Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times


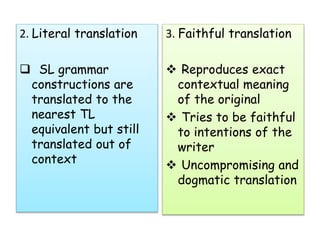
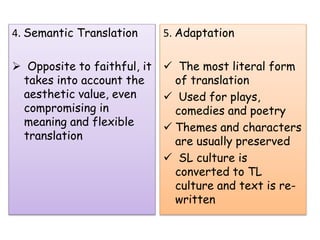


The document outlines 8 methods of translation: 1. Word for word translation which preserves source language word order but translates each word individually without context. 2. Literal translation which translates the grammar structures of the source language to the nearest equivalent in the target language but still lacks context. 3. Faithful translation which reproduces the exact contextual meaning and intentions of the original text in an uncompromising manner.





