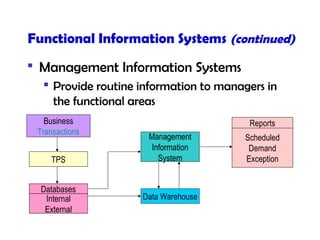
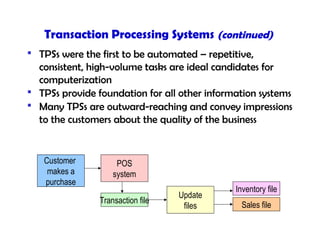
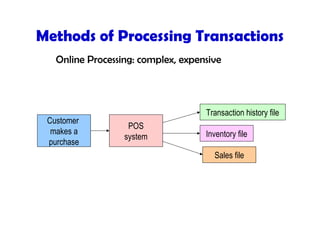
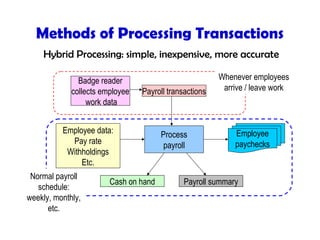
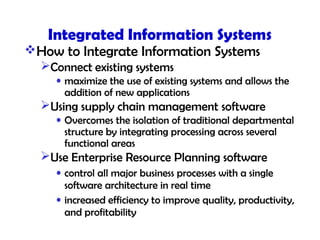
This document discusses key concepts in information systems, including transaction processing systems (TPS), management information systems (MIS), and how information systems support various business functions like accounting, sales, production, and human resources. It also covers integrating functional systems, interorganizational systems, and issues in designing global information systems.