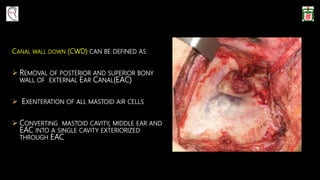
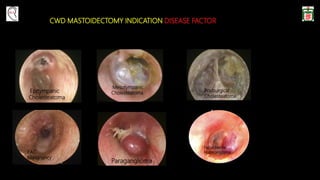
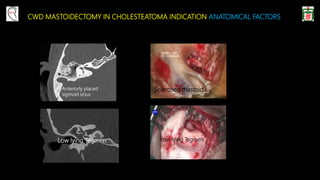
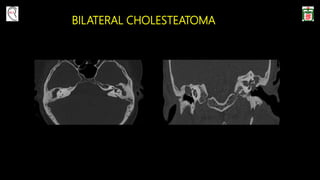
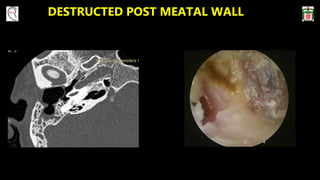
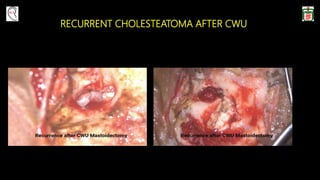
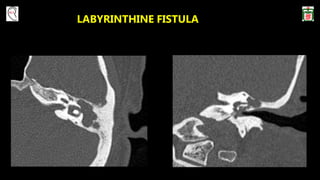
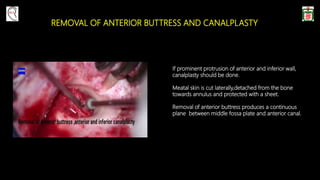
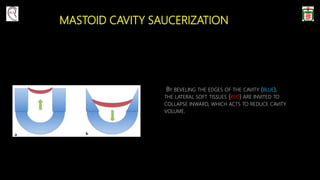
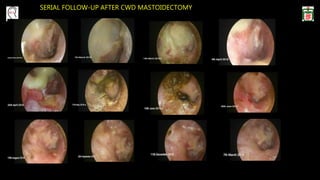
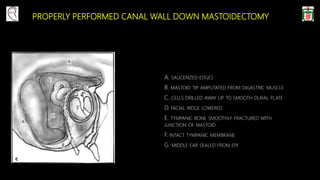
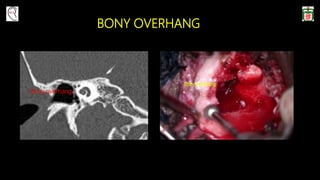
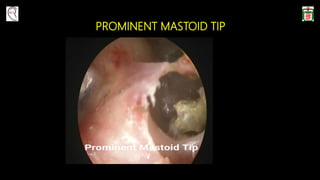
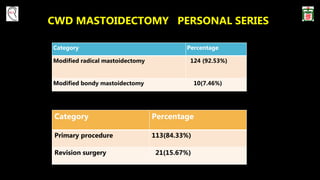
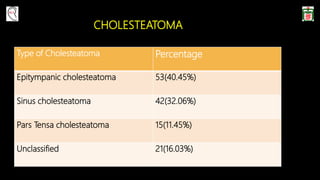
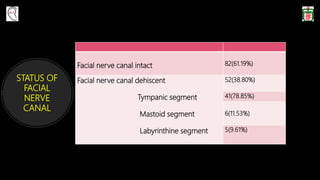
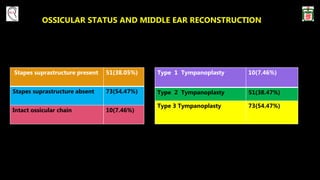
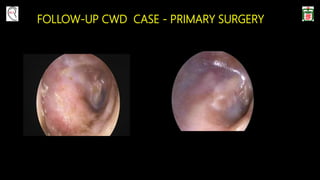
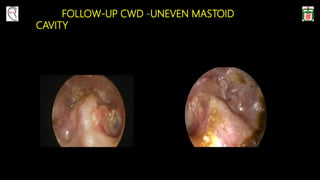
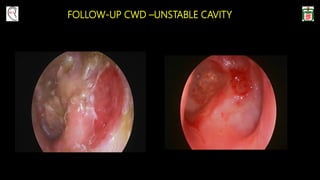
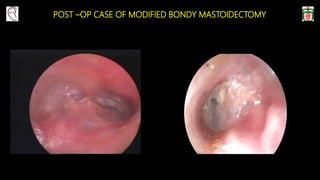
This document provides information on canal wall down (CWD) mastoidectomy surgery. It defines CWD mastoidectomy as the removal of the posterior and superior bony walls of the external ear canal and excision of all mastoid air cells, converting the mastoid cavity, middle ear, and ear canal into a single cavity exteriorized through the ear canal. It discusses indications for CWD mastoidectomy such as cholesteatoma, tumors, and anatomical factors like a low-lying tegmen. The document outlines the surgical technique and considerations like facial ridge lowering. It also addresses outcomes, complications, and the challenges of long-term management after CWD mastoidectomy.