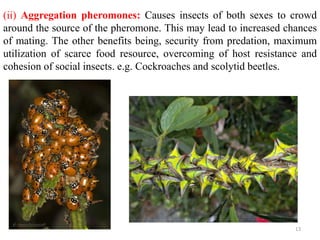
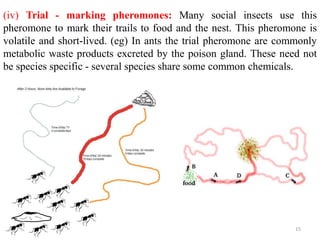
This document discusses insect communication and interactions with plants. It covers how insects communicate through semiochemicals like pheromones, light production, sound production, and body language. Specific examples are provided, such as fig wasps and fig trees having a mutualistic relationship where the wasp pollinates the fig in exchange for food. Different types of pheromones are classified, including sex, aggregation, spacing, trail-marking, and alarm pheromones. The roles of light production and sound production in courtship and prey finding are also briefly explained.