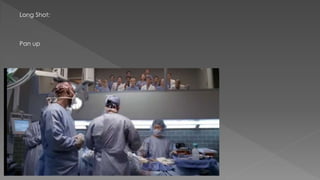
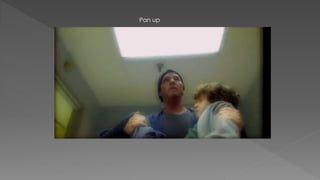
This document discusses different camera shots and angles used in TV dramas and how audiences may interpret them. It provides examples of close-up, medium, and long shots from shows like Grey's Anatomy, Criminal Minds, and Tracy Beaker. Close-ups show intimacy and emotion, helping audiences understand a character's feelings. Medium shots display personal relationships or actions and allow for negotiated readings. Long shots provide context and allow for negotiated readings by showing the setting. It also discusses techniques like pans, tilts, dolly shots, fades, cuts, and wipes used to convey meaning to audiences.