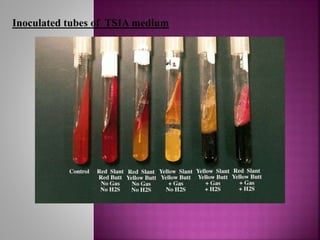
This document describes how to use TSIA medium to identify enteric pathogens through carbohydrate fermentation patterns and hydrogen sulfide production. The procedure involves inoculating TSIA medium in test tubes with microbial cultures, incubating the tubes, and observing the color changes in the slant and butt portions which indicate different fermentation reactions and hydrogen sulfide production. Based on the observed results, the microbe can be identified by comparing to an interpretation table provided. Precautions include properly sterilizing glassware, carefully inoculating the butt region, and loosely covering tubes during incubation.