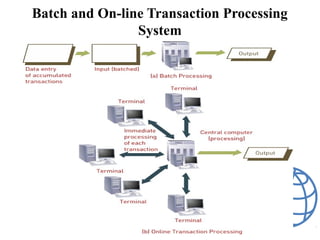
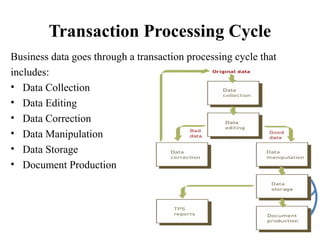
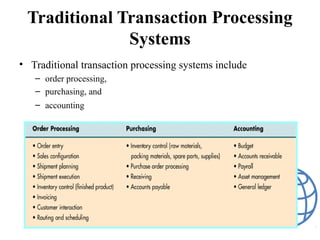
A transaction processing system (TPS) collects, stores, modifies, and retrieves data about business transactions. TPS are designed to efficiently process large volumes of routine transactions through automation. The objectives of a TPS are to accurately process transaction data, maintain data integrity, produce timely reports, and increase efficiency. A TPS has users within the owning organization and participants who conduct transactions. It uses either batch processing, where transactions are collected and processed in batches, or online transaction processing, where each transaction is immediately processed. The transaction processing cycle includes data collection, editing, correction, manipulation, storage, and document production.