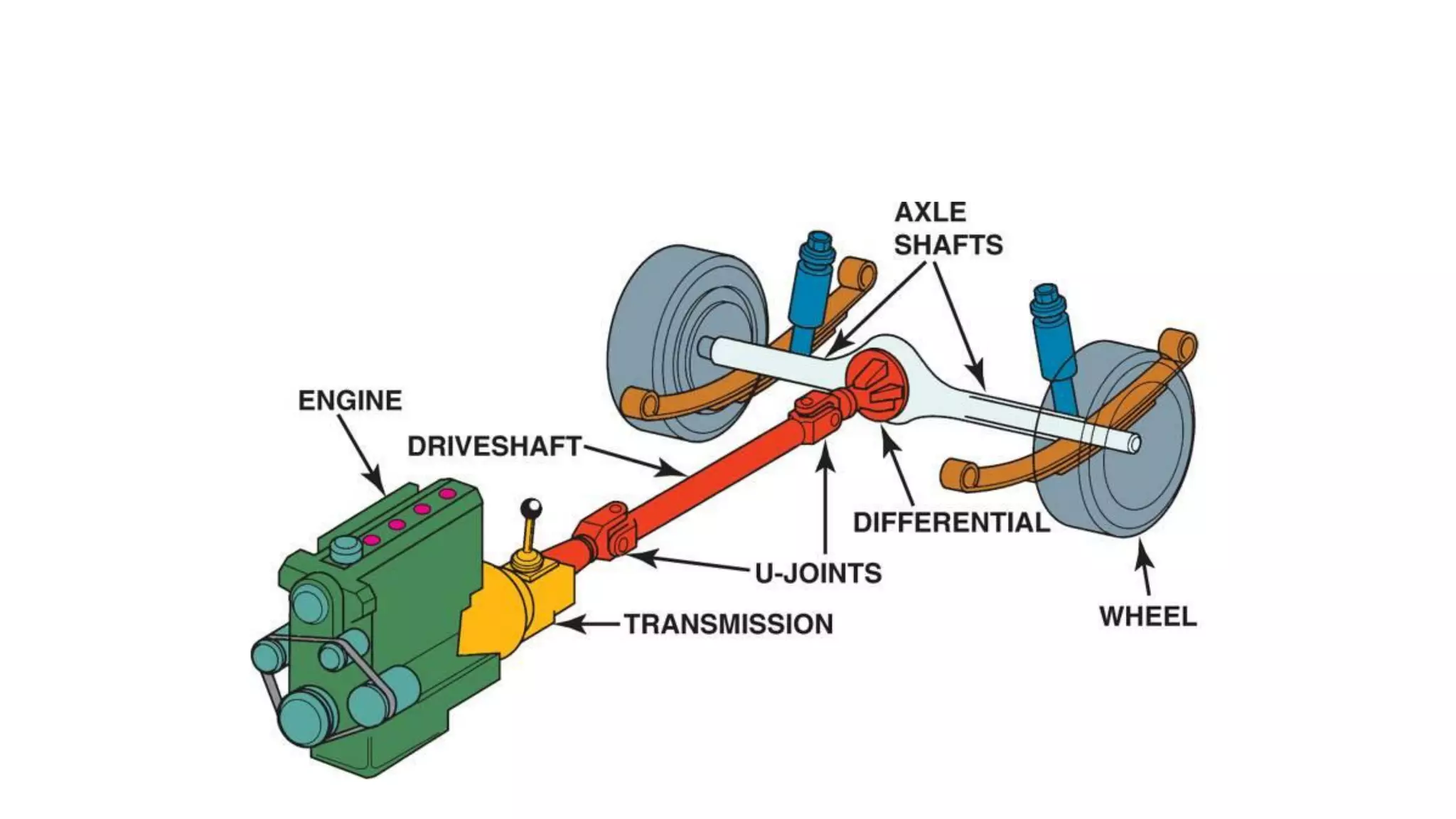
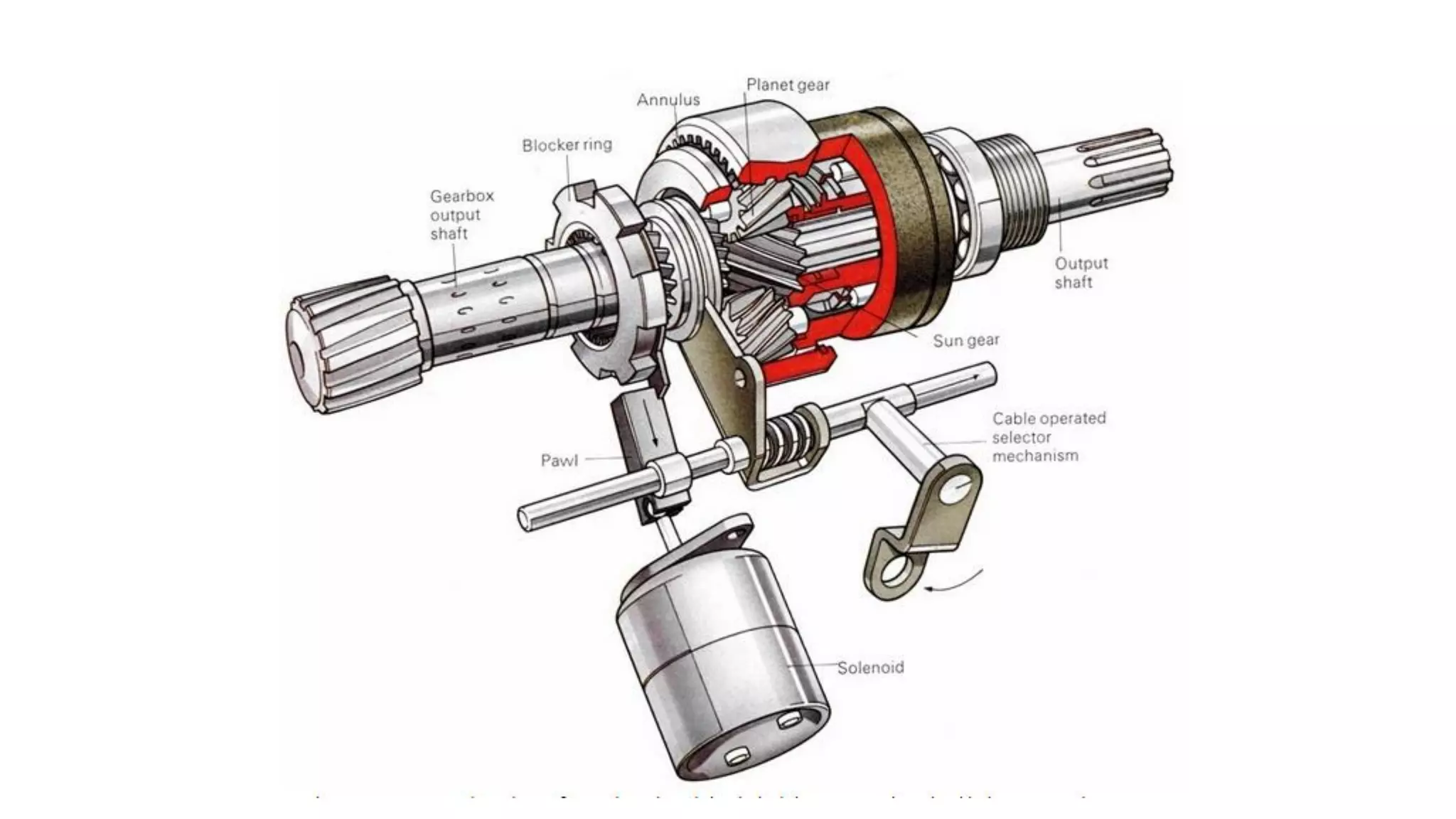
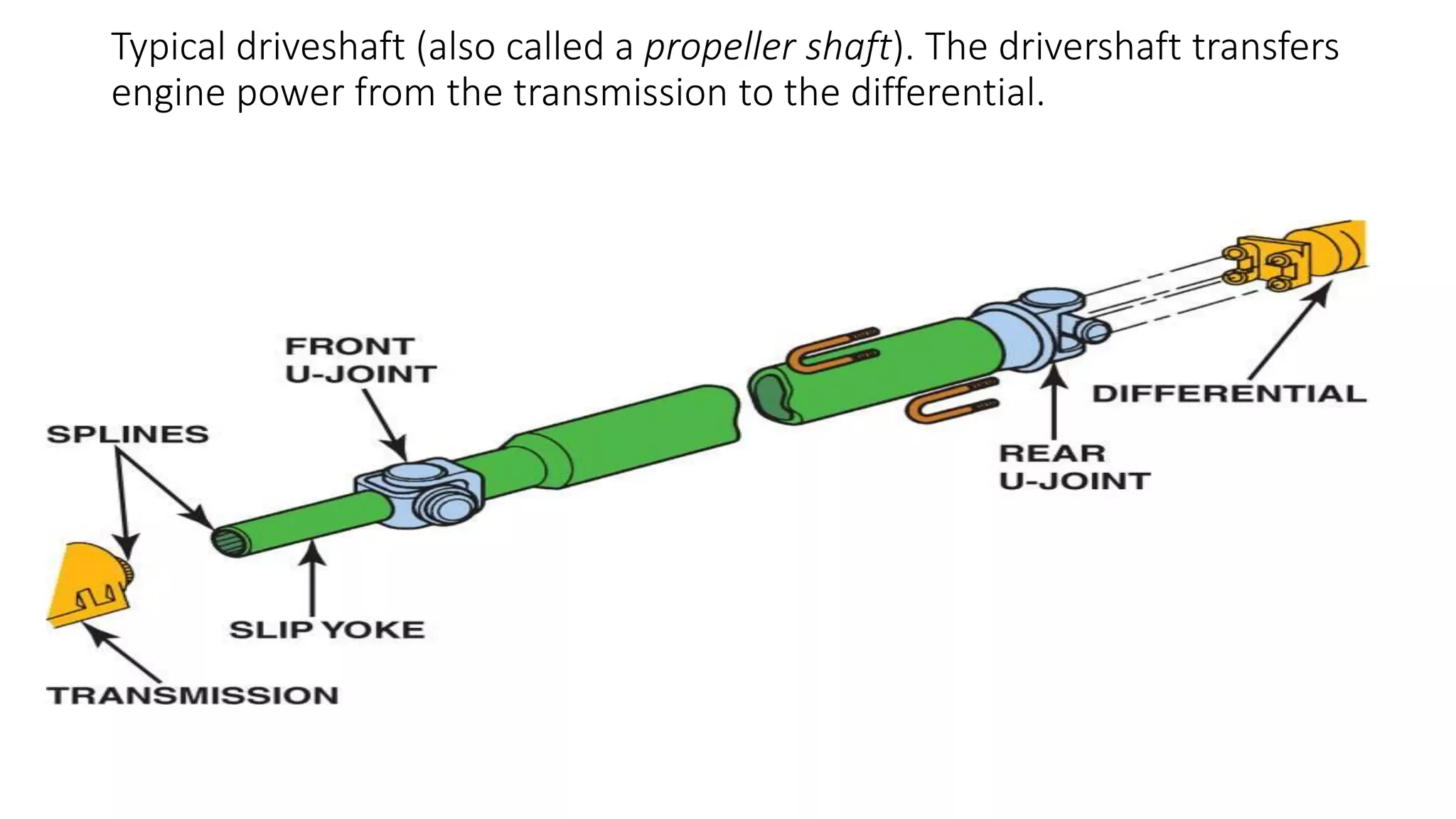
