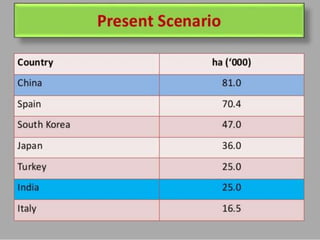
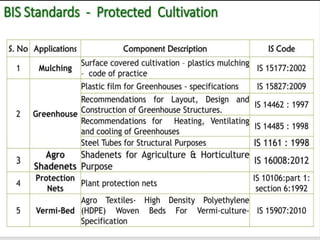
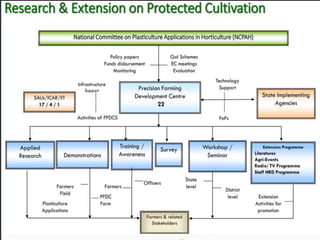
The document discusses the importance of protected cultivation in horticulture, highlighting its benefits such as higher productivity, better quality, and efficient resource use. It details various types of polyhouses and cultivation methods, including hydroponics and aeroponics, as well as government initiatives to promote these practices. The text also outlines the criteria for site selection, advantages and disadvantages of polyhouse technology, and potential crops suitable for protected cultivation.