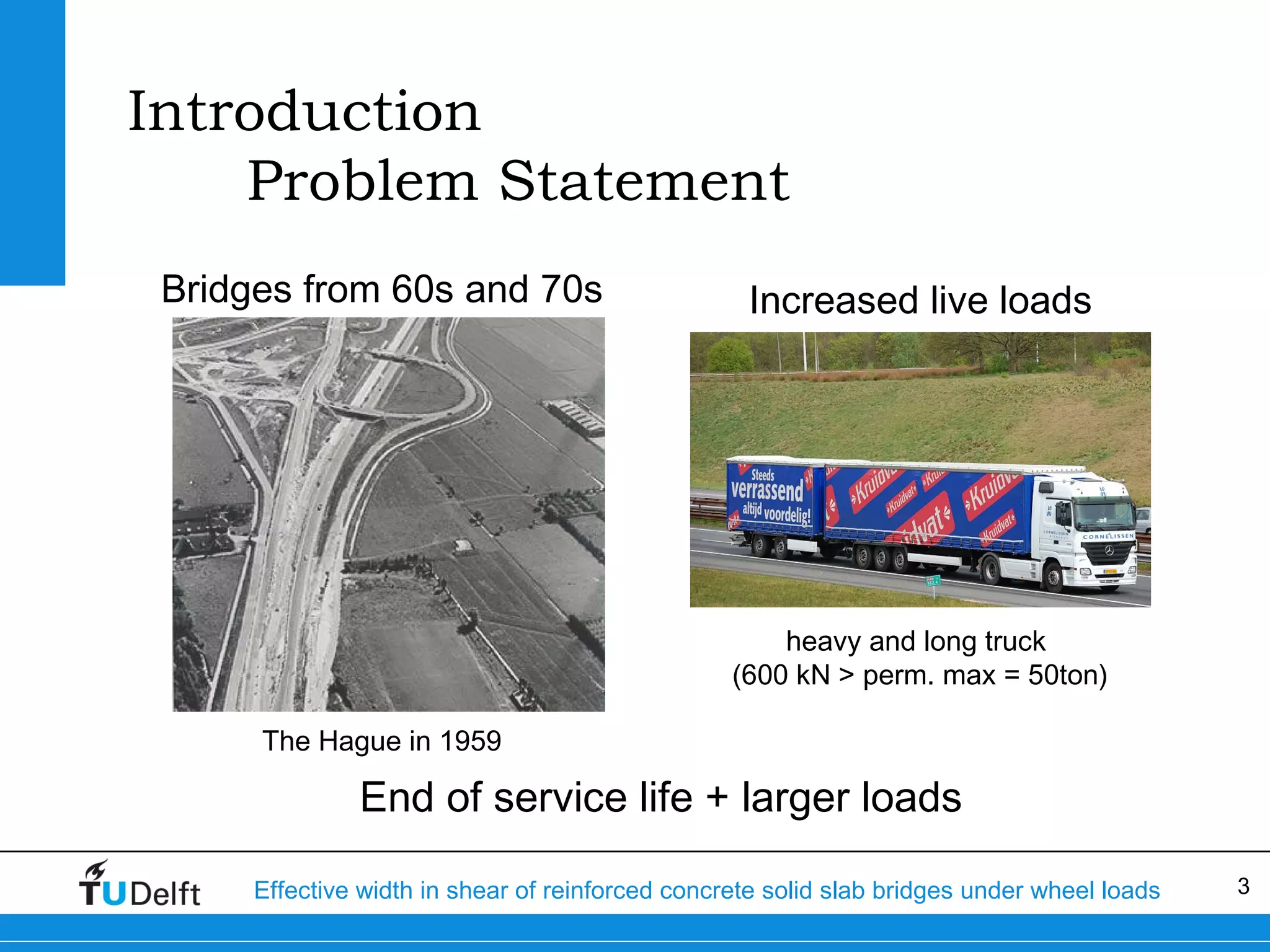
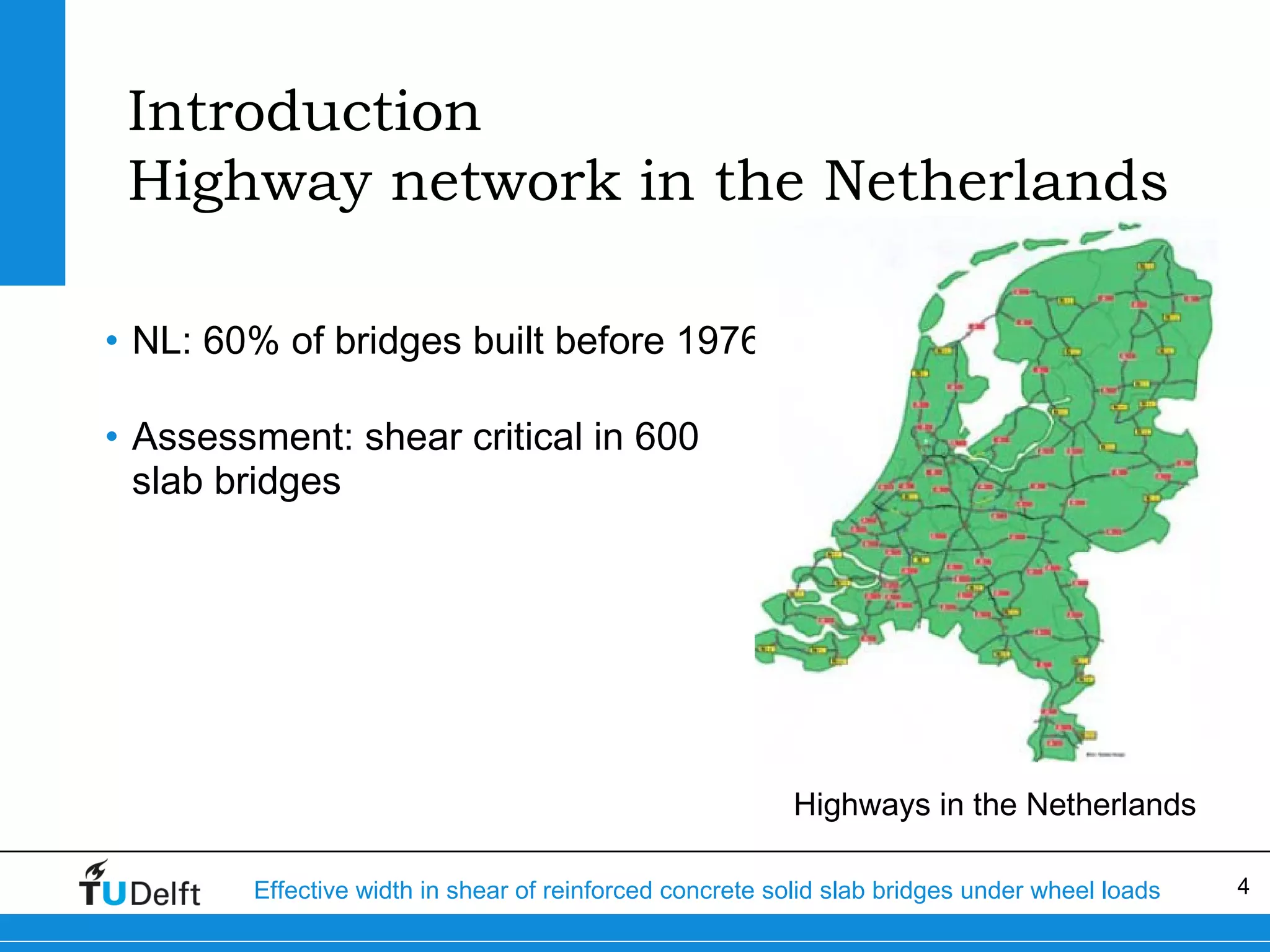
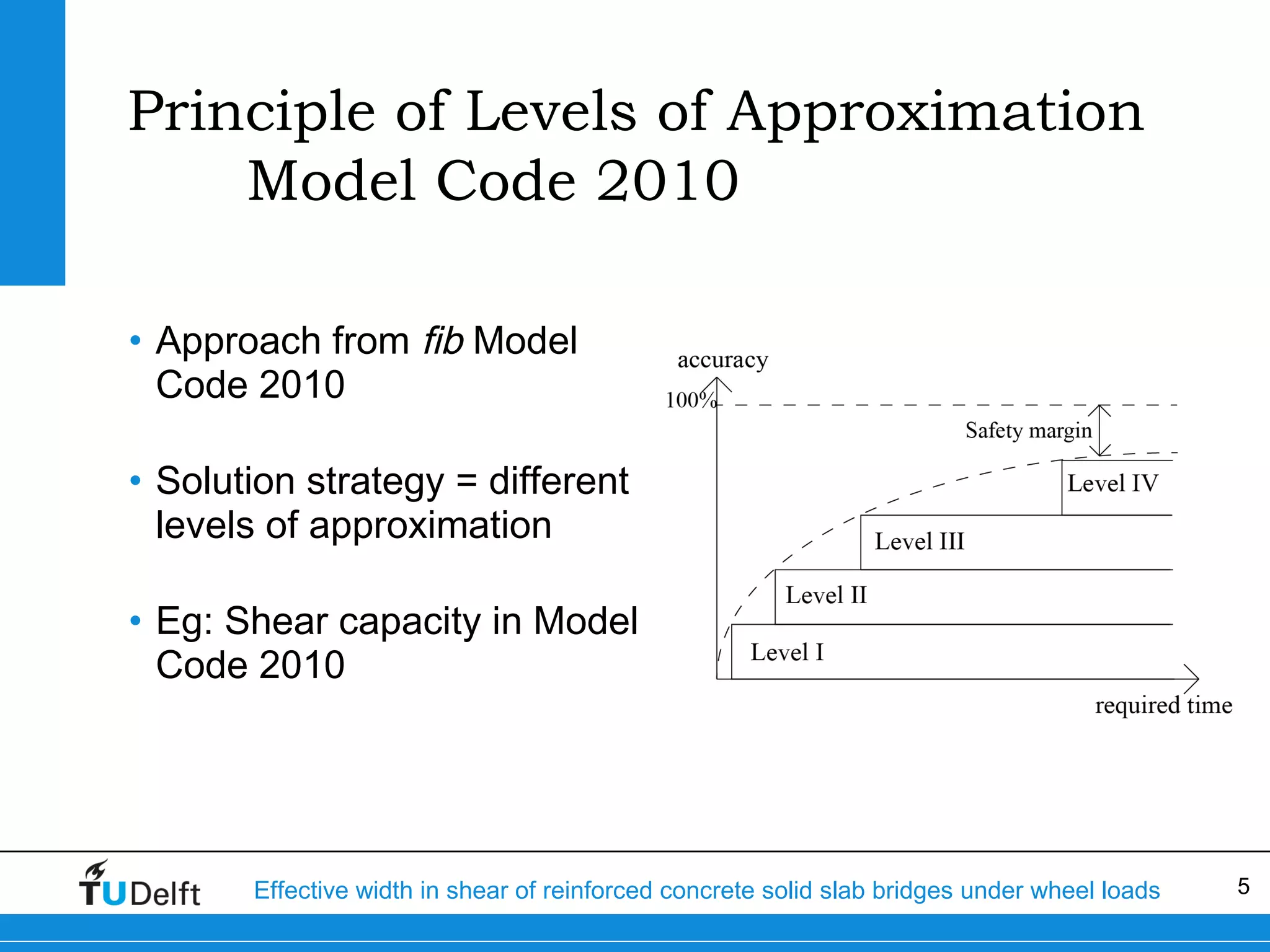
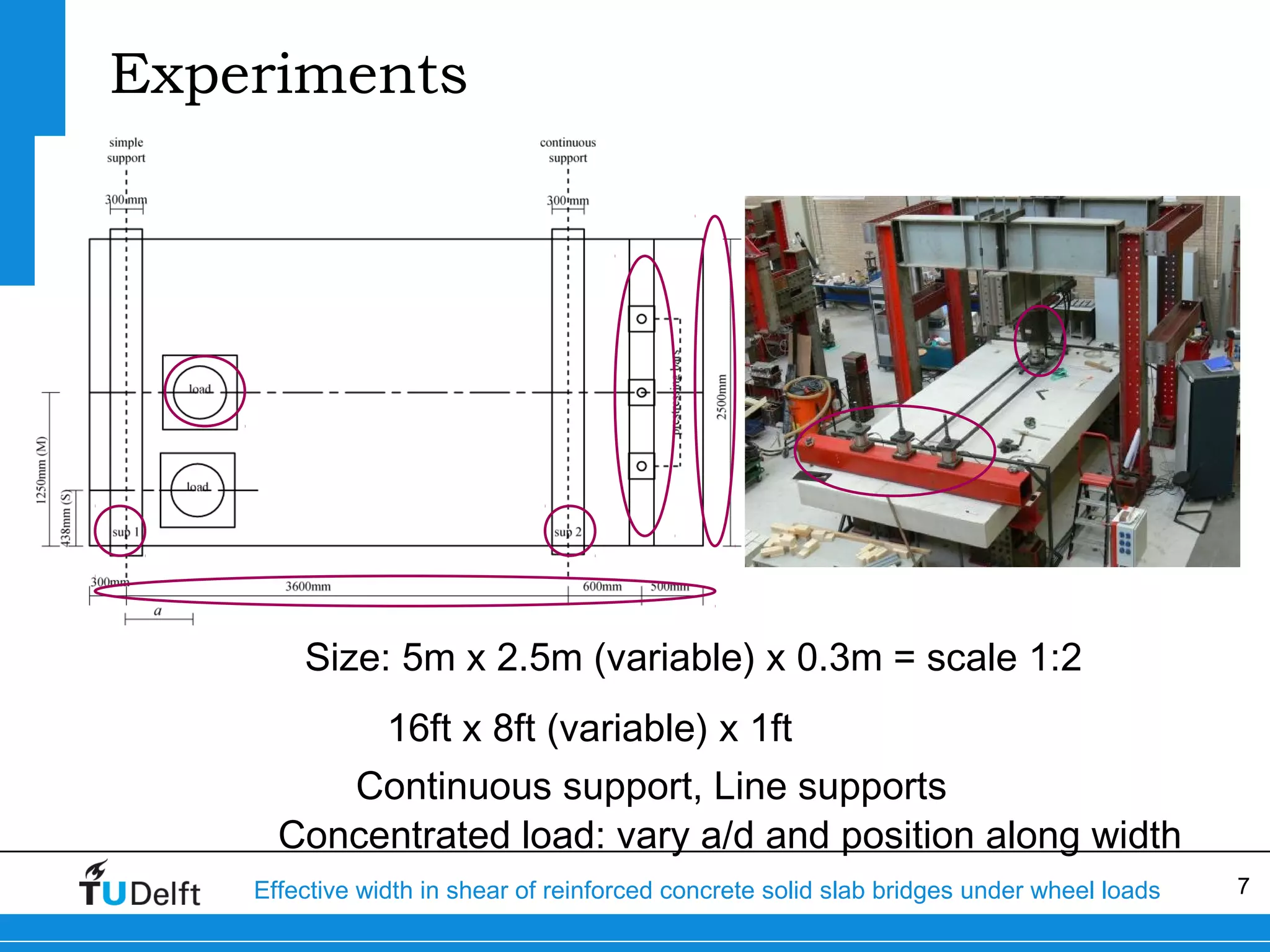
