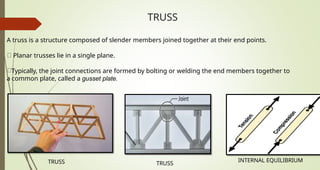
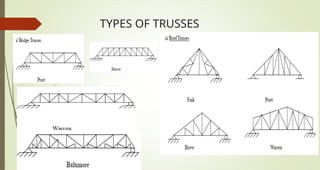
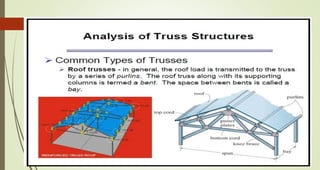
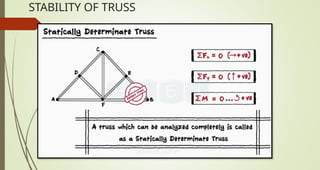
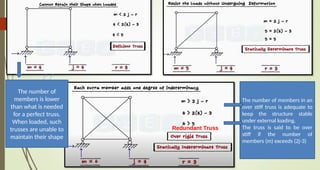
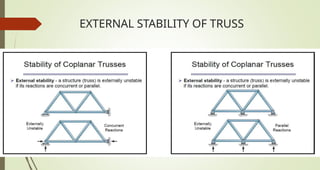
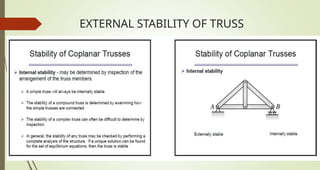
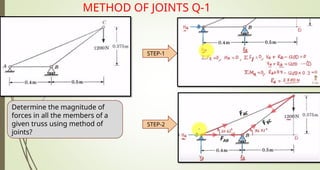
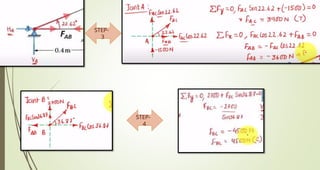
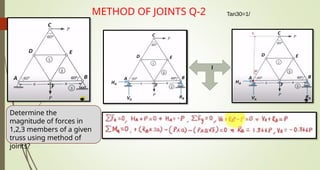
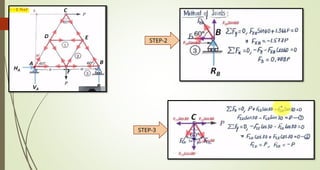
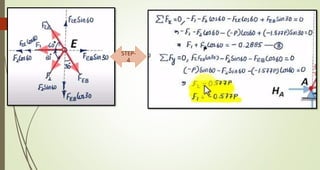
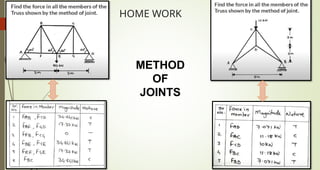
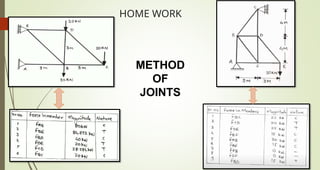
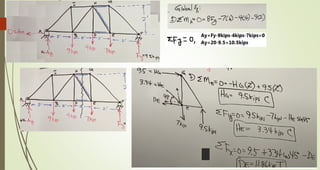
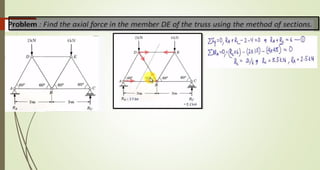
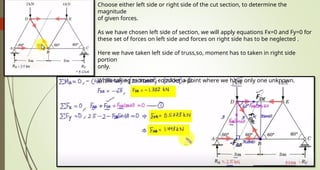
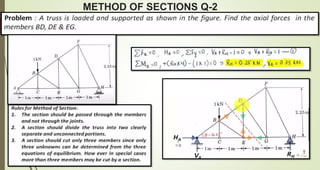
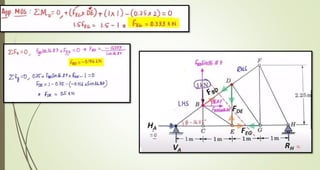
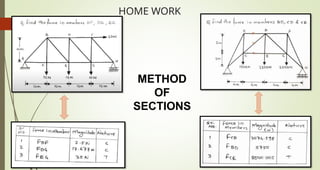
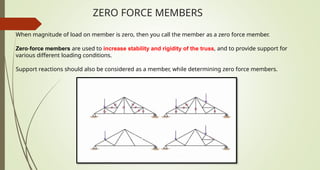
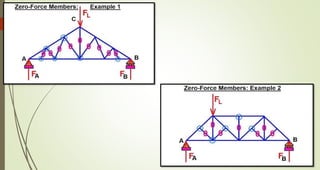
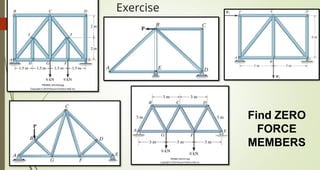
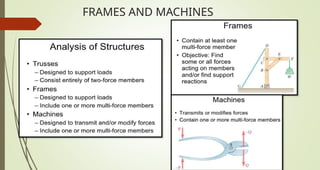
