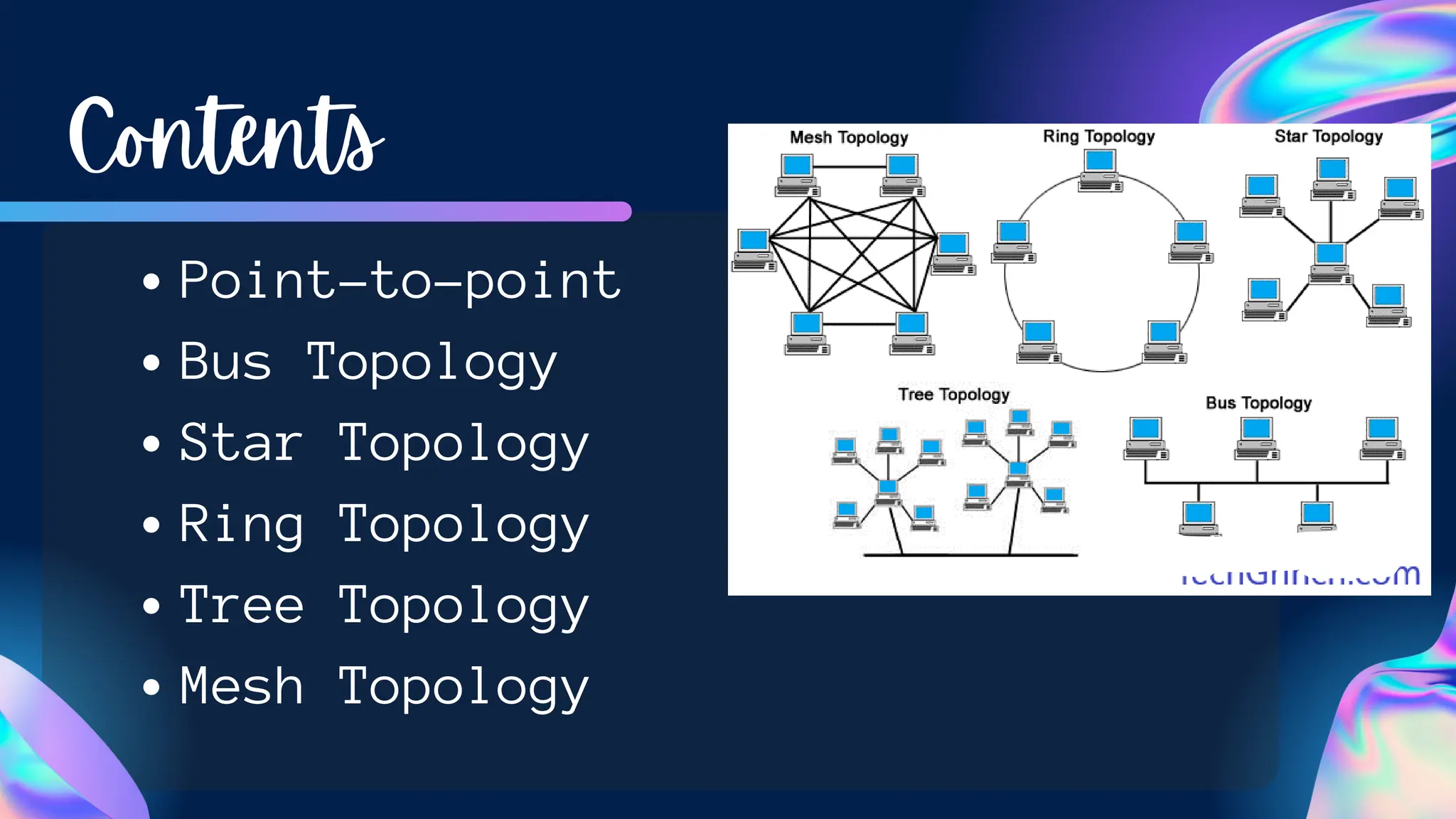
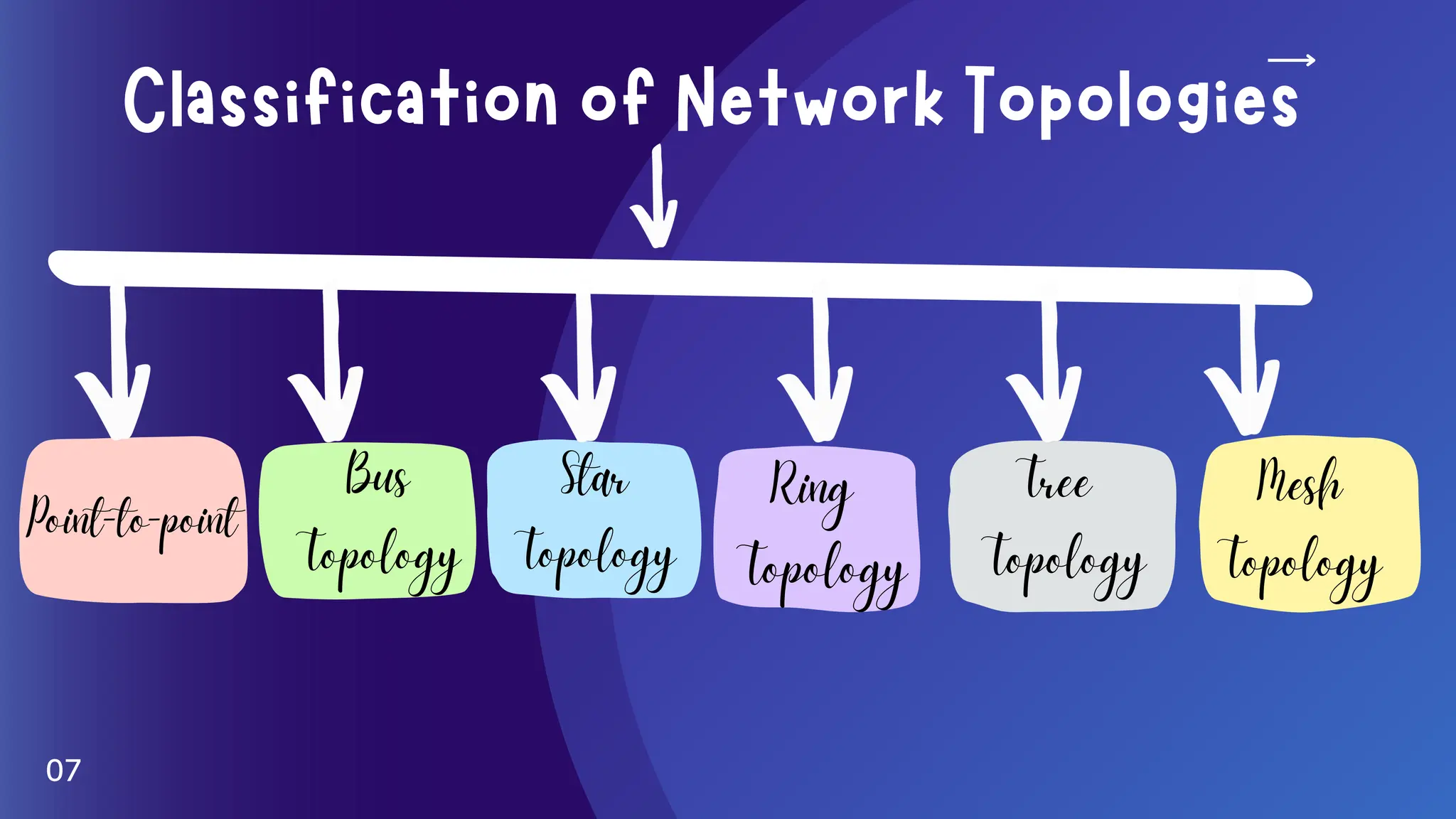
