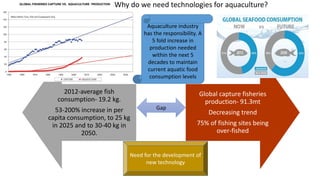
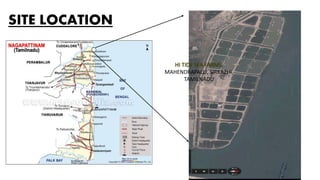
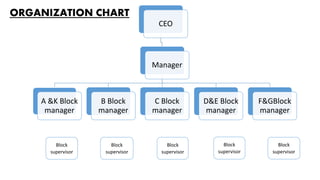
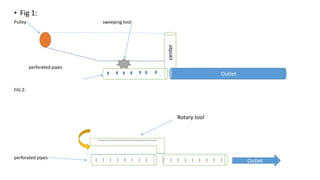
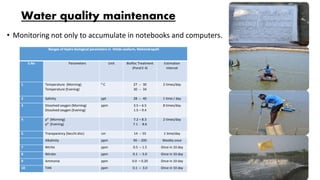
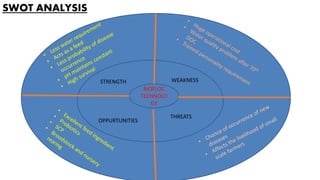
The document discusses the increasing demand for fish and the need for sustainable aquaculture technology as global per capita consumption is projected to rise significantly. It details specific practices and protocols for managing biofloc ponds, including water treatment, aeration, feeding methods, and monitoring water quality to ensure healthy shrimp production. Additionally, it highlights the challenges of over-fishing and the necessity for new technologies to enhance aquaculture efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.