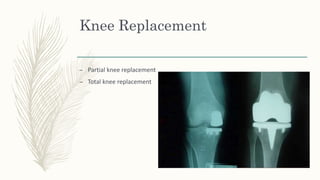
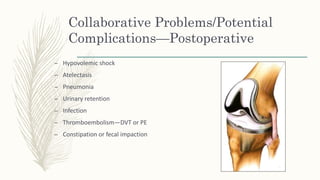
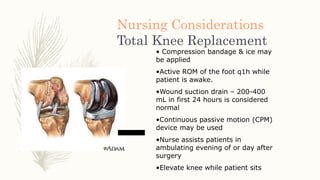
Total knee replacement surgery aims to relieve pain and restore function and mobility in knees affected by conditions such as arthritis, deformity, or injury. Candidates for total knee replacement have severe daily pain and limited activities due to advanced radiographic changes in the knee. After surgery, patients undergo physical therapy and rehabilitation to regain mobility and strength, including range of motion exercises. Nurses monitor vital signs and provide wound care to prevent complications like infection, deep vein thrombosis, and pneumonia during the postoperative recovery period.