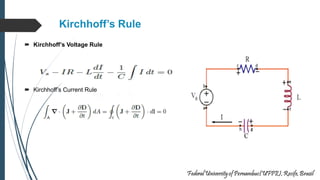
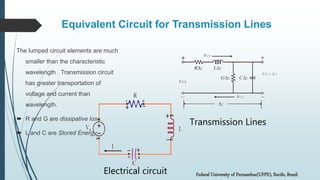
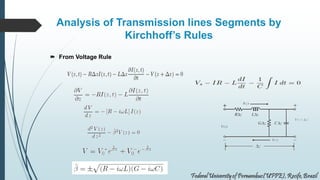
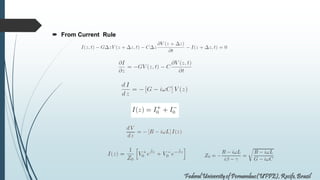
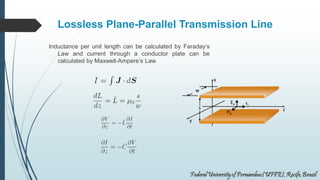
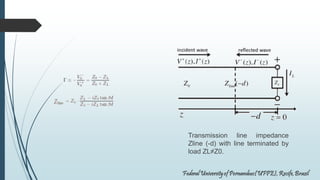
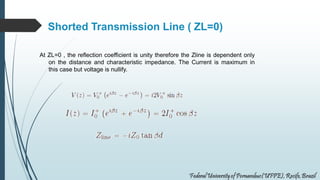
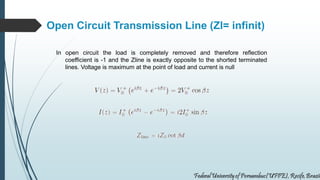
This document discusses transmission lines and their equivalent circuits. It introduces Kirchhoff's rules for analyzing transmission line segments. A lossless plane-parallel transmission line model is presented. Reflection on lossless terminated transmission lines is analyzed. Special termination cases are explored, including shorted lines where current is maximum and open lines where voltage is maximum. The impedance of lines at half-wave and quarter-wave points is also examined.