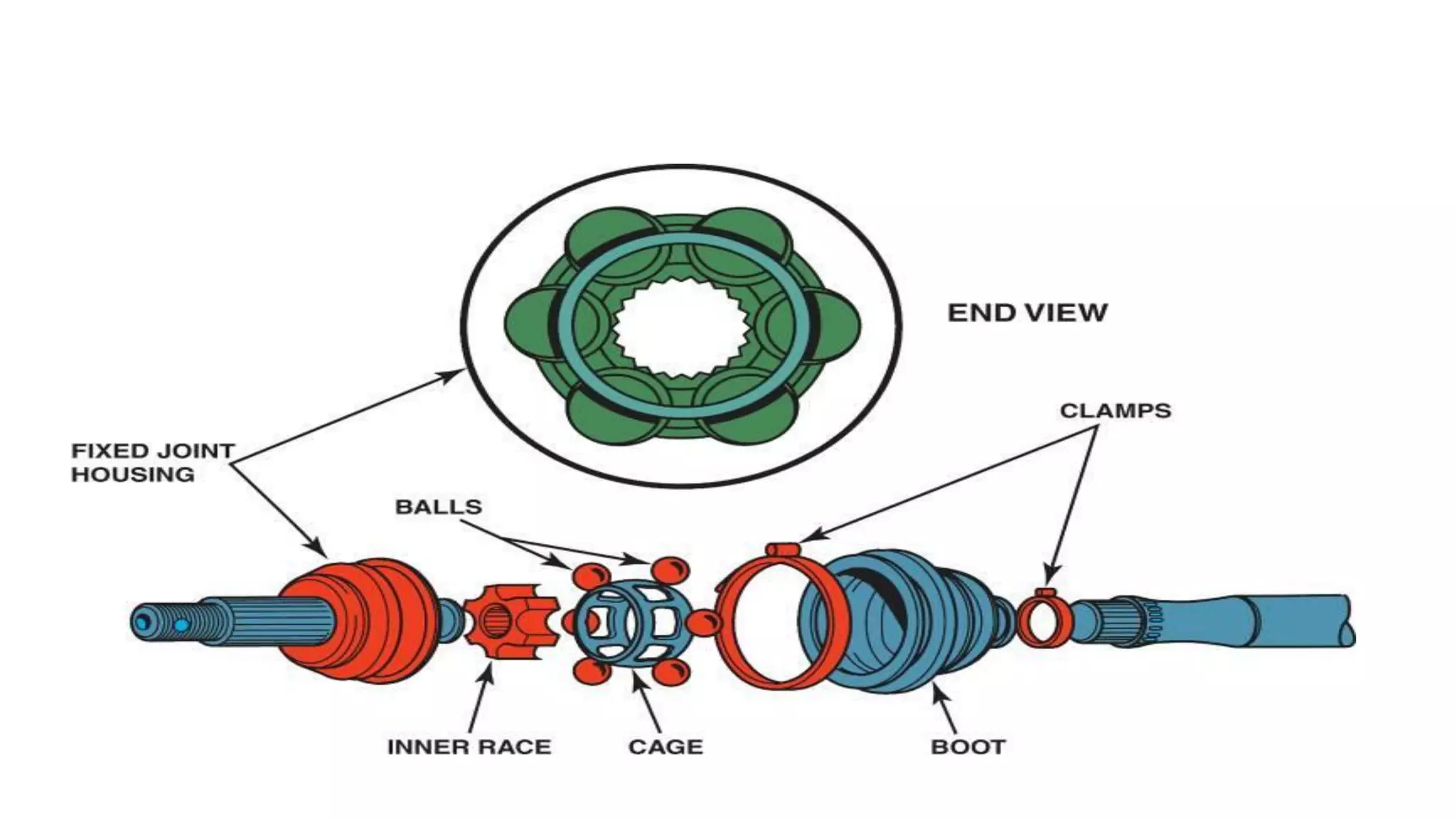
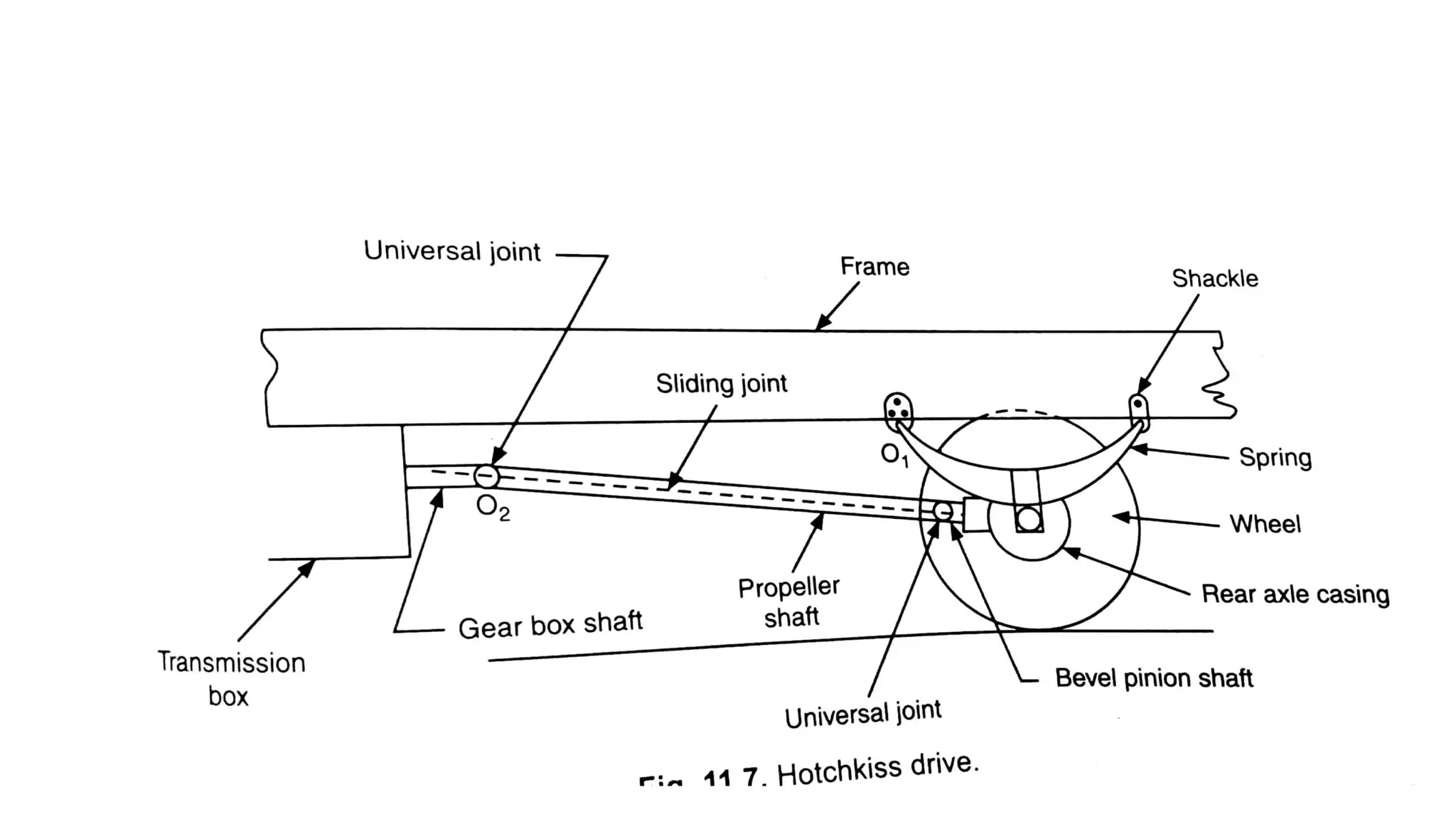
