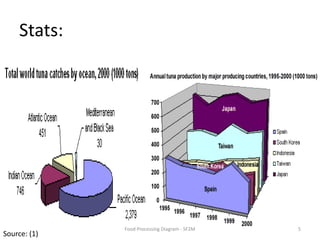
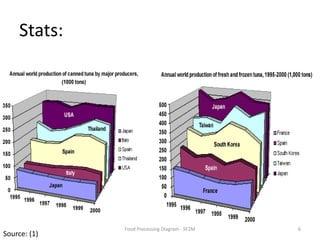
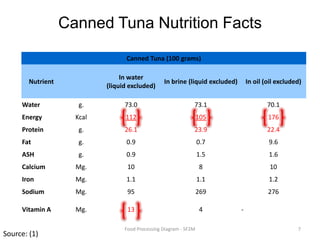
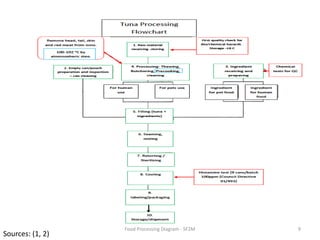
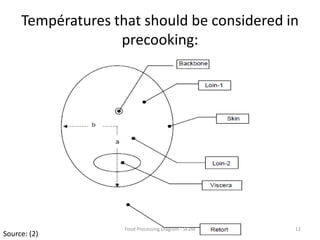
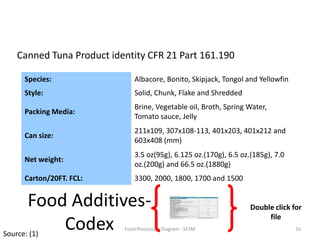
The document summarizes the tuna processing and production process. It discusses that tuna is caught using methods like purse seining and longlining. After catching, tuna are rapidly cooled. They then undergo precooking using atmospheric steam, which is a critical process before retorting. Precooking involves cooking the tuna to a target temperature to facilitate canning. It also provides nutritional information and discusses laws and regulations for canned tuna standards.