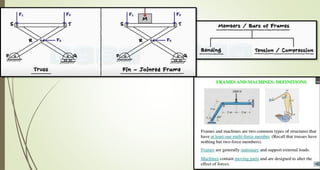
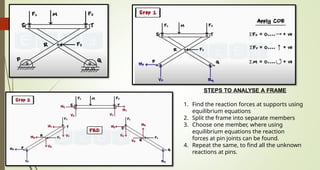
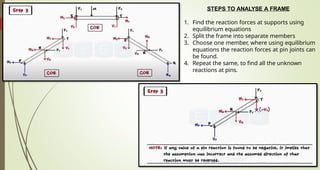
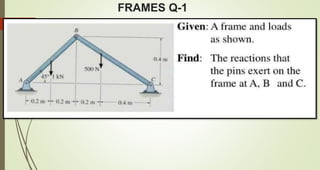
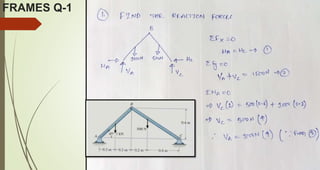
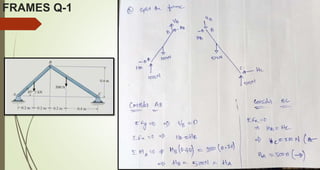
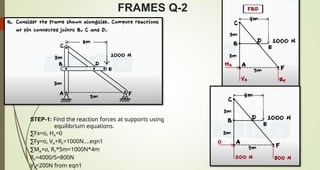
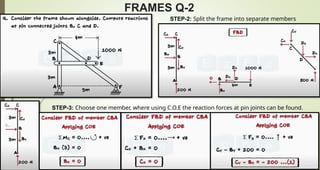
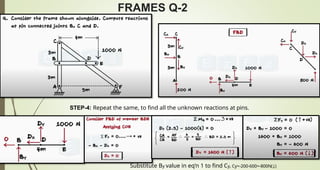
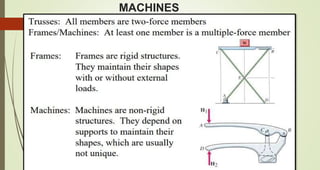
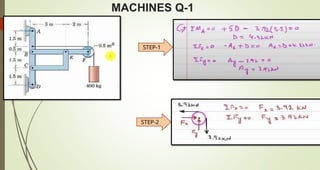
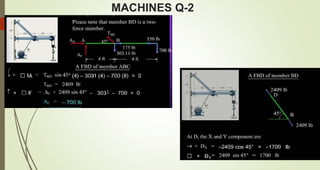
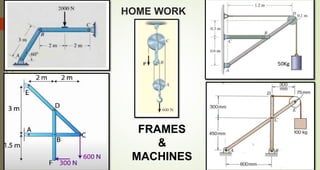
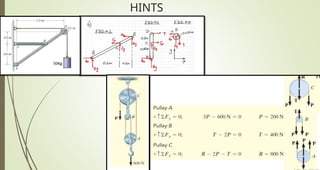
This document discusses the principles of trusses, frames, and machines, focusing on the analysis and stability of trusses. It details methods for force analysis including the method of joints and method of sections, as well as the identification of zero-force members. Additionally, it outlines steps for analyzing frames and machines to determine reaction forces and member stability.