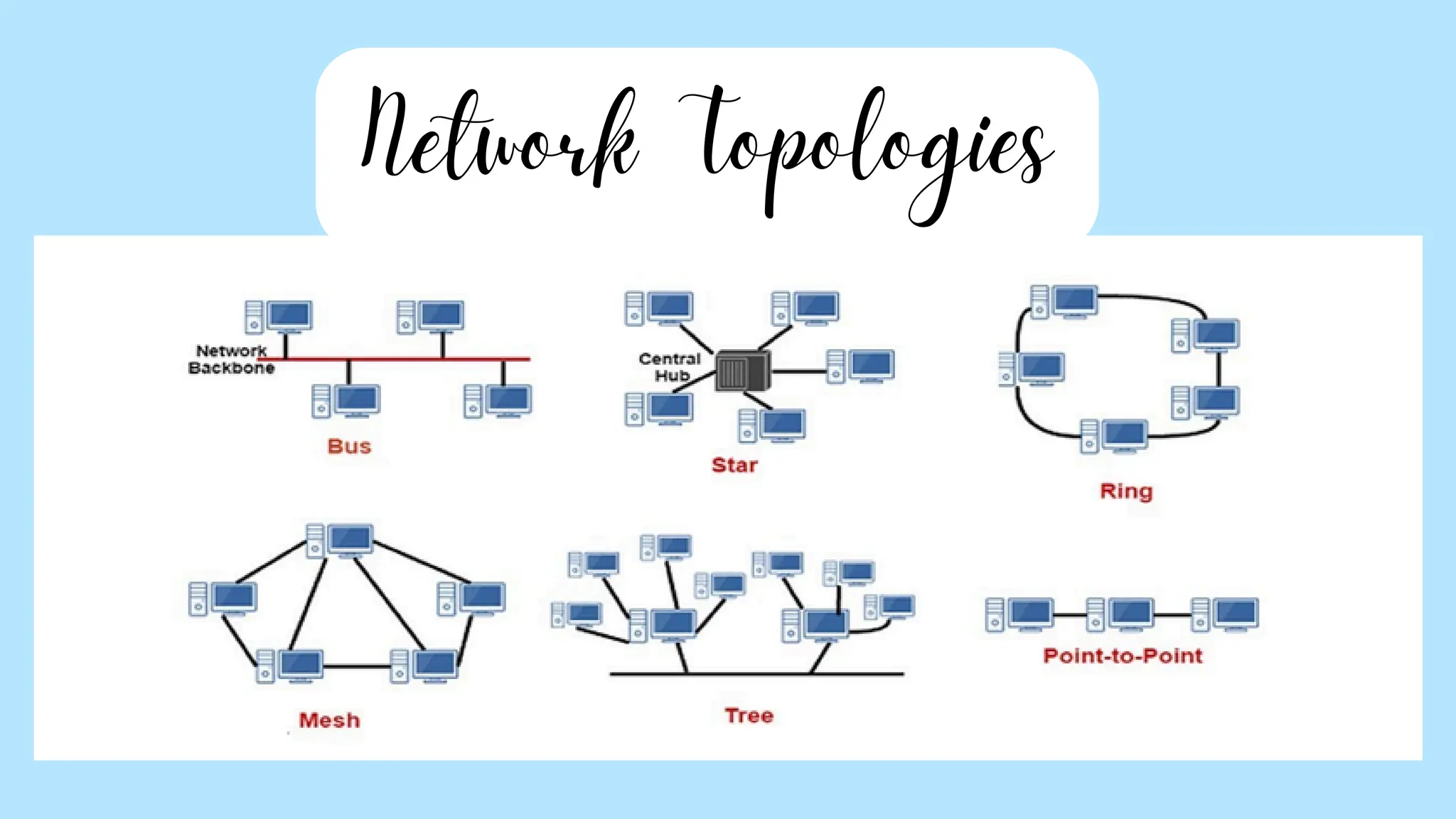
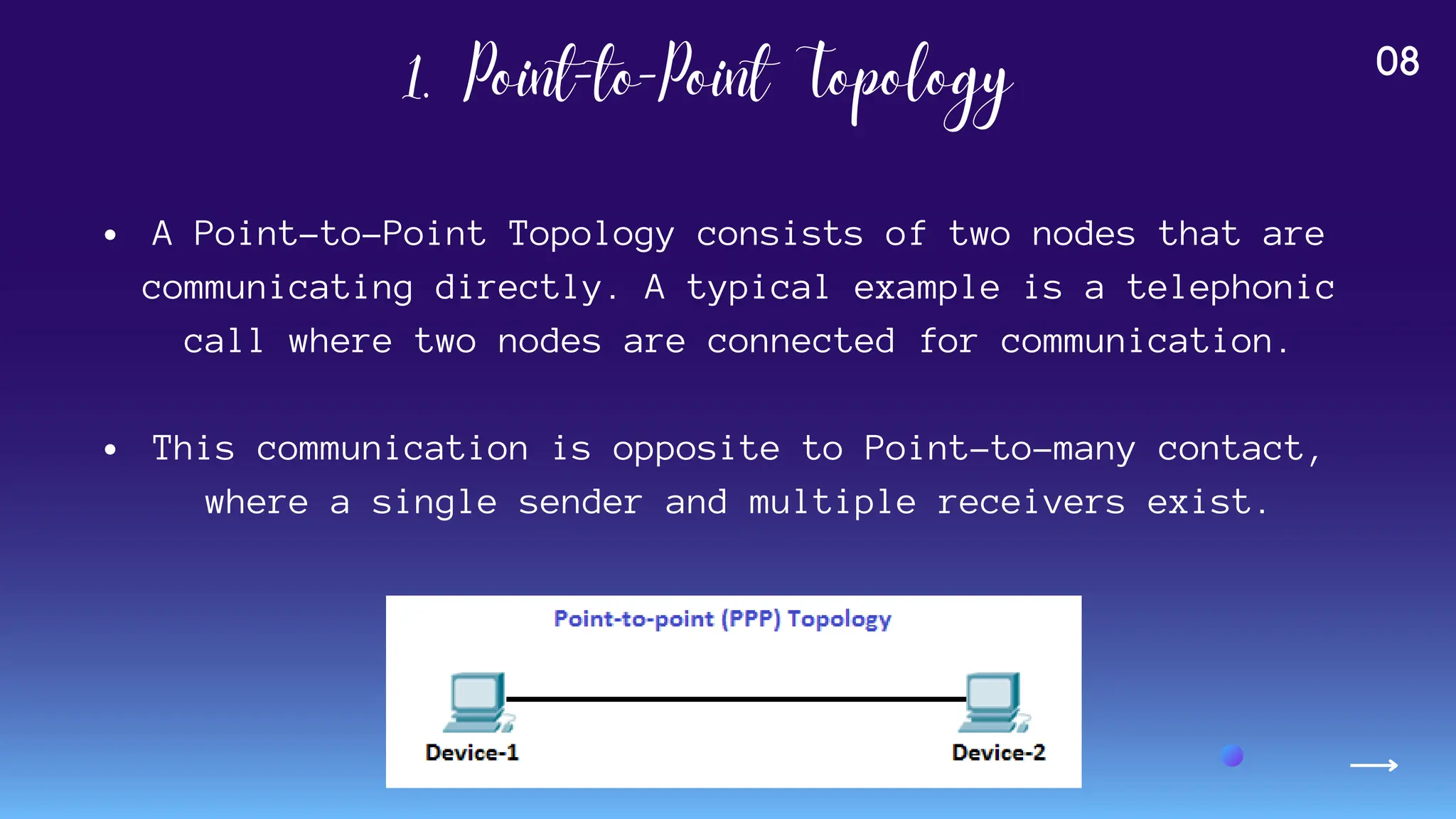
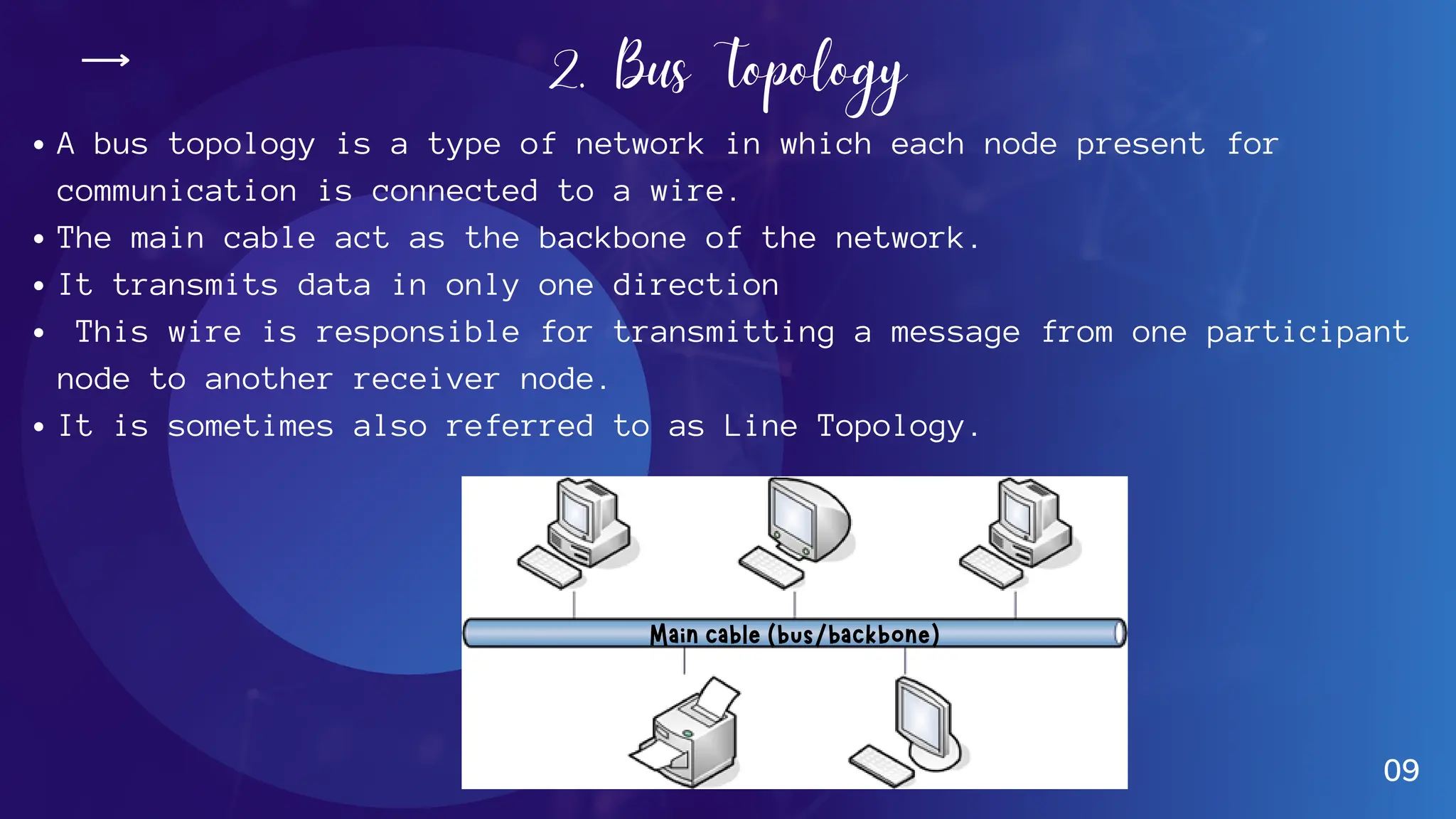