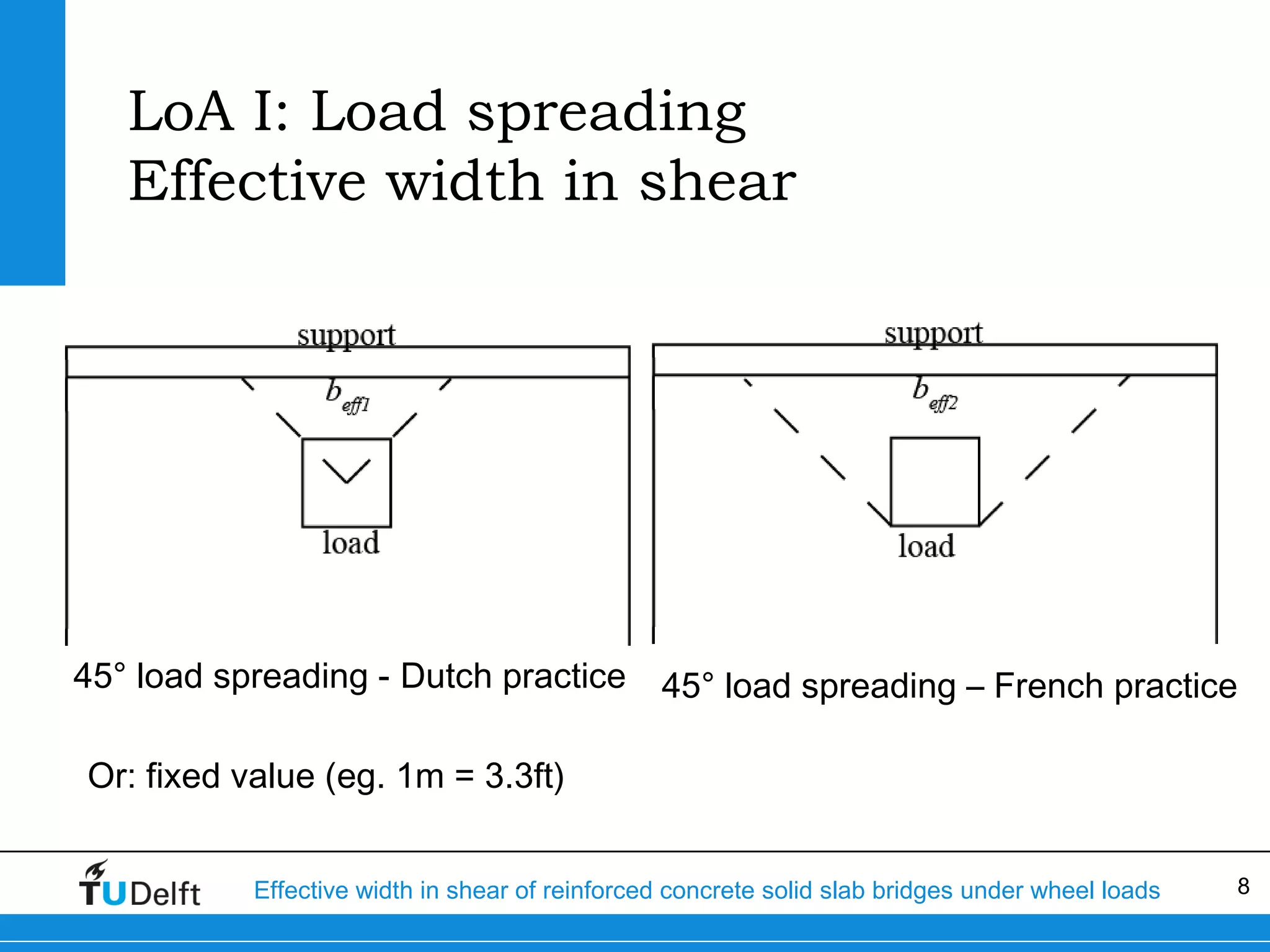
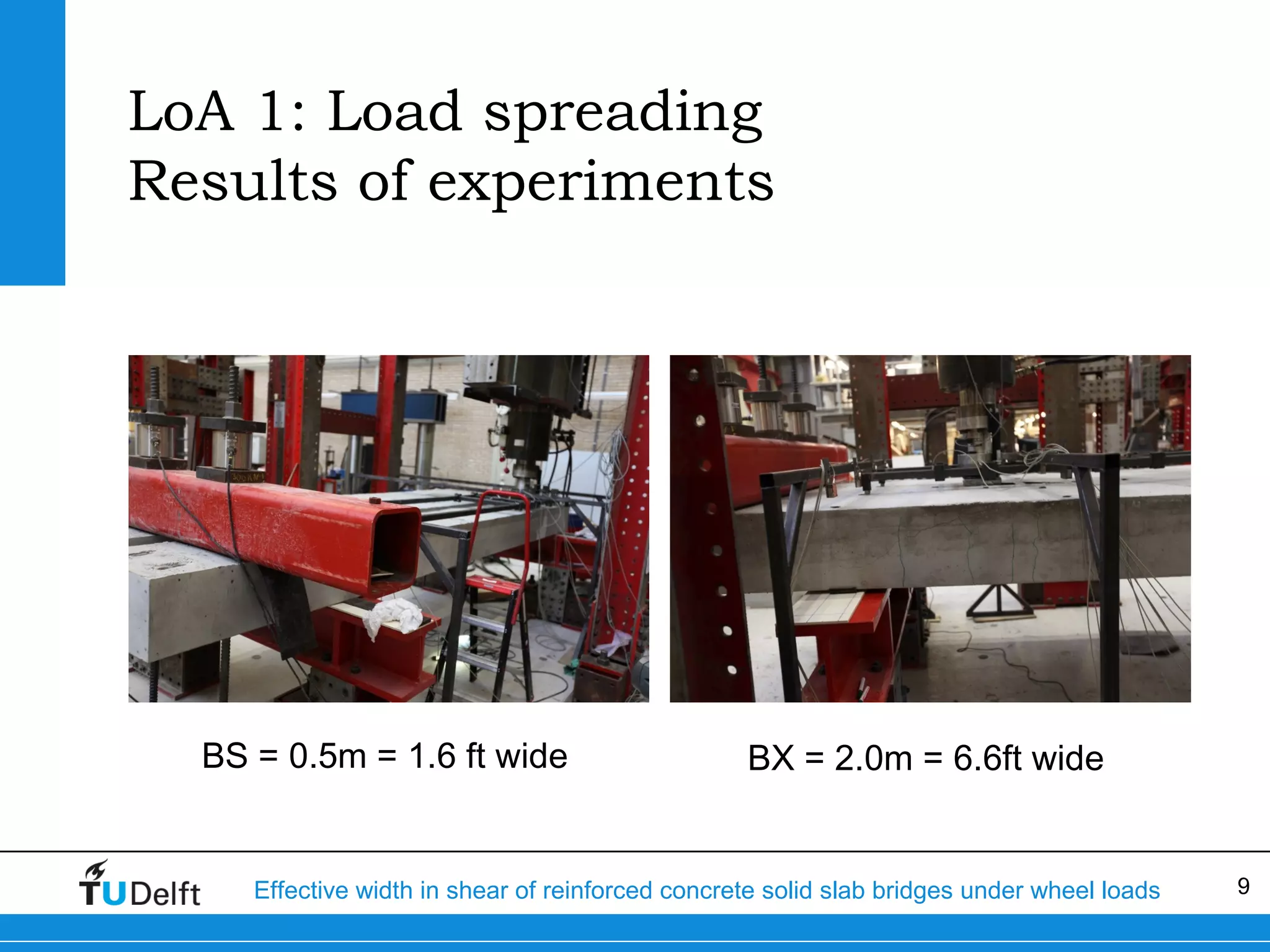
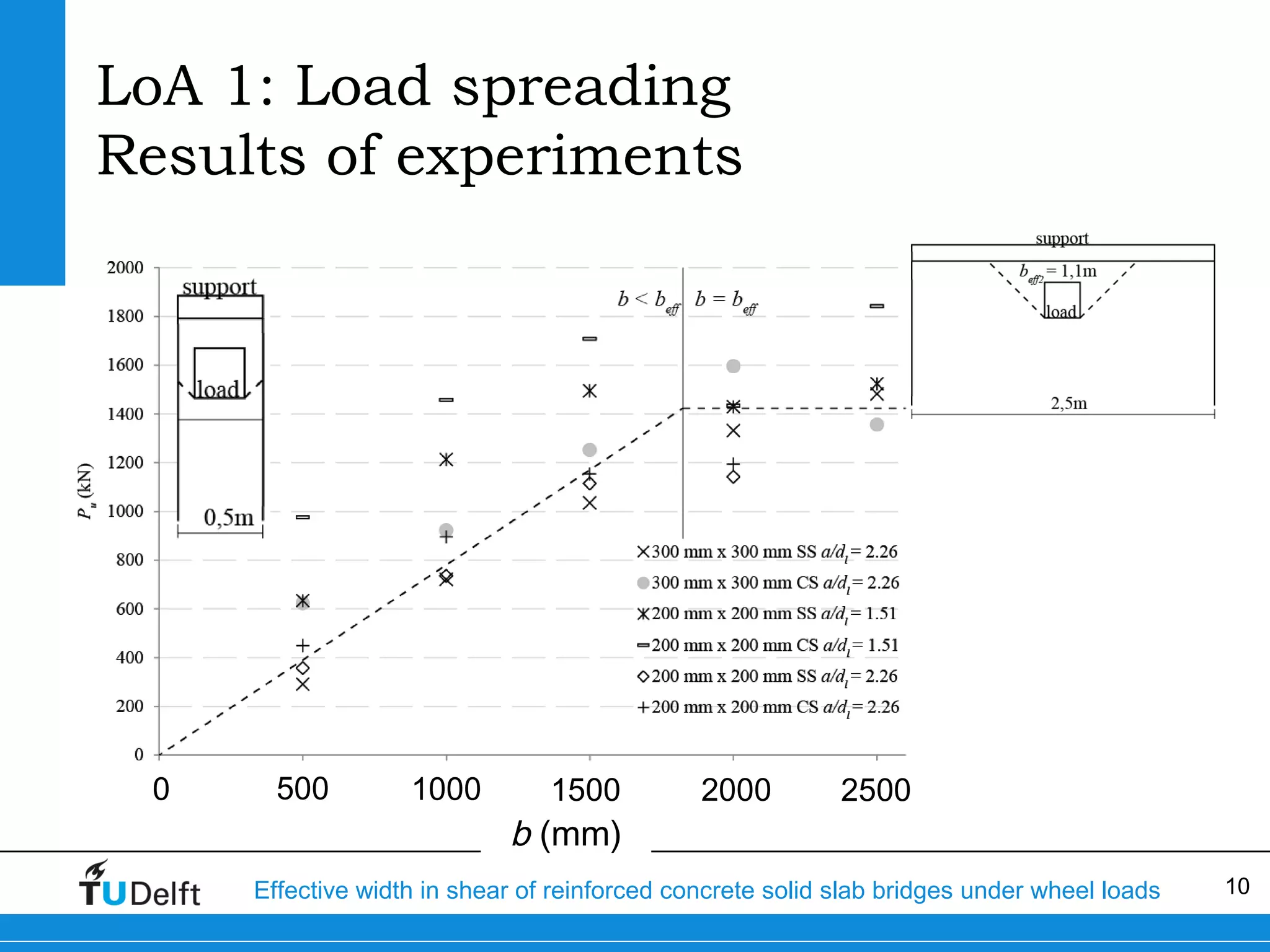
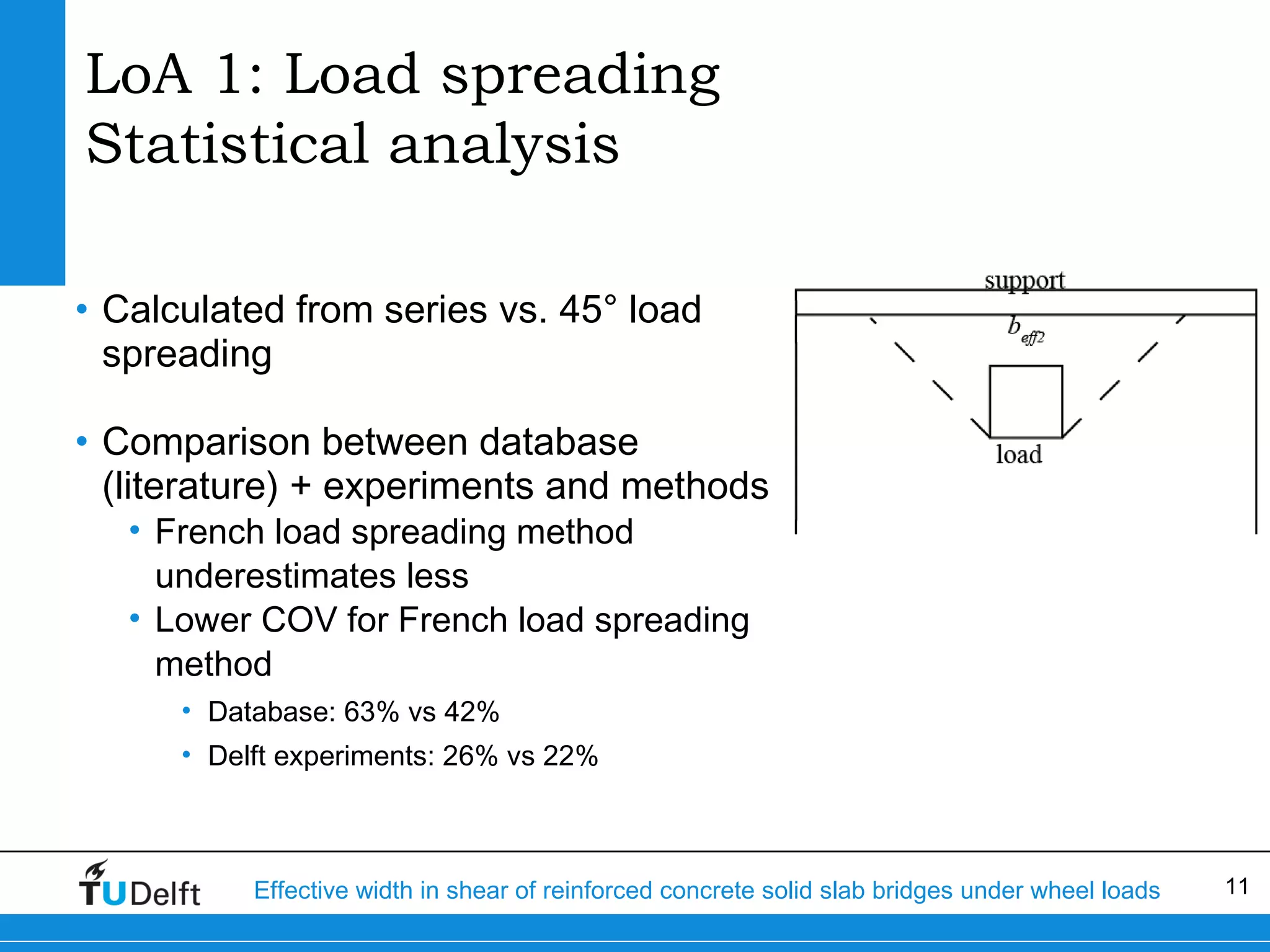
