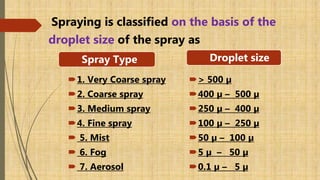
The document discusses different types of pesticide application techniques and ecosystems. It describes four main types of pesticide application: high volume spraying, low volume spraying, ultra low volume spraying, and aerial spraying. Each technique is defined based on droplet size and amount of spray fluid used per hectare. Advantages and disadvantages of each technique are also provided. The document also outlines three main ecosystem types - agro ecosystems, terrestrial ecosystems, and aquatic ecosystems - and provides examples of insects commonly found in each.