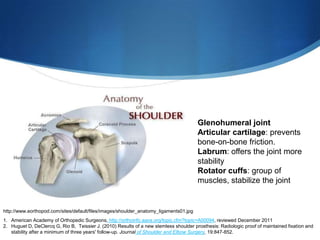
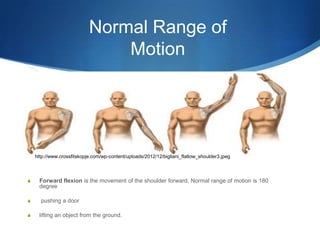
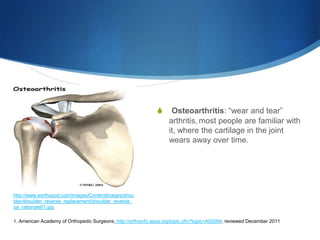
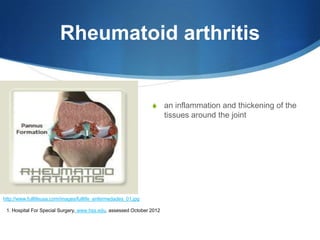
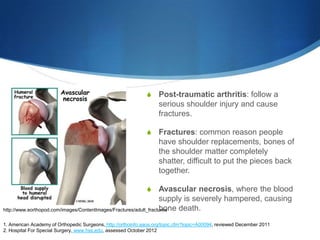
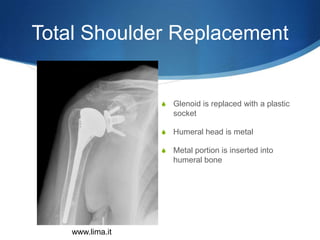
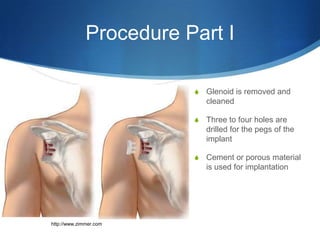
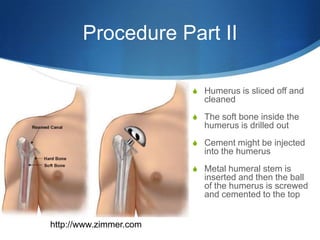
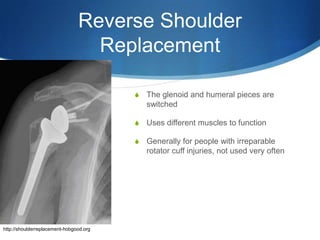
This document provides information about total shoulder replacement surgery. It discusses the anatomy of the shoulder joint and causes for replacement such as arthritis. The surgical procedure is described including removing damaged bone and inserting artificial components. Experimental plans are outlined for a clinical trial comparing a new device to an existing one by measuring range of motion outcomes over time. Statistical analysis methods including power analysis, normality tests, and parametric/nonparametric tests are proposed to analyze the data.