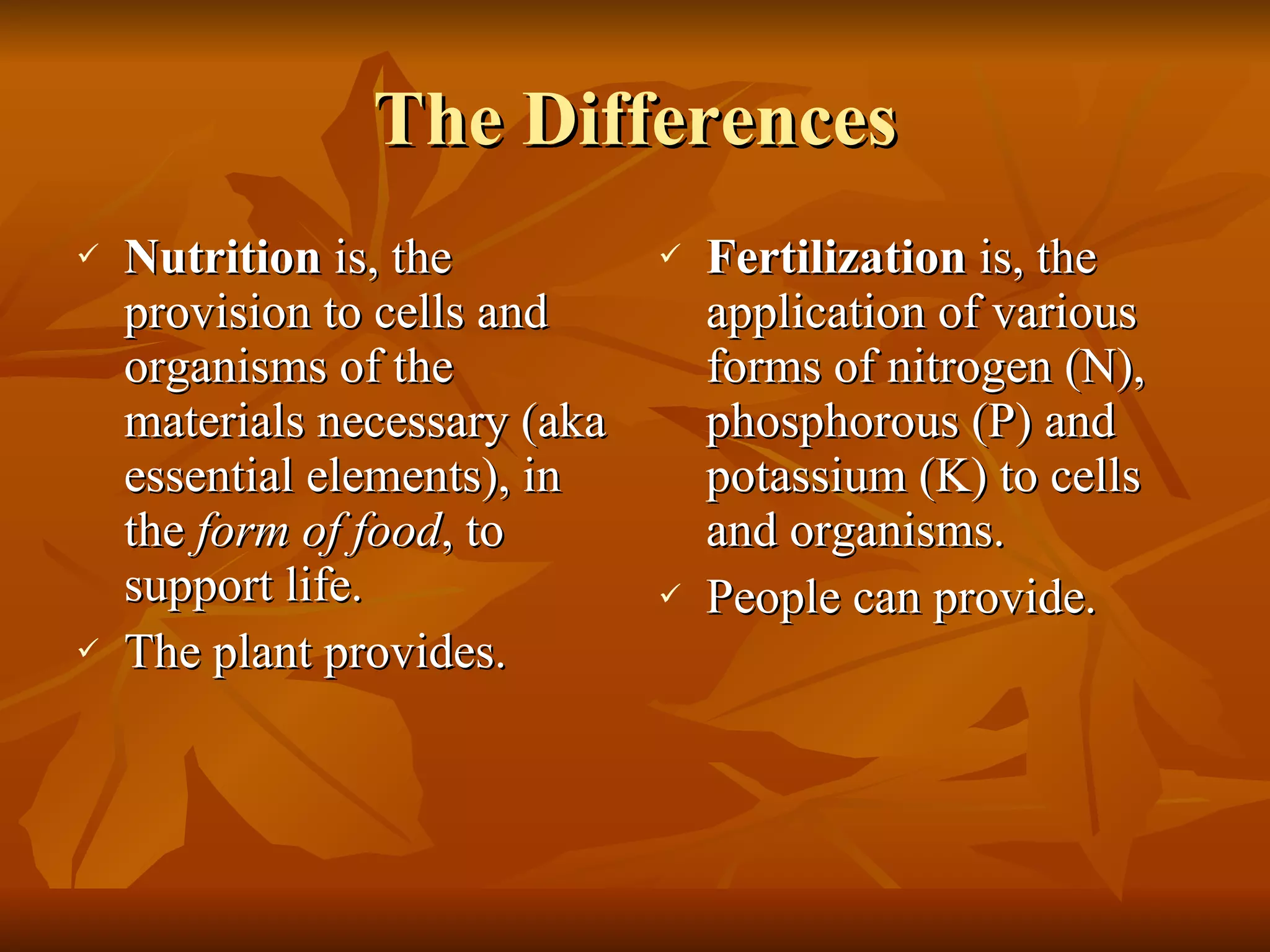
1. The document discusses proper tree nutrition and fertilization, emphasizing that determining a tree's specific nutritional requirements through soil and foliar analysis is essential before providing fertilizer.
2. Fertilizer should only be applied to address a verified nutrient deficiency, and excessive fertilization can cause problems.
3. Diagnosing a tree's needs through soil and foliar analysis is important to determine what, if any, nutrients need to be supplemented before prescribing and applying the right fertilizer.