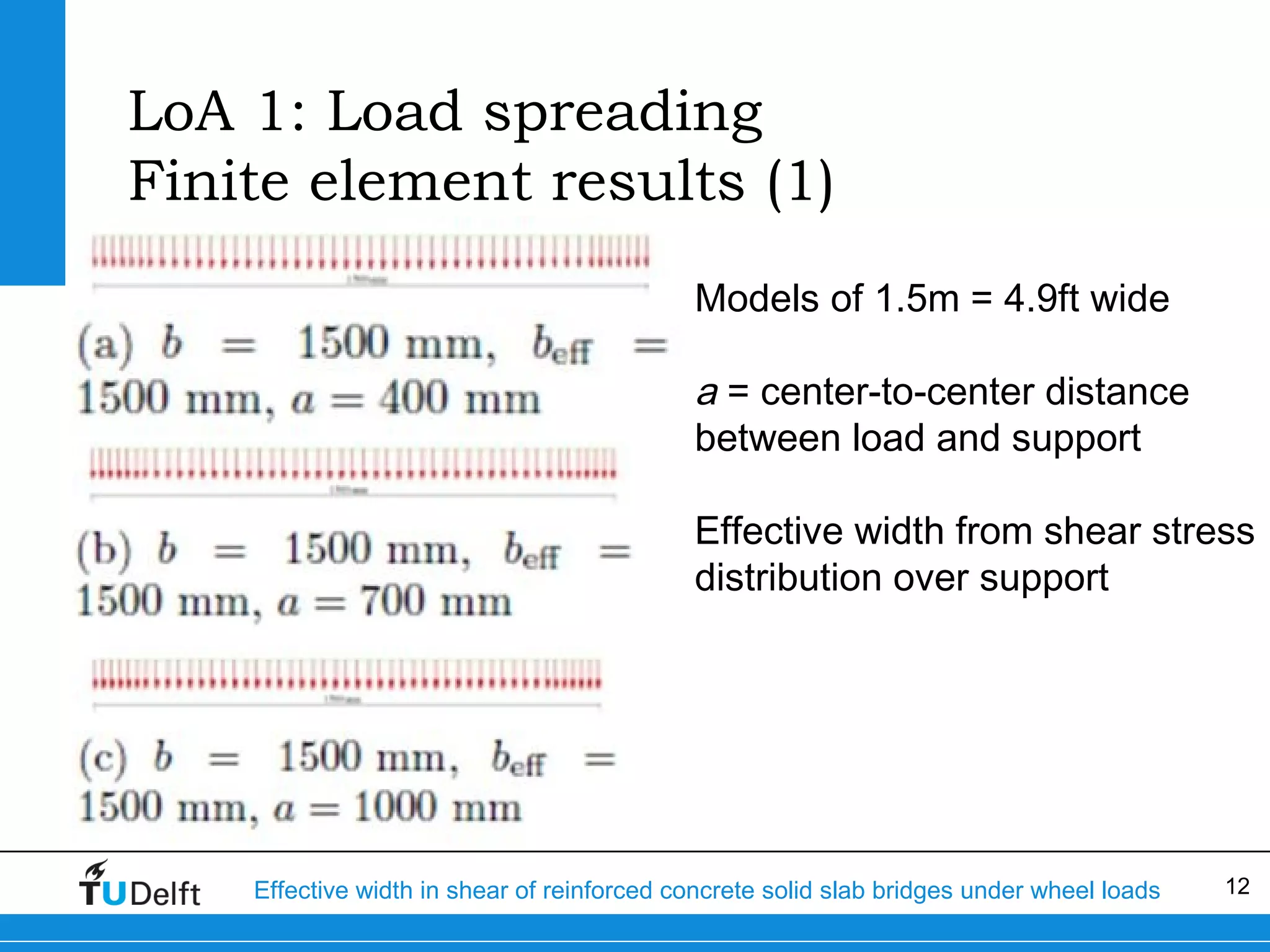
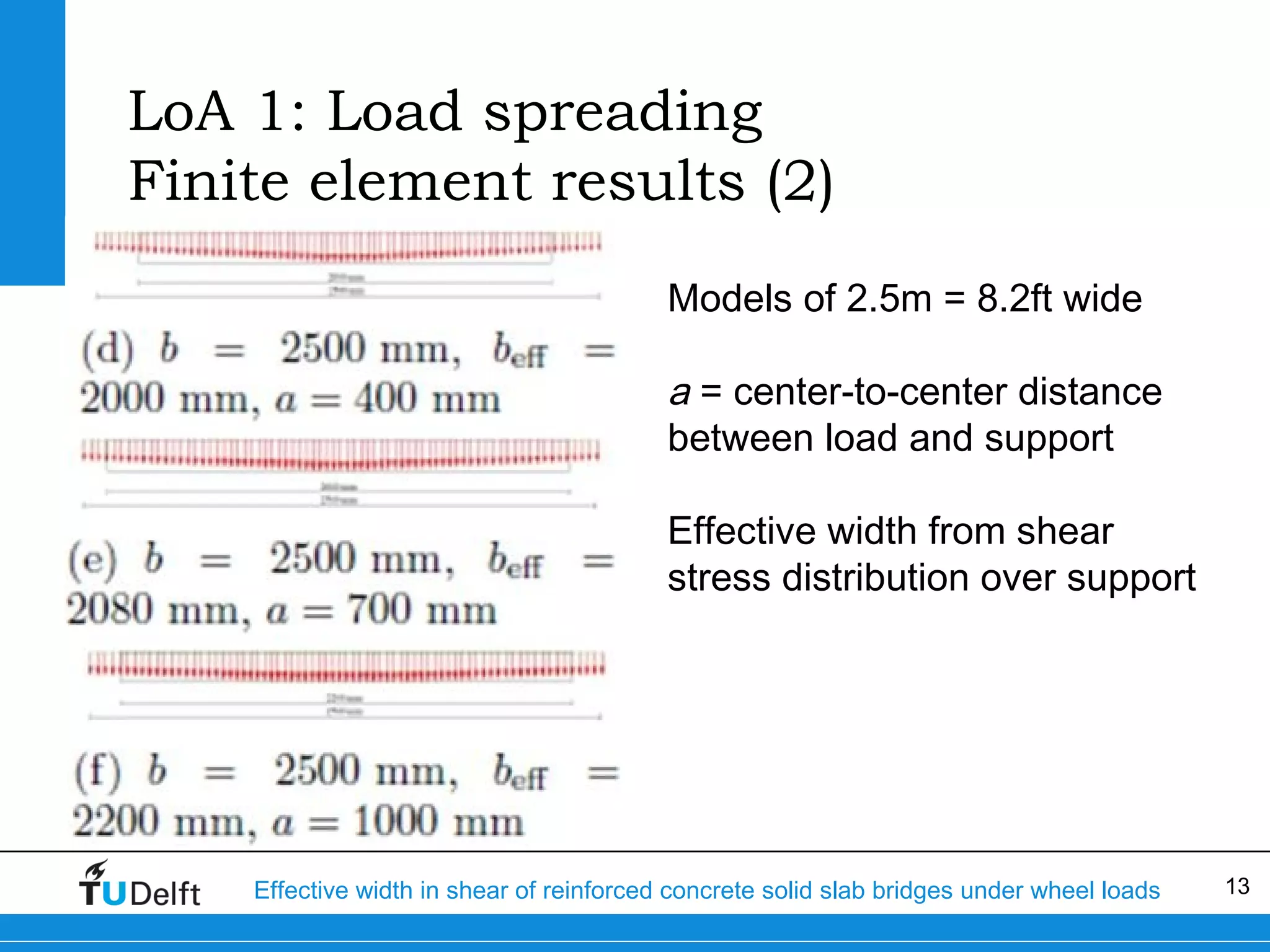
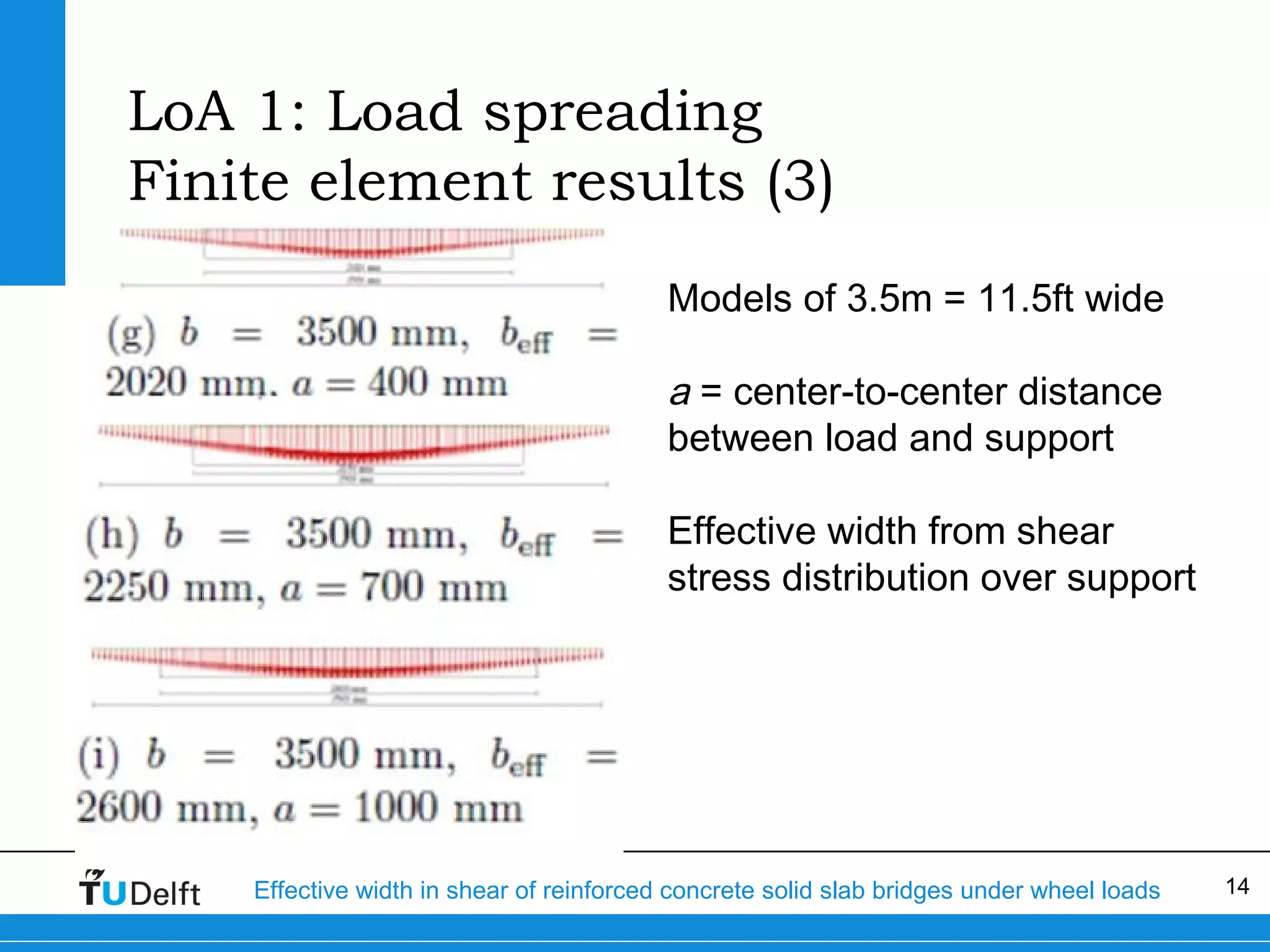
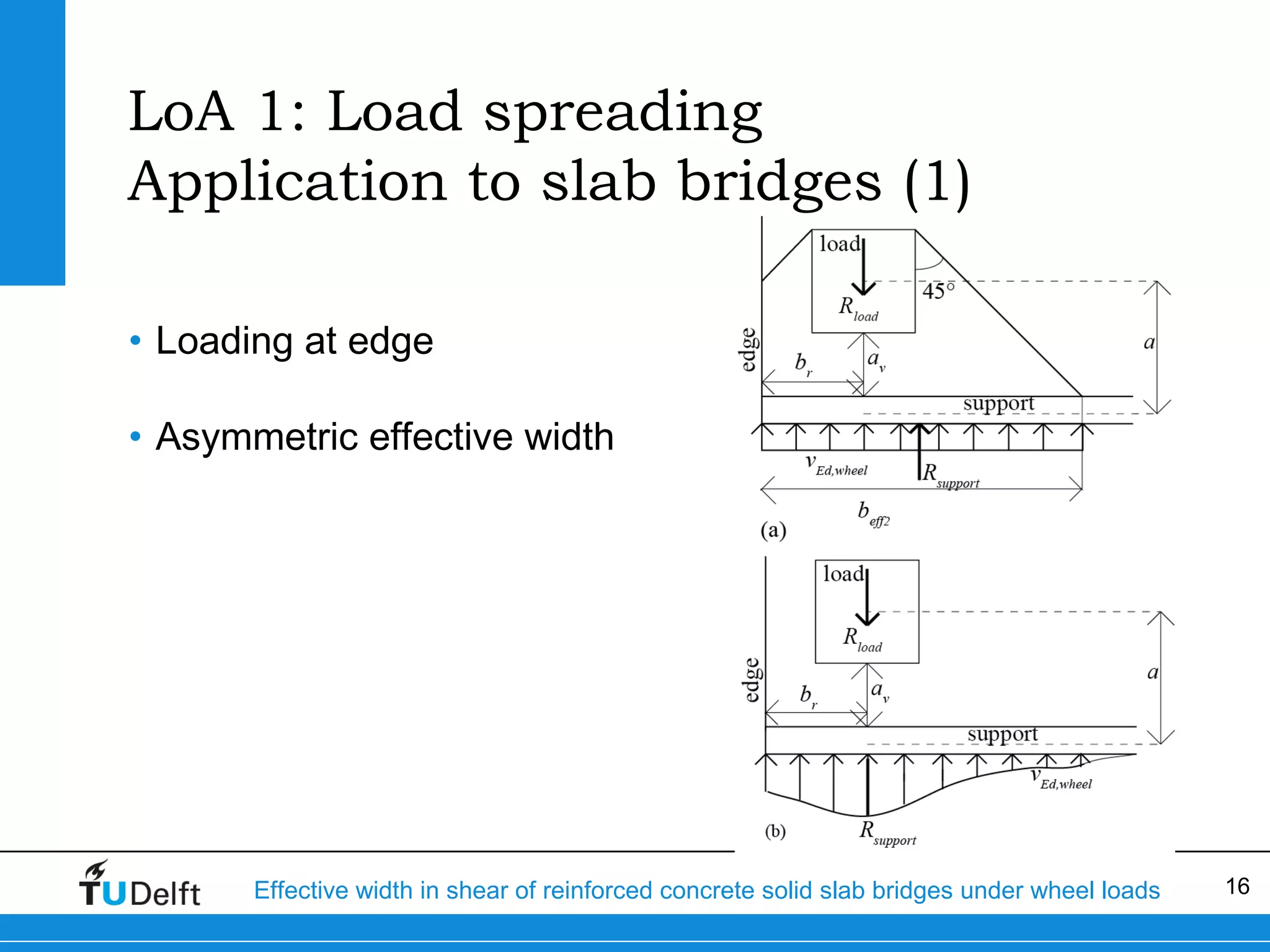