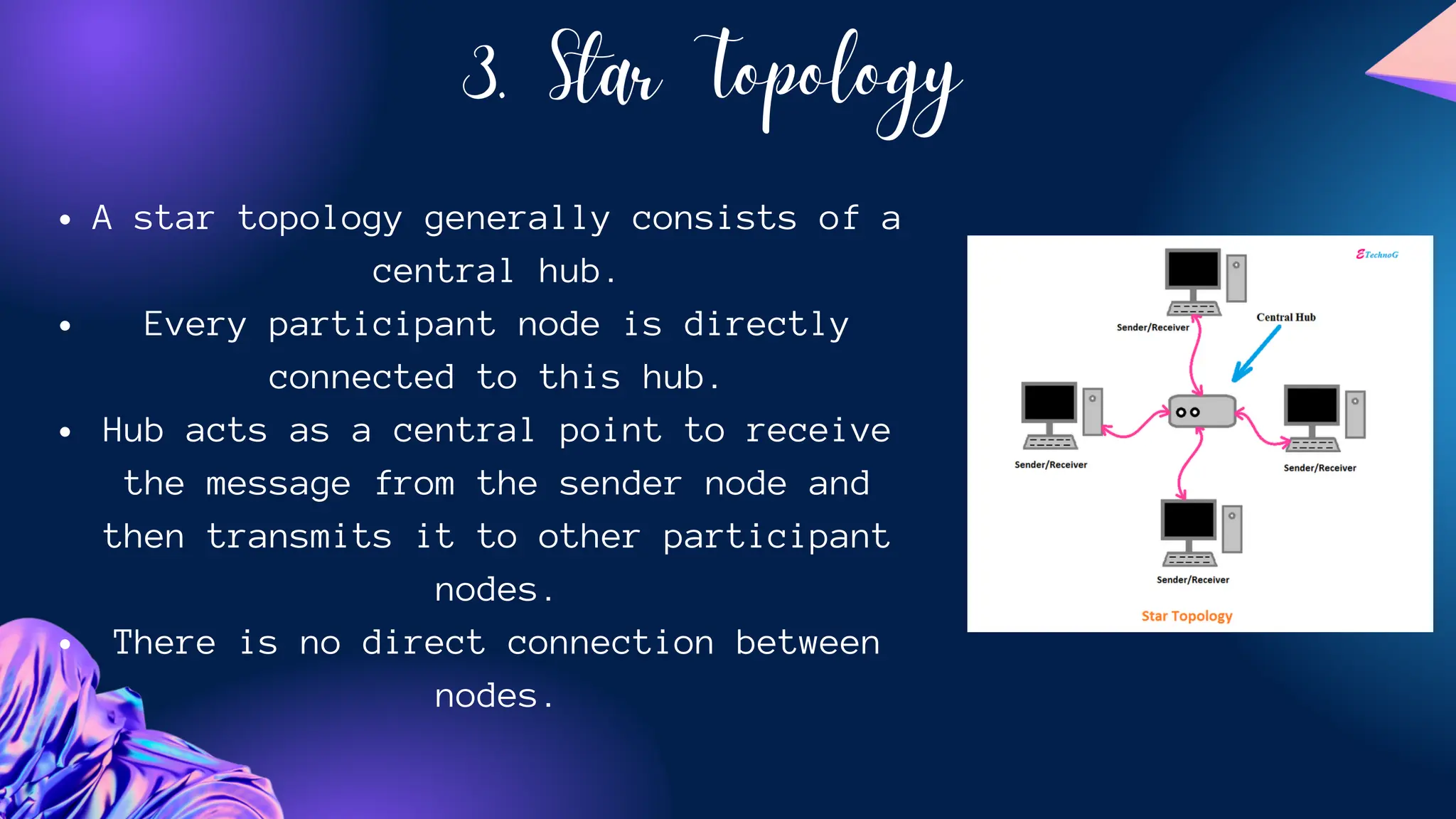
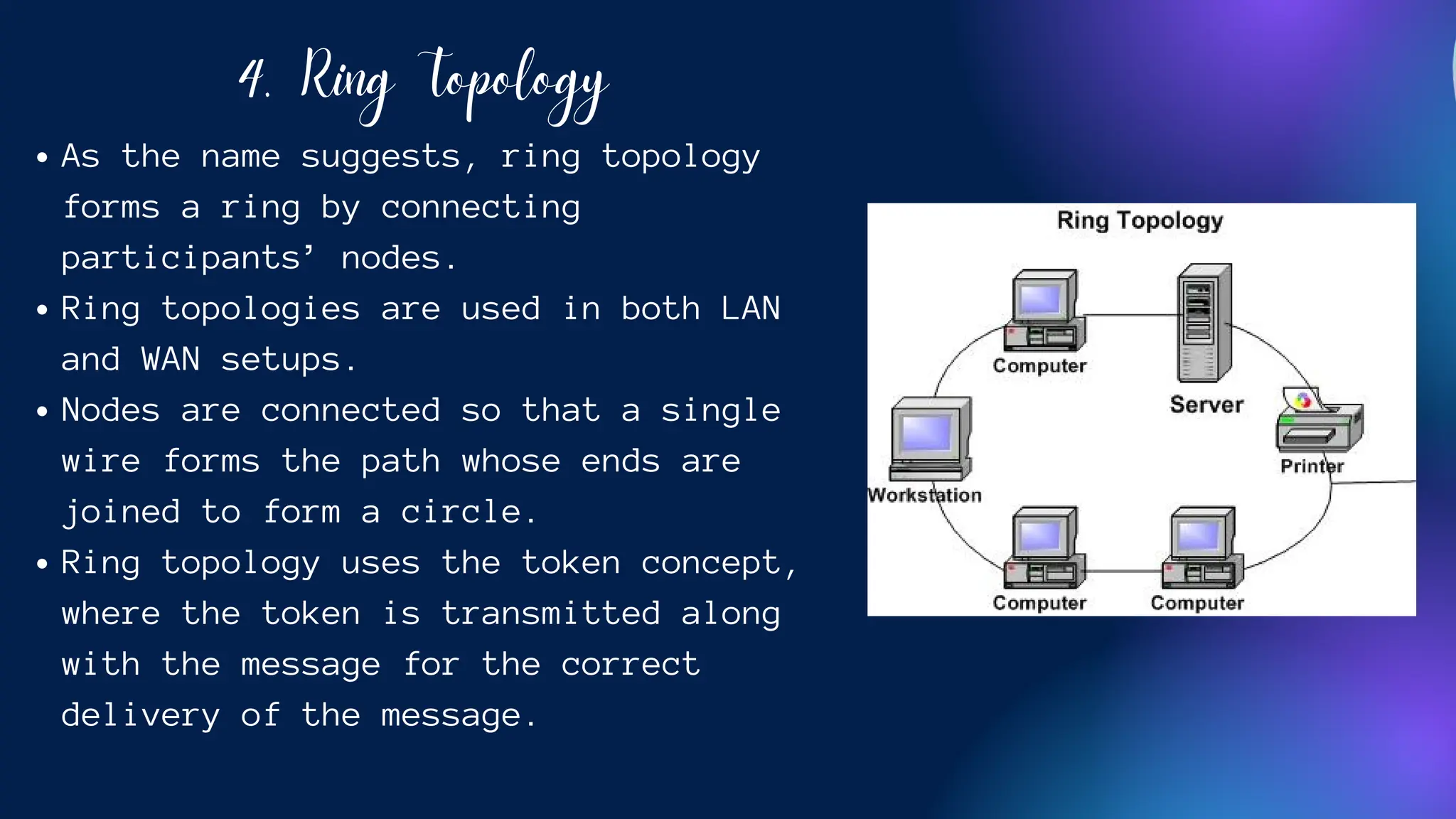
