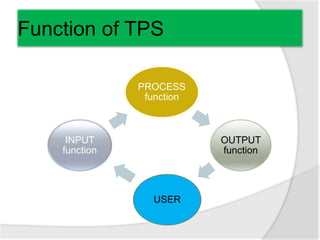
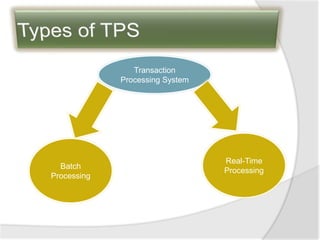
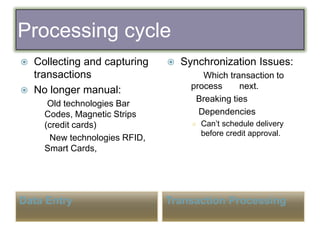
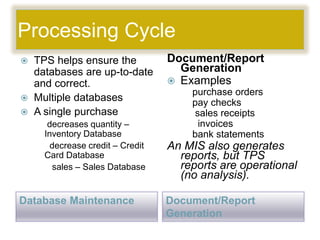
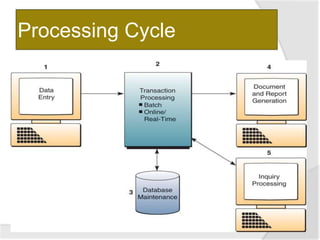
This document discusses transaction processing systems (TPS). It defines a TPS as an information system that captures and processes data from daily business transactions like deposits, payments, orders or reservations. A TPS has several functions including processing transactions, outputting information, and accepting user inputs. It discusses the differences between batch processing, which collects and stores data to update databases later, and real-time processing, which immediately processes transactions. Key features of TPS include rapid response, reliability, inflexibility, and controlled processing. TPS must pass the ACID test of atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability to qualify. The document outlines the five stages of transaction processing: data entry, processing, database maintenance, document/report