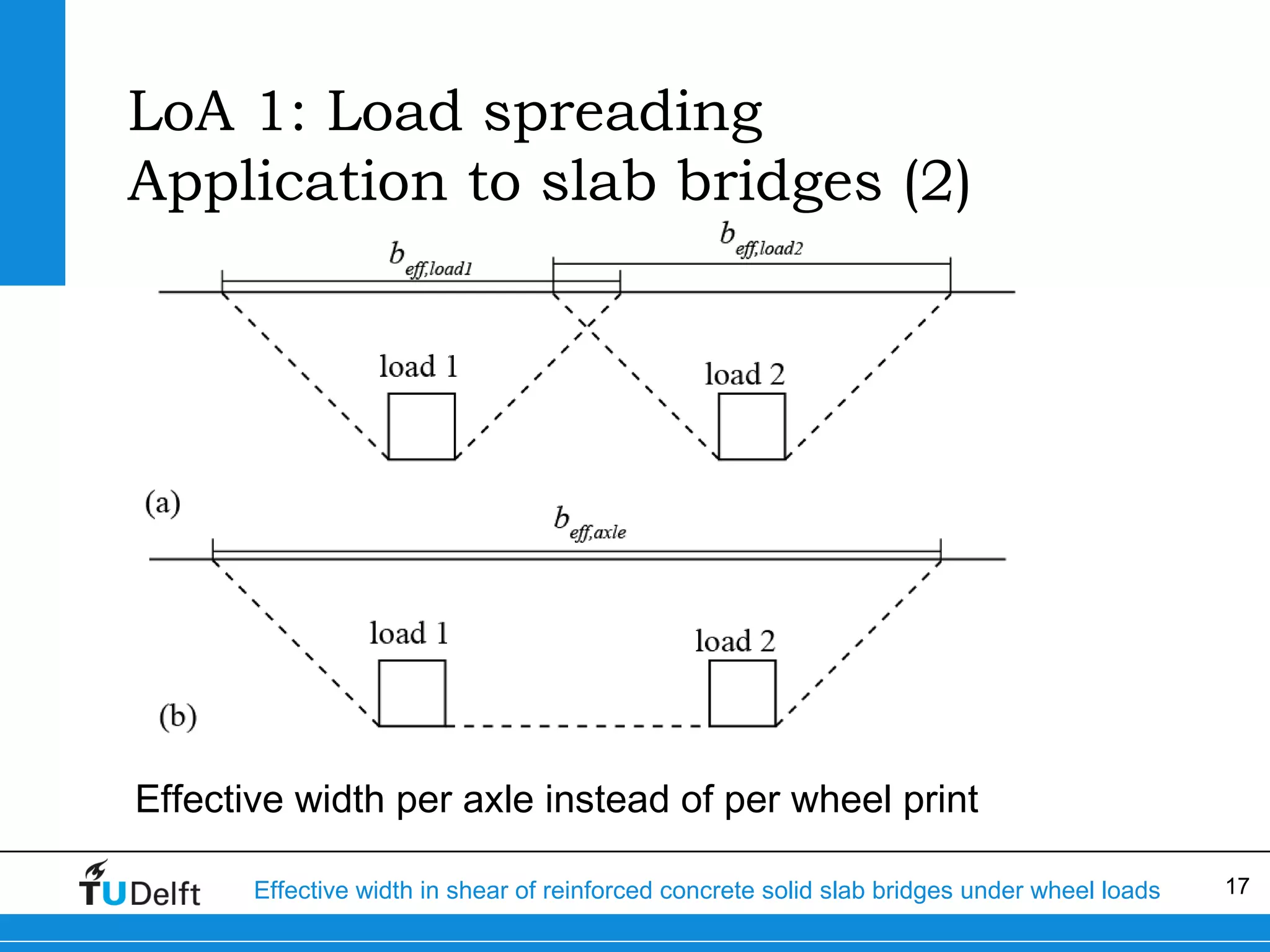
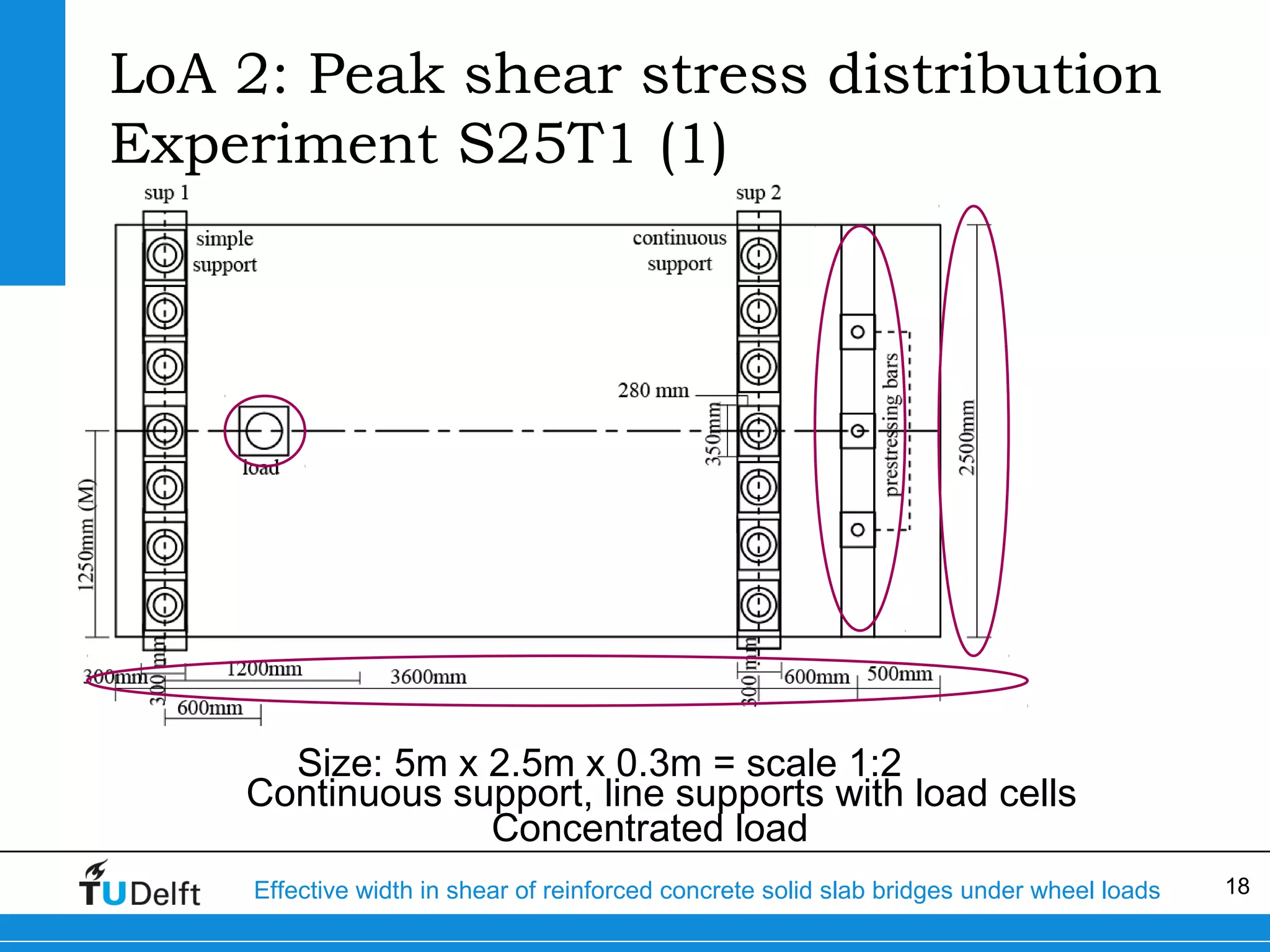
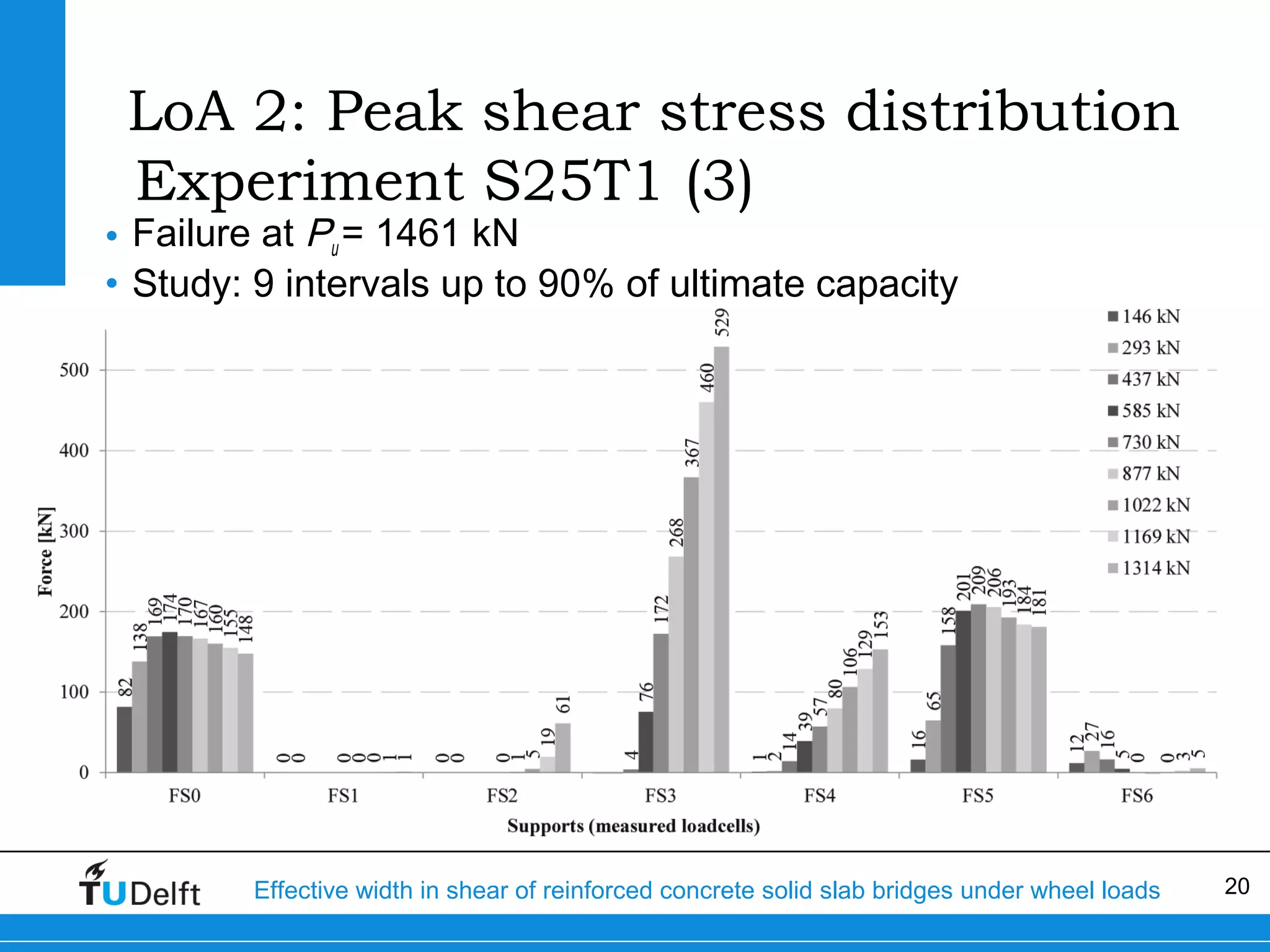
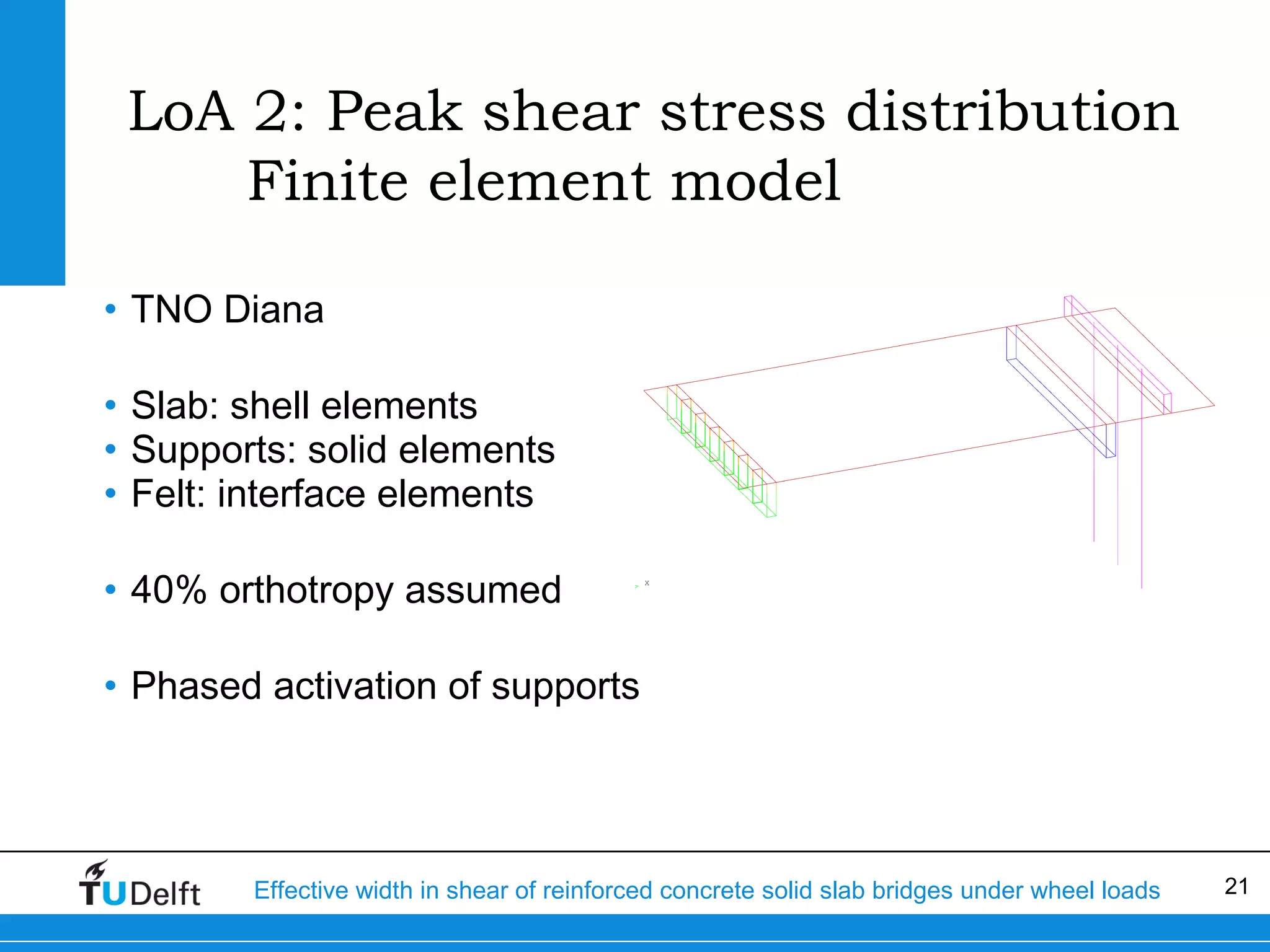