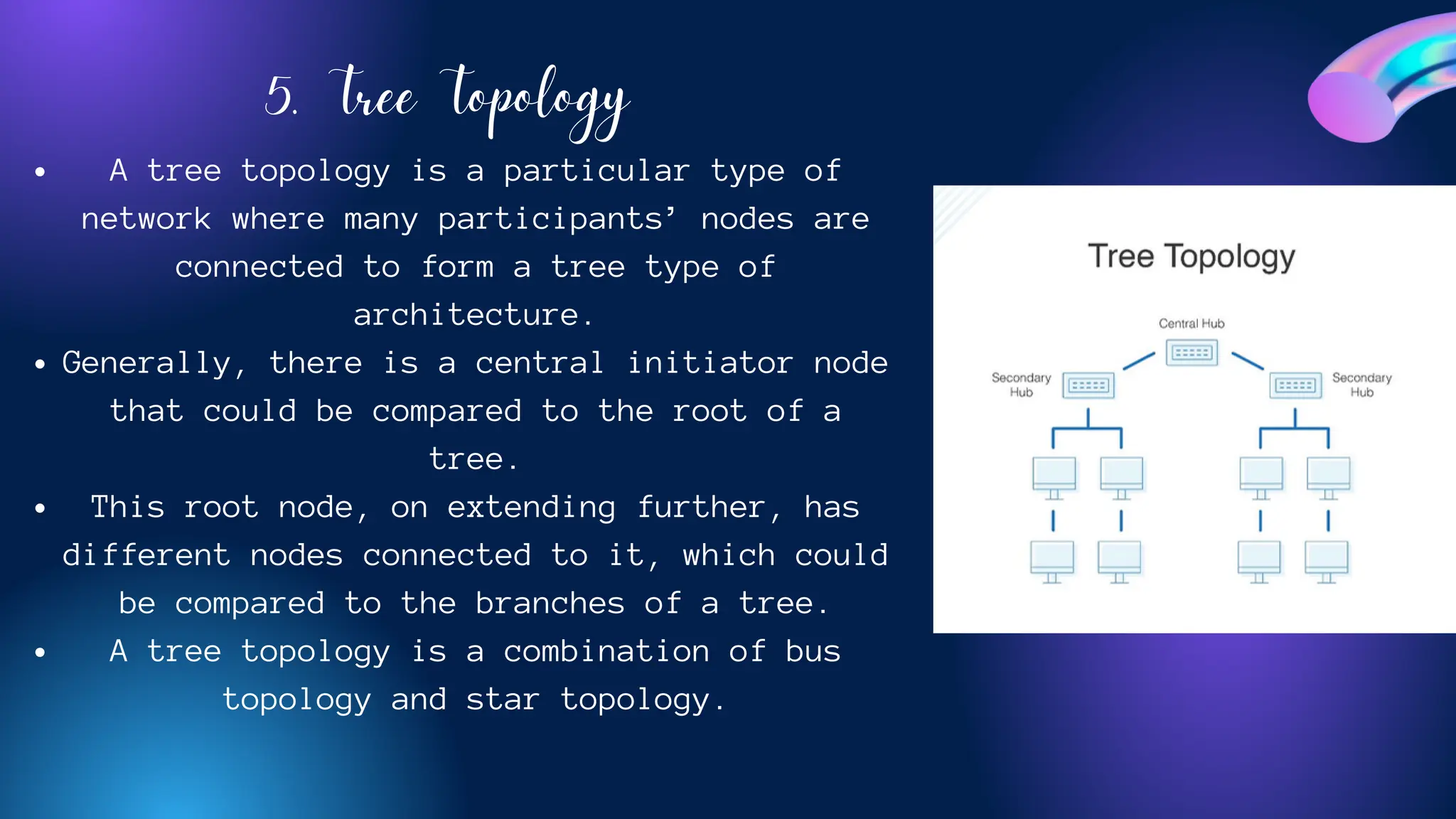
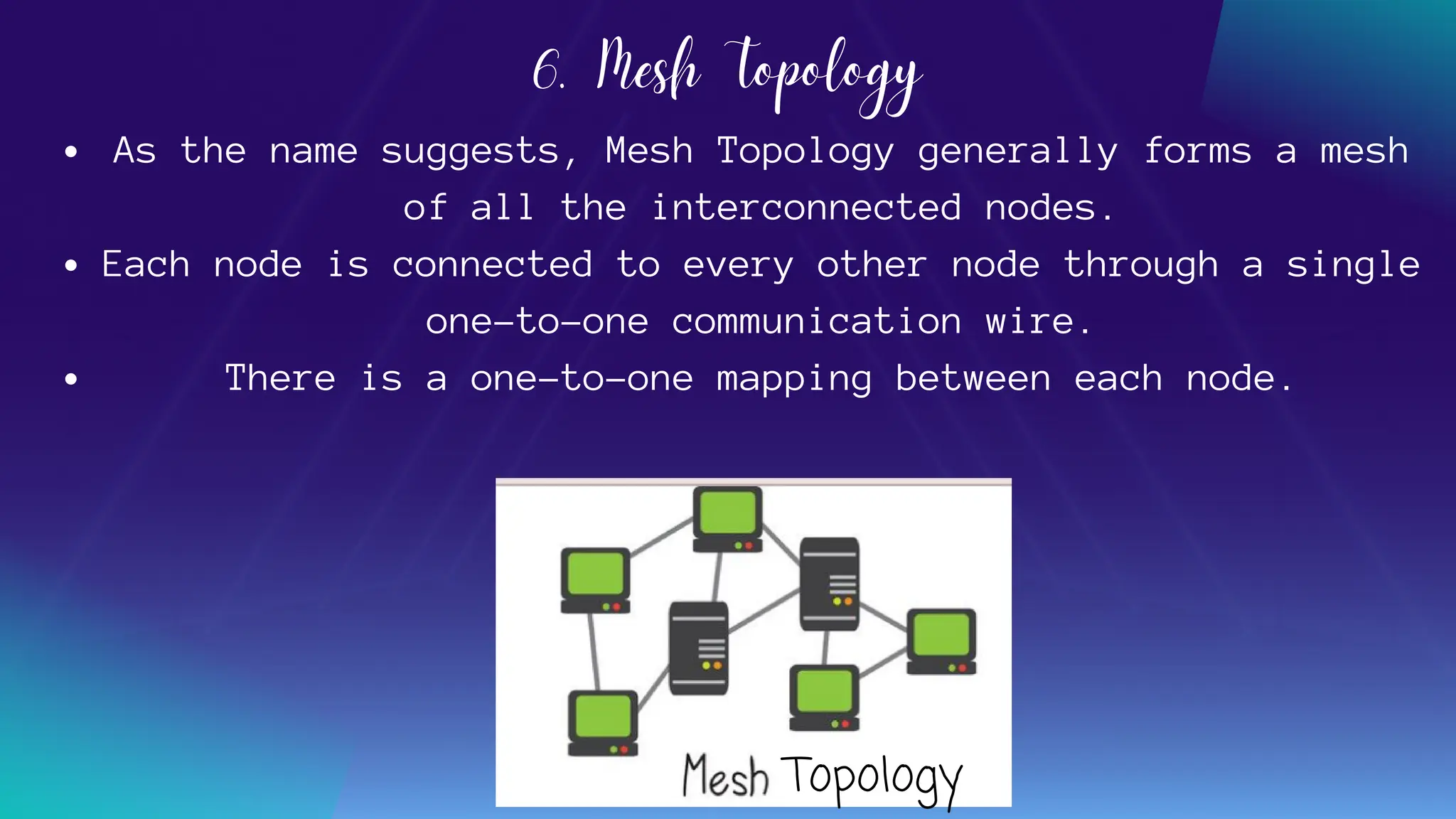
The document provides an overview of various network topologies, including point-to-point, bus, star, ring, tree, and mesh topologies. It explains the structure, advantages, and disadvantages of each topology, emphasizing their applications in network communication. The information highlights the significance of topology in governing data flow and overall network efficiency.