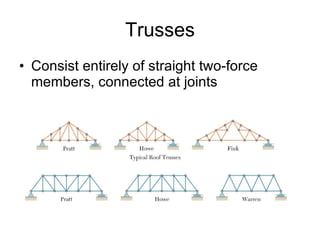
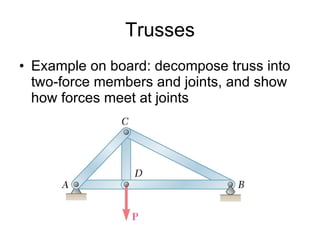
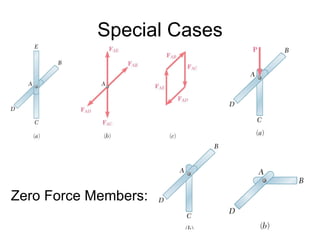
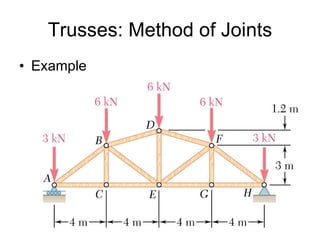
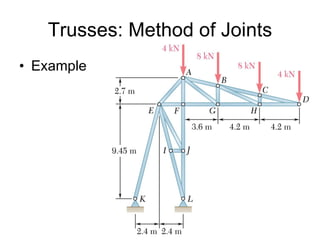
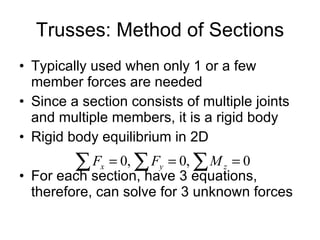
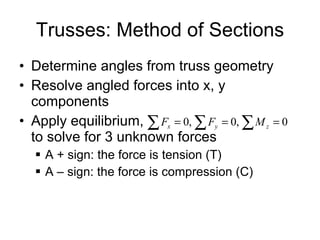
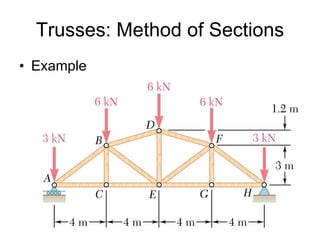
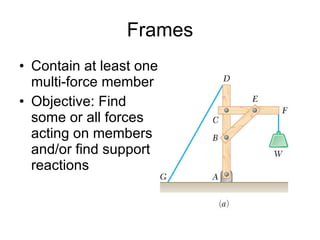
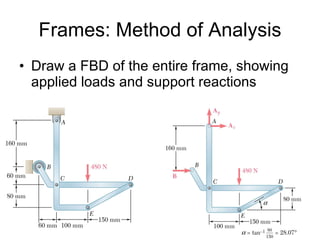
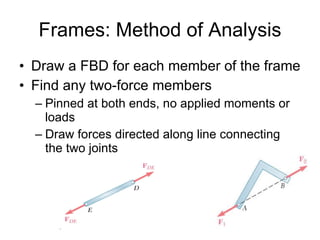
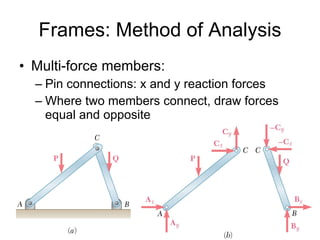
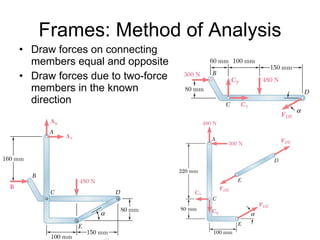
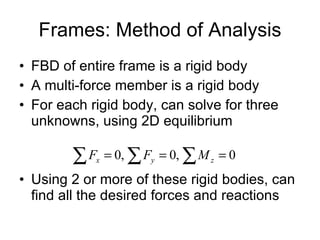
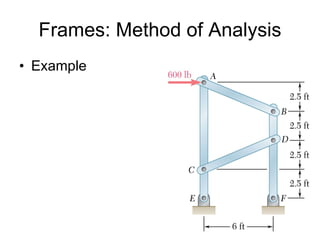
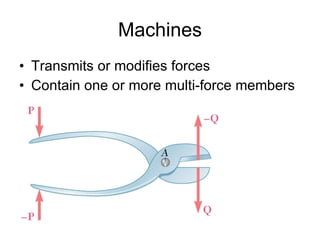
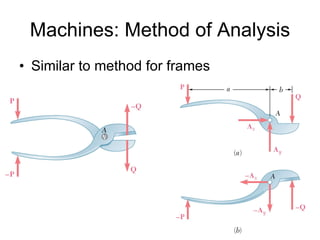
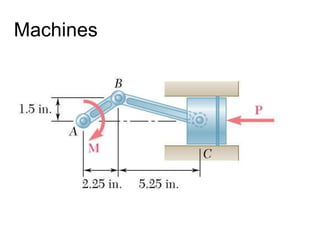
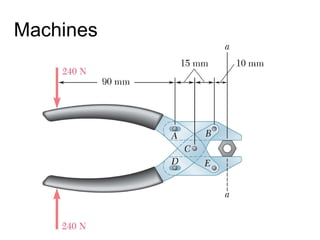
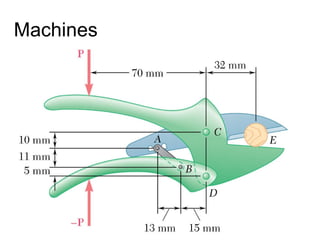
The document discusses analysis methods for trusses, frames, and machines. Trusses consist of two-force members and can be analyzed using the method of joints or method of sections. The method of joints uses particle equilibrium at joints to solve for forces. The method of sections uses rigid body equilibrium to solve for forces by cutting the truss into sections. Frames contain multi-force members and can be analyzed by drawing free body diagrams of individual members and applying equilibrium equations. Machines contain multi-force members and are analyzed similarly to frames.