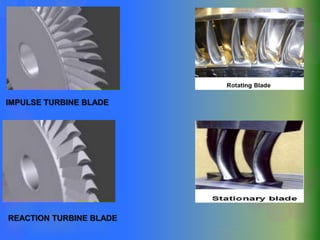
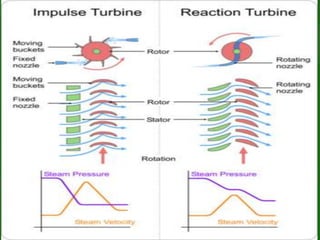
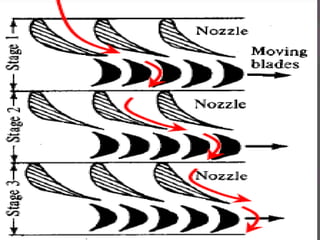
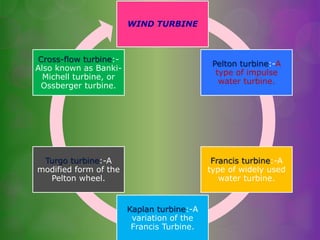
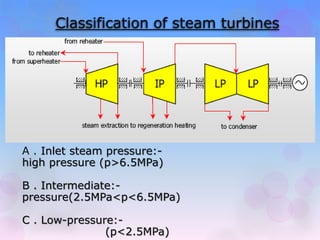
The document discusses turbines and provides classifications. Turbines convert kinetic, potential, or intermolecular energy of a fluid into rotational mechanical energy. They have a rotor assembly with blades that create rotation from fluid flow. Turbines operate via impulse or reaction theories. Impulse turbines use fluid velocity changes pre-nozzle, while reaction turbines develop torque from pressure changes through the blades. Turbines are classified by type of fluid (steam, gas, water) and variations in design. Steam turbines are widely used to generate electricity from heat sources like coal.