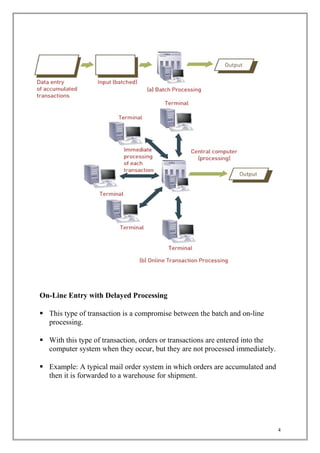
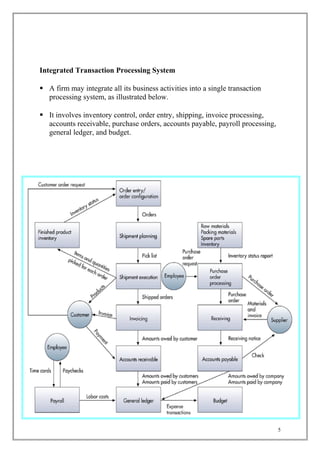
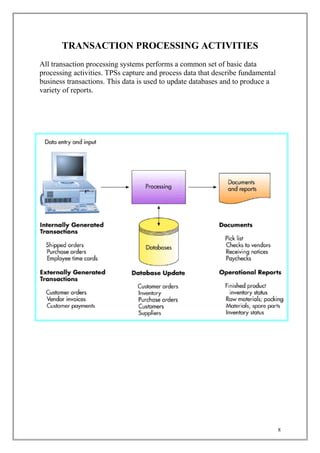
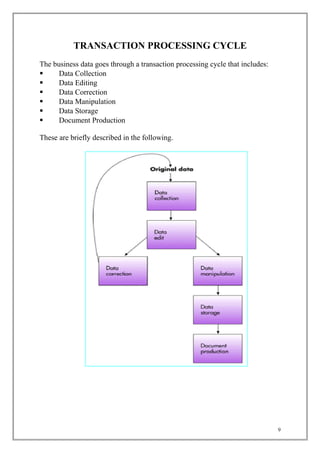
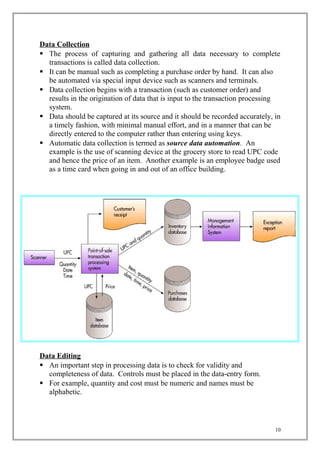
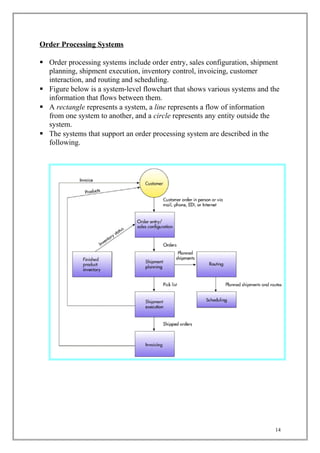
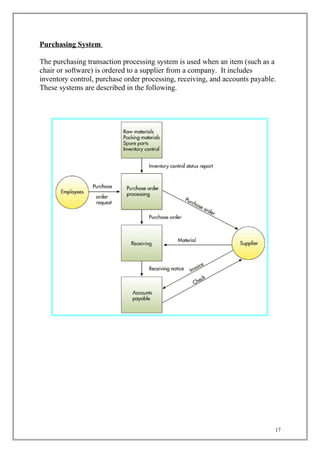
The document discusses transaction processing systems. It defines transaction processing systems as systems that perform routine business operations like order entry, inventory control, and payroll. It describes different types of transaction processing like batch processing and real-time processing. It outlines the objectives of transaction processing systems like ensuring data accuracy, producing timely reports, and increasing efficiency. It then explains the typical transaction processing cycle of data collection, editing, correction, manipulation, storage, and document production.