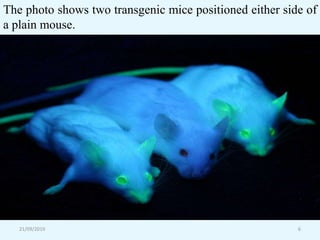
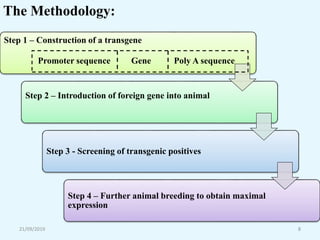
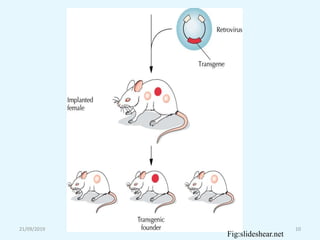
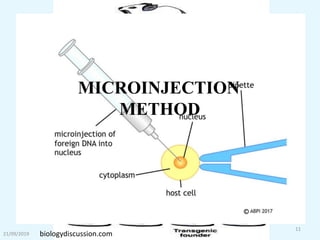
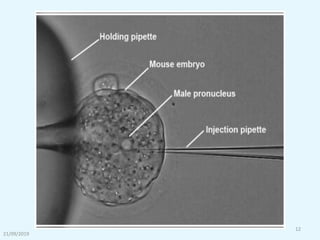
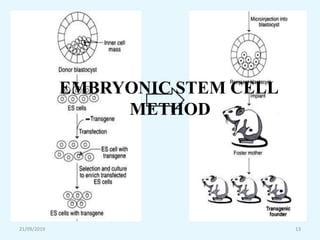
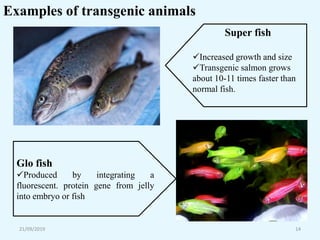
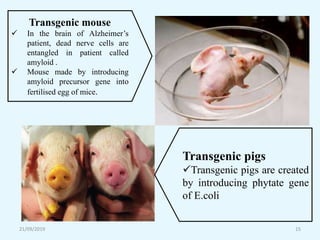
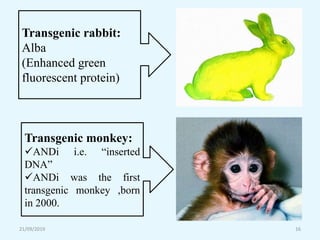
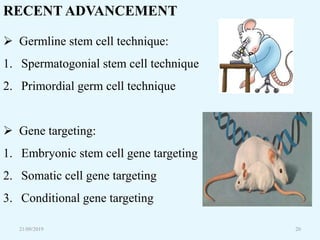
Transgenic animals are organisms that have had genes from another species inserted into their genome. The first transgenic animal was a mouse created in 1982 by inserting a growth gene. Methods for creating transgenic animals include microinjection of DNA into fertilized eggs or use of retroviruses. Transgenic animals have applications in medicine as disease models, in agriculture for improved growth, and in biotechnology for producing human proteins. Recent advances allow gene targeting in embryonic stem cells or germ cells for generating transgenic animals.
![21/09/2019 1
Presented By:
Krishna Bharat Patil
M.Pharmacy 1st year [Pharmacology]
SNJB's SSDJ College of Pharmacy,
Chandwad.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transgenicanimals-200202170411/75/Transgenic-animals-1-2048.jpg)


![21/09/2019 5
History:
Ralph L. Brinster
[American geneticist ]
(1982)
Rudolf Jaenisch
[Professor of Biology]
(1974)
Richard Palmiter
[Professor of biochemistry]
(1982)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transgenicanimals-200202170411/85/Transgenic-animals-5-320.jpg)