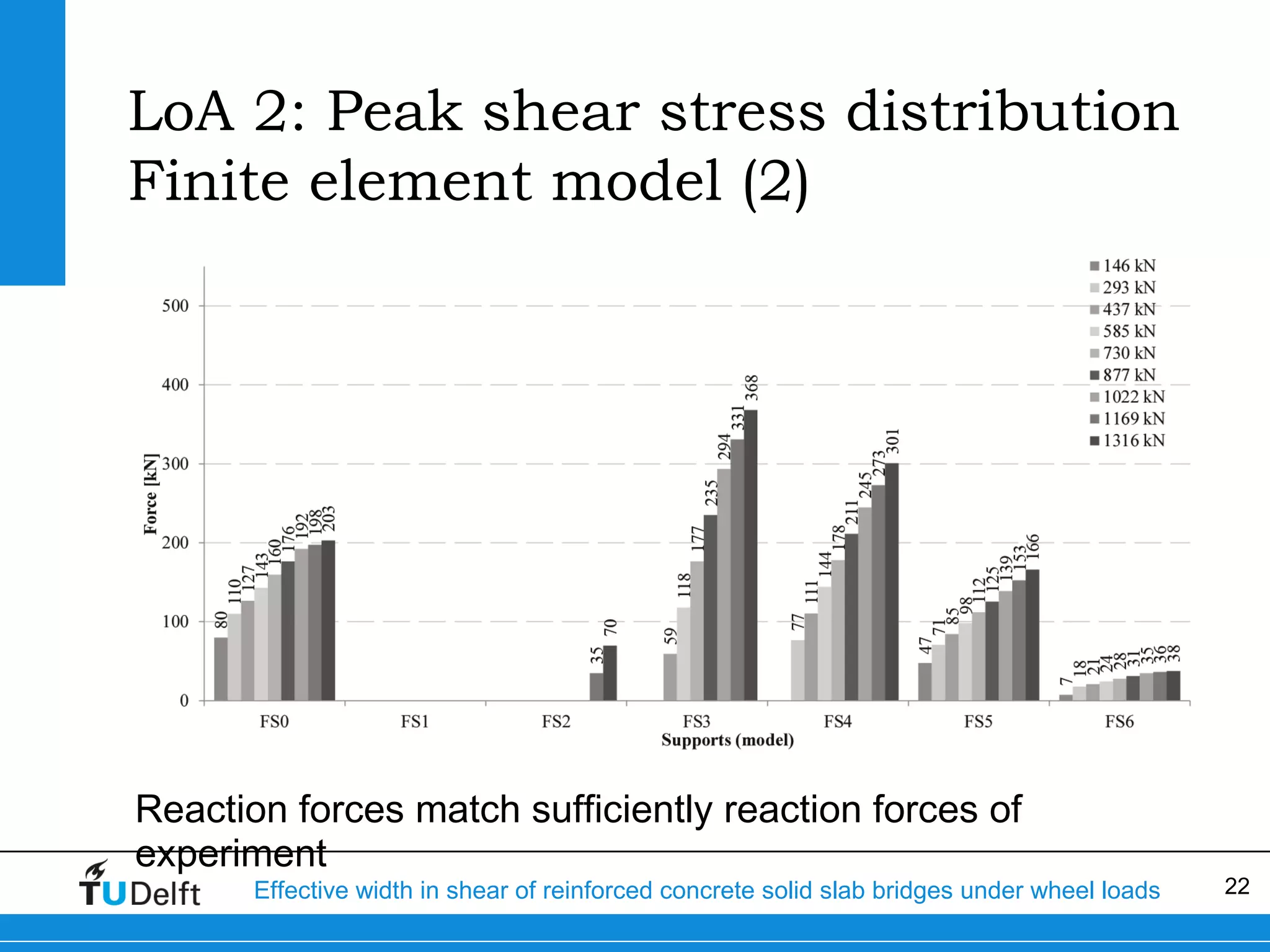
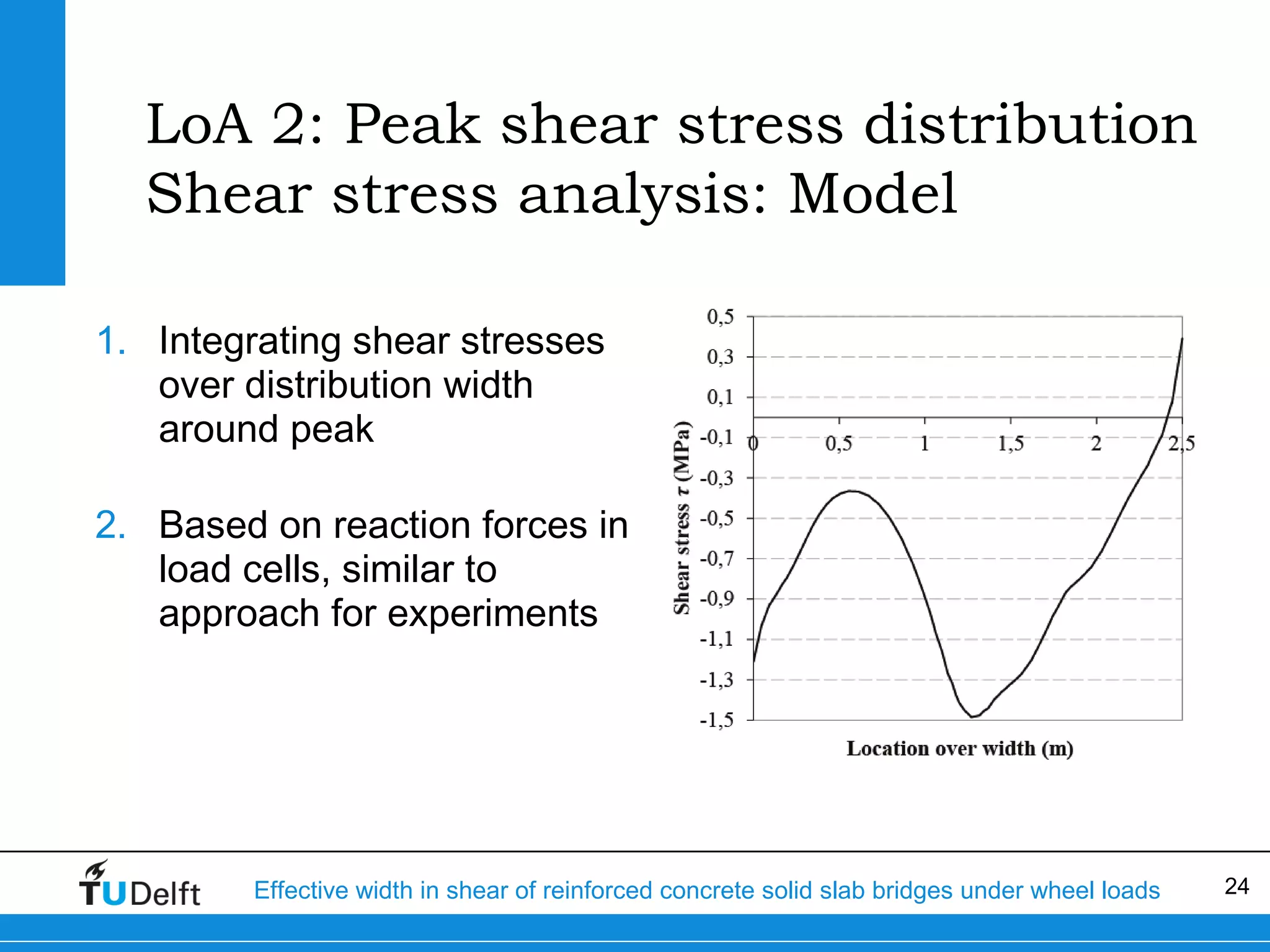
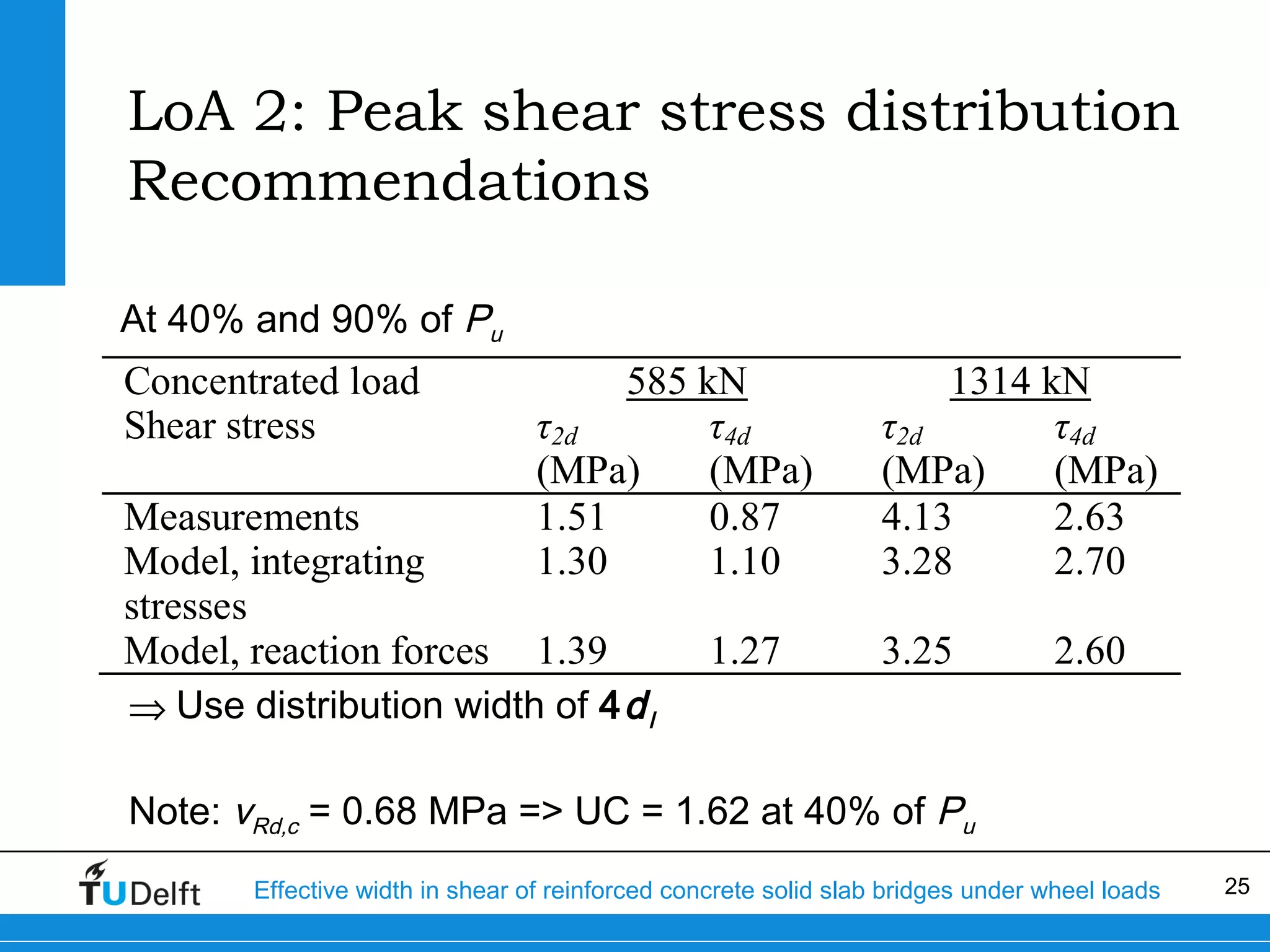
The document discusses the assessment of effective width in shear for reinforced concrete solid slab bridges under heavy wheel loads, focusing on methodologies from the fib model code 2010 and experimental findings. It compares two levels of assessment: a quick scan method and a finite element analysis, highlighting the conservative nature of the quick scan in assessing shear capacity. A case study illustrates that the quick scan method is more conservative compared to the finite element model results.