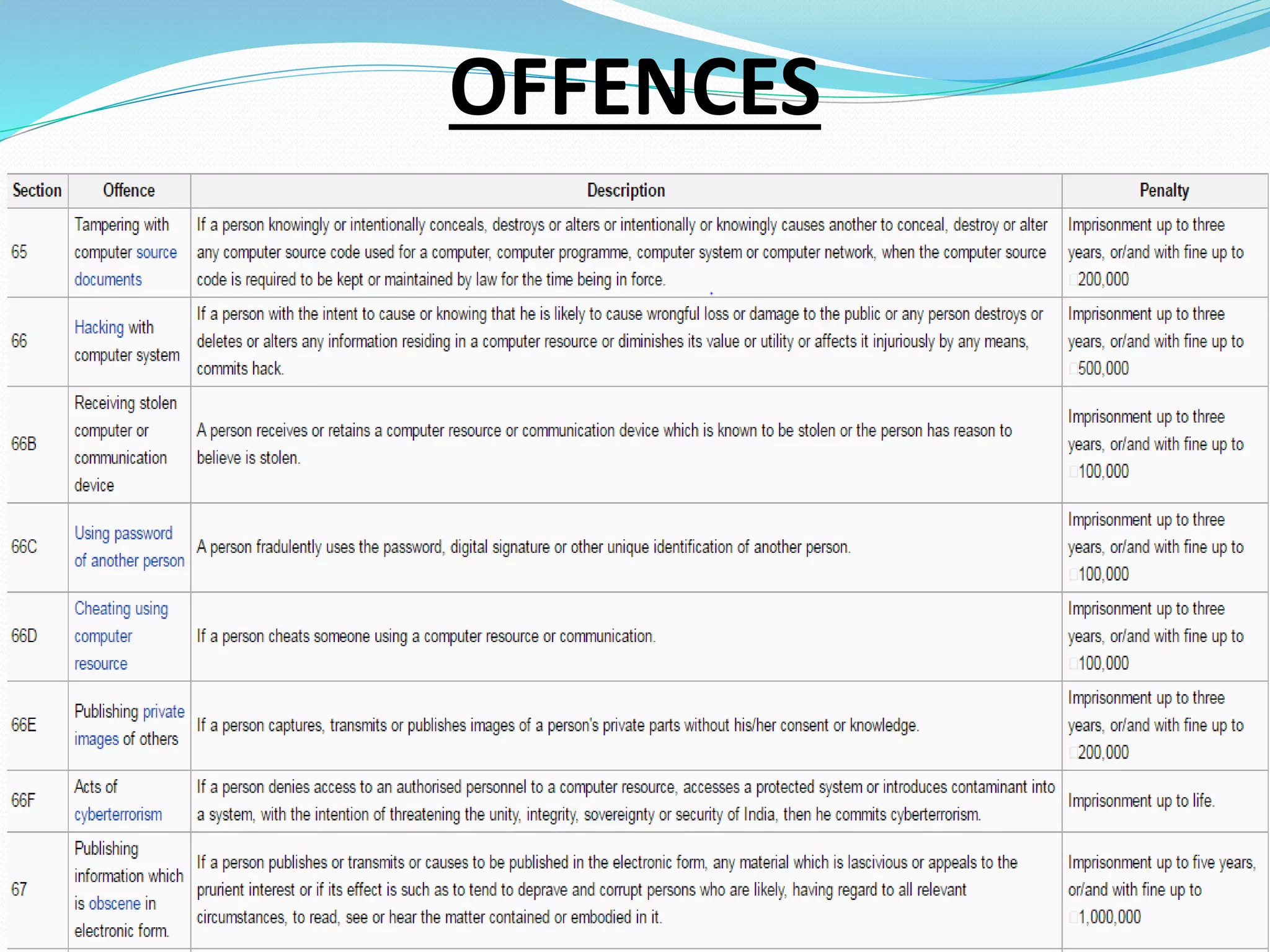
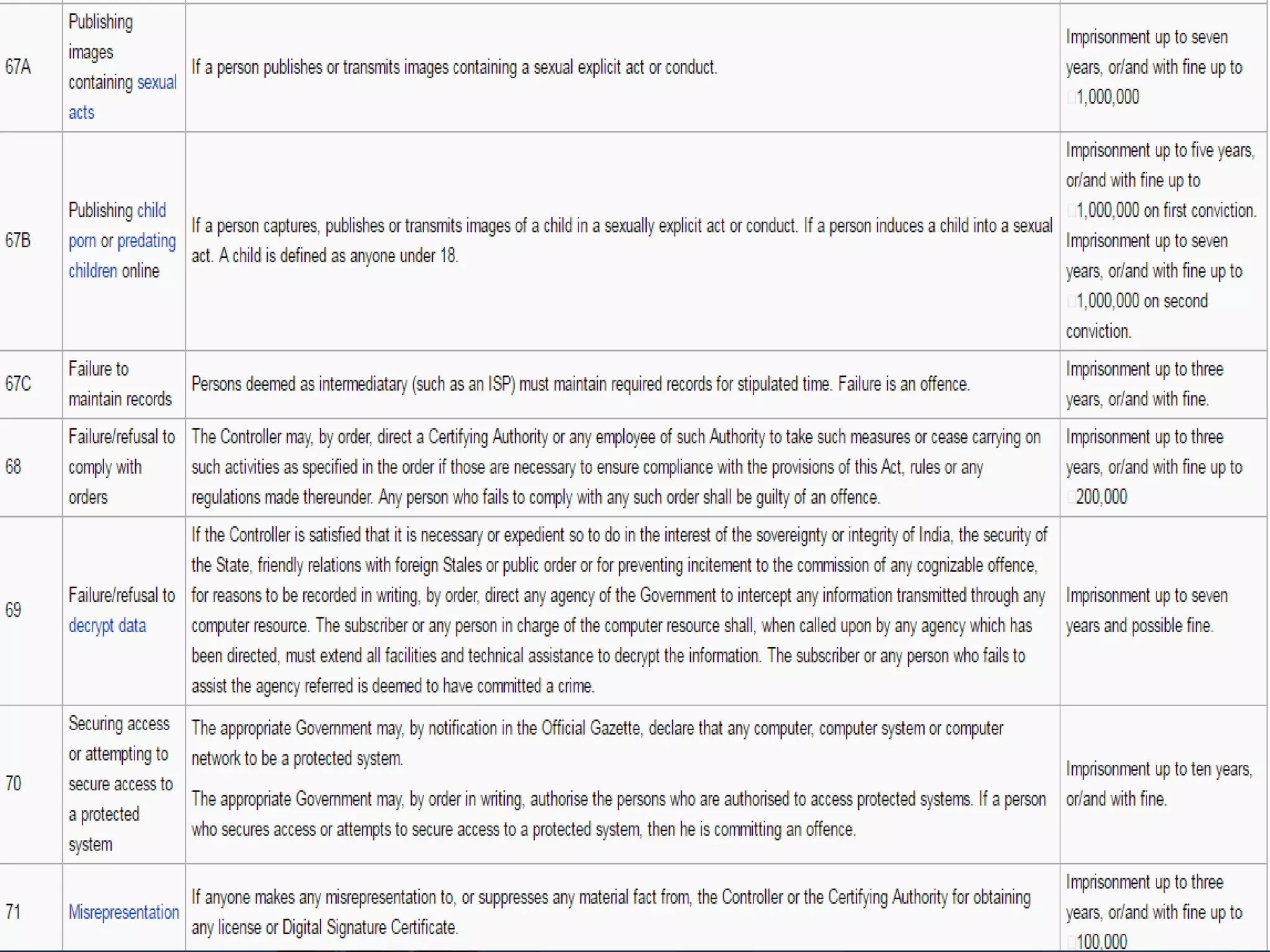
The document provides an overview of the Information Technology Act, 2000 which is the primary law dealing with cybercrime and electronic commerce in India. It was enacted based on a UN model law to provide legal recognition to electronic transactions and facilitate e-commerce. The key points covered include objectives of the act, scope and applications, amendments introduced, provisions related to digital signatures, roles of certifying authorities, duties of subscribers, and penalties for offences.