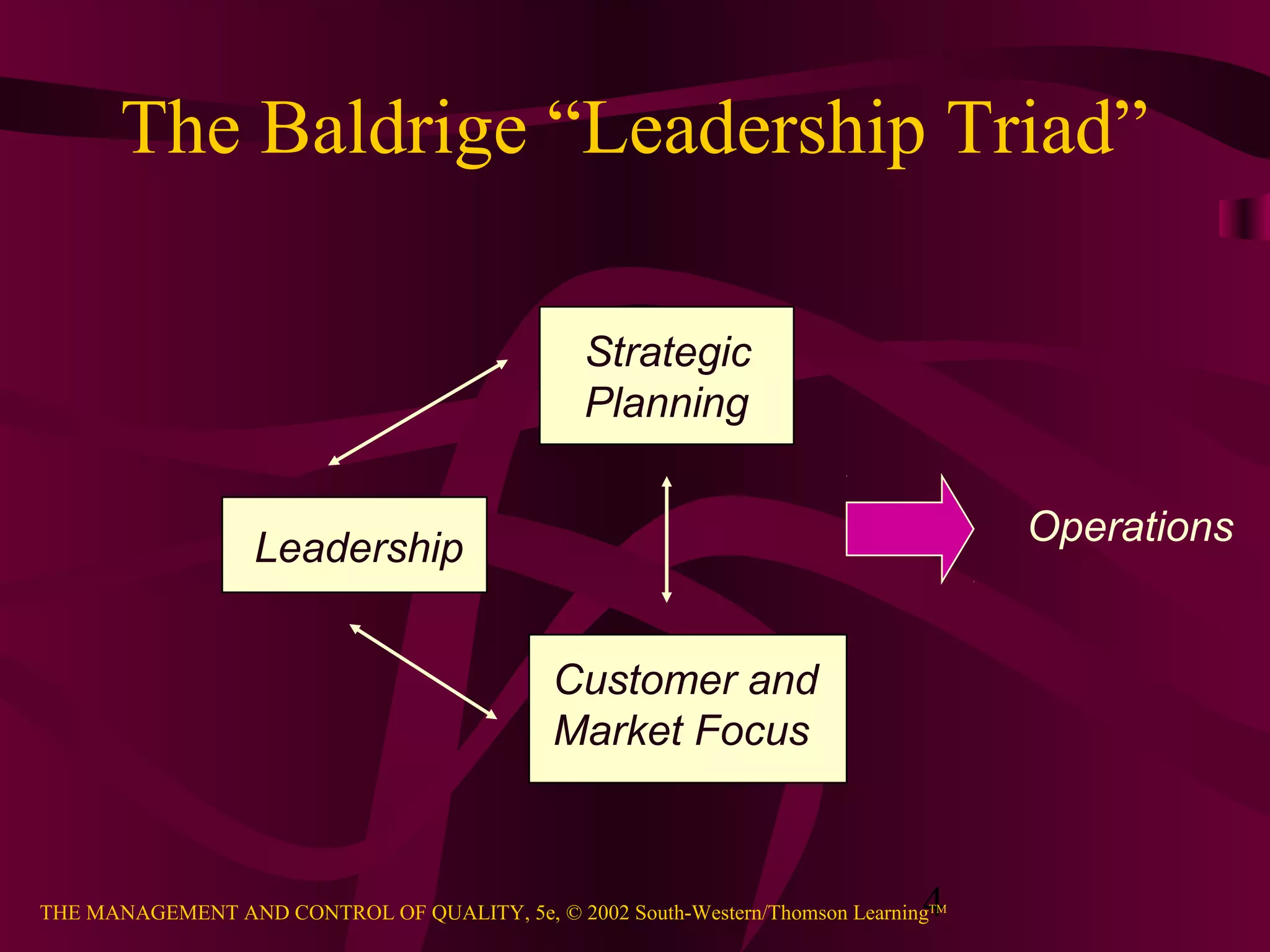
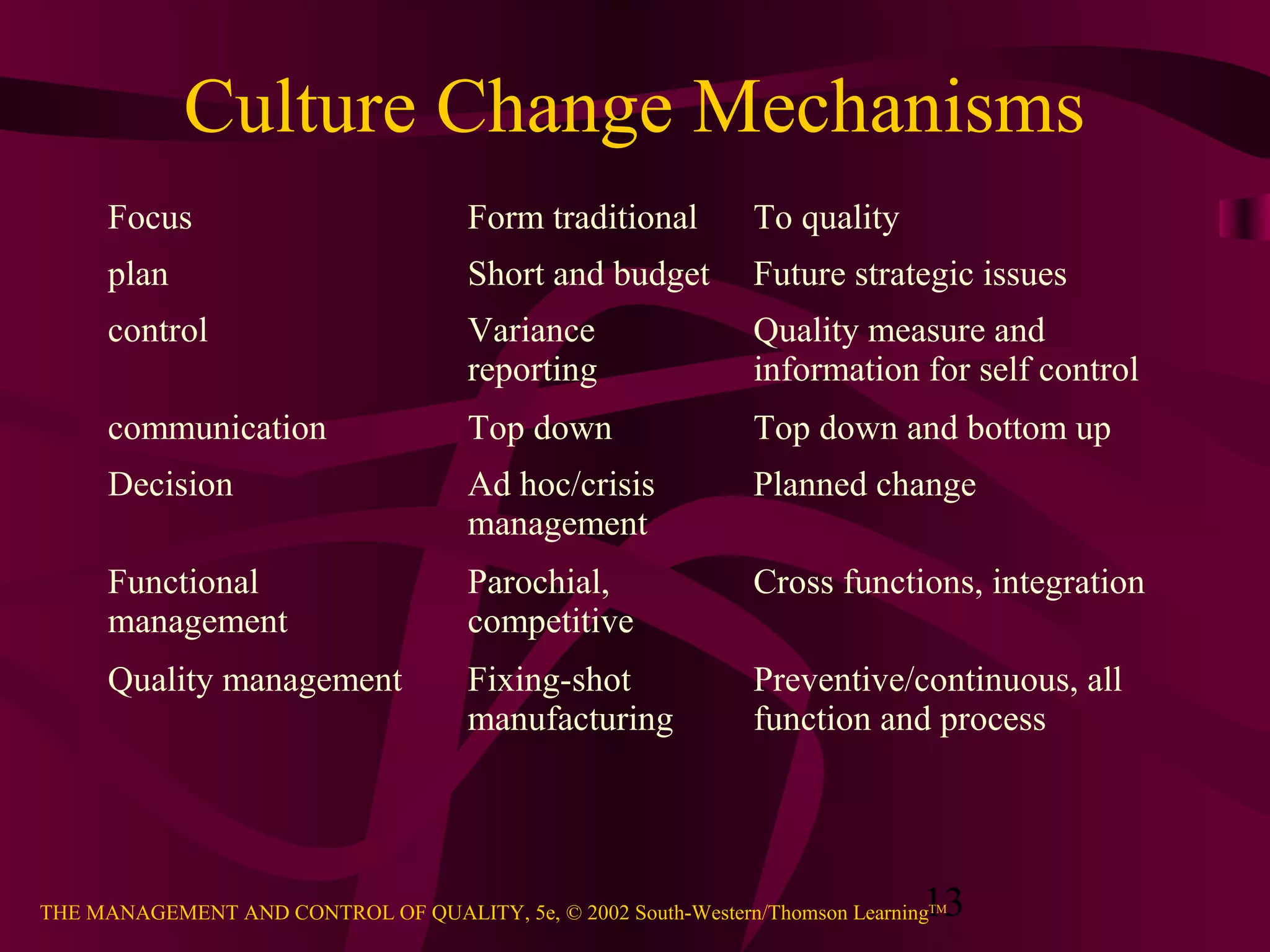
The document discusses the importance of leadership for total quality management (TQM). It describes leadership as influencing people and systems to have an impact and achieve results. A key part of leadership is strategic planning to envision the organization's future. The Baldrige criteria examine how senior leaders address values, directions, performance expectations and focus on customers. Effective leadership requires visible commitment from top management, clear communication, and embedding a culture of quality throughout the organization.