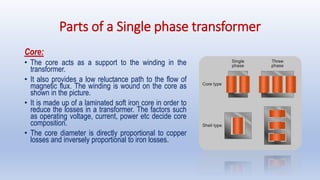
- A transformer is a device that increases or decreases alternating current voltages through electromagnetic induction. It works by using a primary and secondary coil around an iron core to induce a voltage in the secondary coil proportional to the voltage in the primary coil.
- The transformer works based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field in the primary coil induces a voltage in the nearby secondary coil.
- Transformers come in different types depending on their application, including step-up transformers to increase voltage for transmission, step-down transformers to decrease voltage for distribution and end use, and specialty transformers used in devices like radios and televisions.