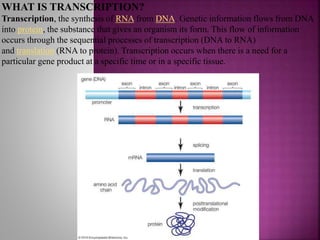
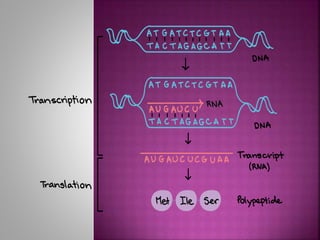
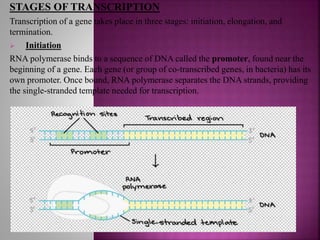
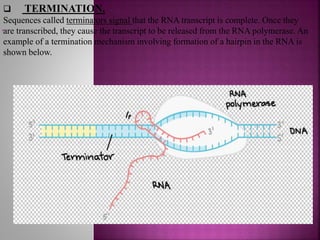
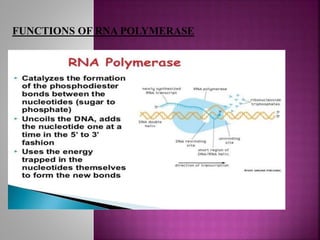
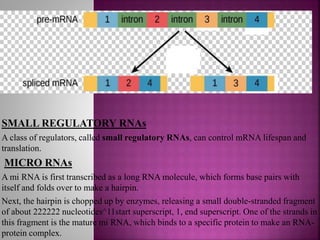
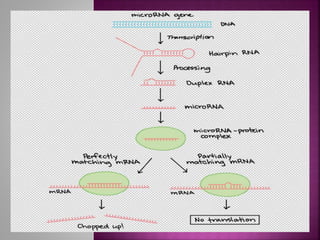
Transcription is the process of copying genetic information from DNA to RNA. It involves three main stages - initiation, elongation, and termination. RNA polymerase binds to promoter sequences near genes and uses the DNA as a template to synthesize complementary RNA strands. In eukaryotes, the primary RNA transcripts undergo further processing including splicing, capping, and polyadenylation. Transcription and its regulation allow genetic information to be selectively expressed as needed and provide an additional layer of gene control.