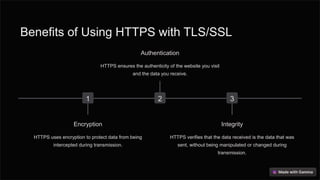
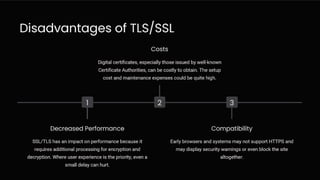
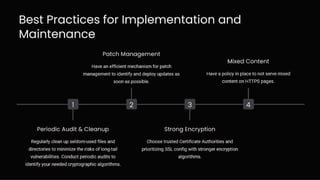
Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL) is essential for secure internet communication, utilizing encryption, authentication, and data integrity. Common use cases include financial transactions, e-commerce, and email, which require protection of sensitive information. As HTTPS becomes more prevalent, users can trust that their data is safeguarded from external threats.