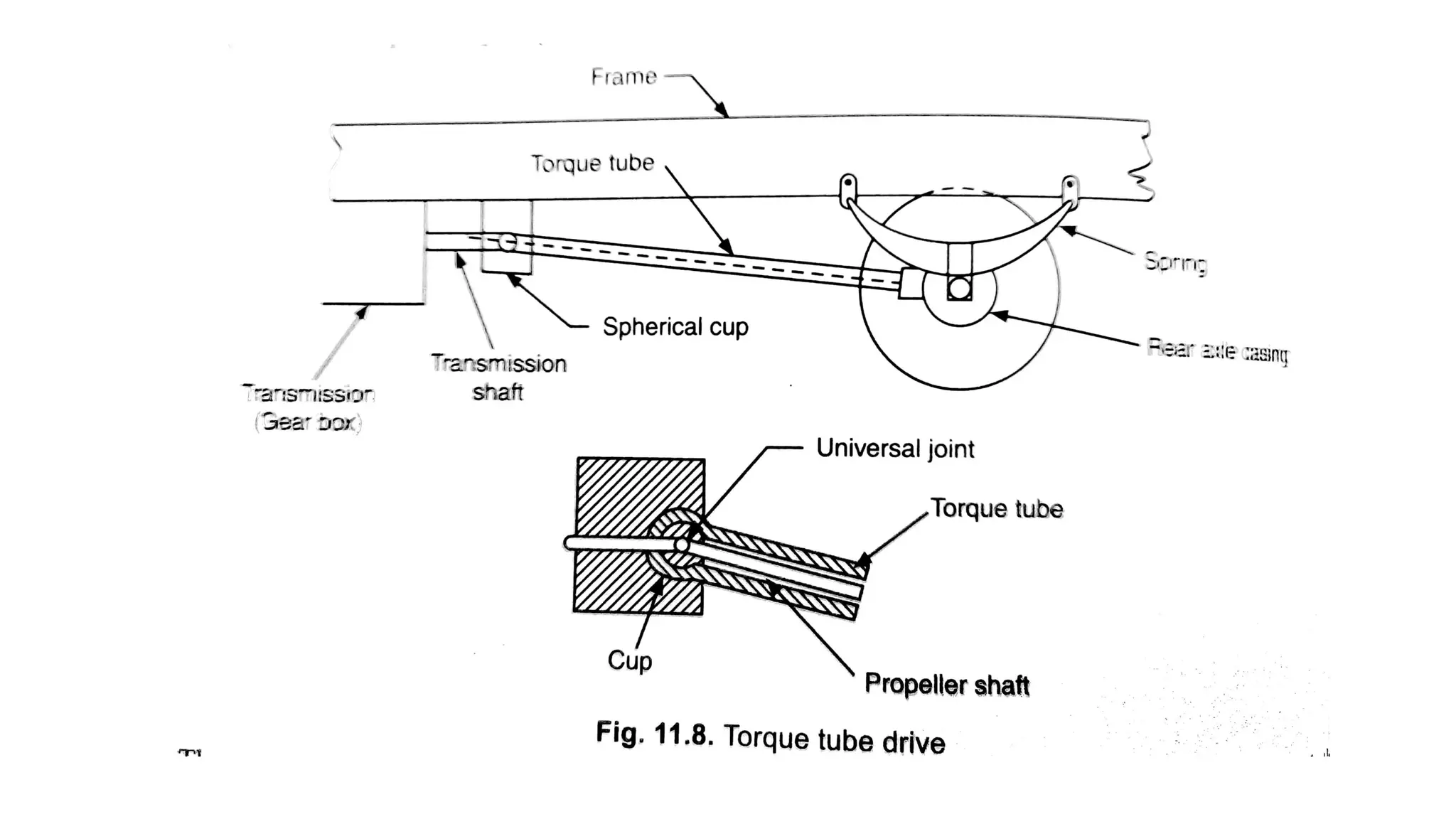
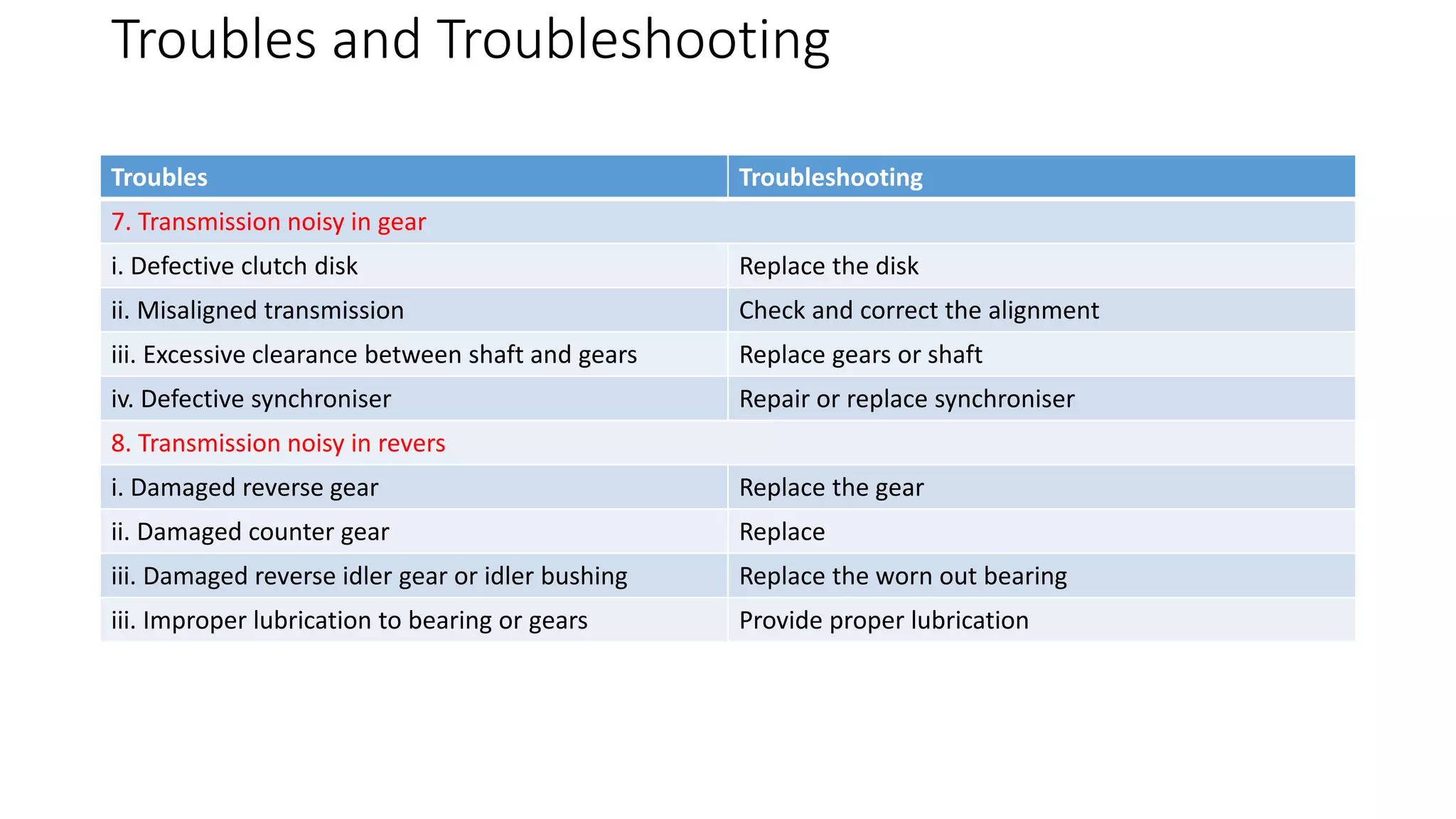
The document describes the components and operation of manual transmissions. It discusses the relationship between gears and torque, and describes the basic types of gears. It outlines the power flow through 3, 4, and 5-speed transmissions. It also names common transmission parts like the synchronizer and driveshaft. Finally, it lists some common transmission troubles like leakage, difficulty shifting, and noise, along with their potential causes and troubleshooting steps.