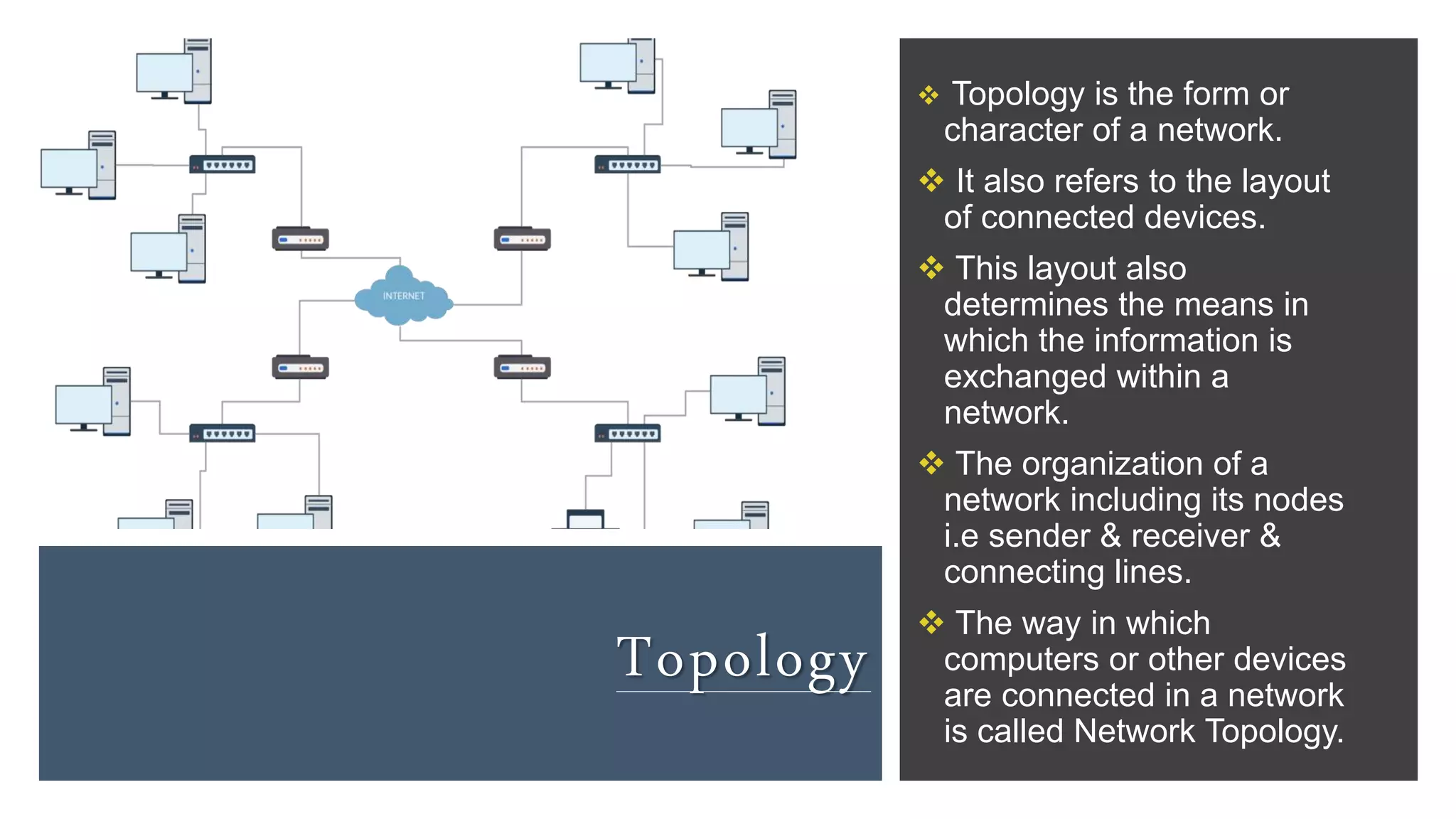
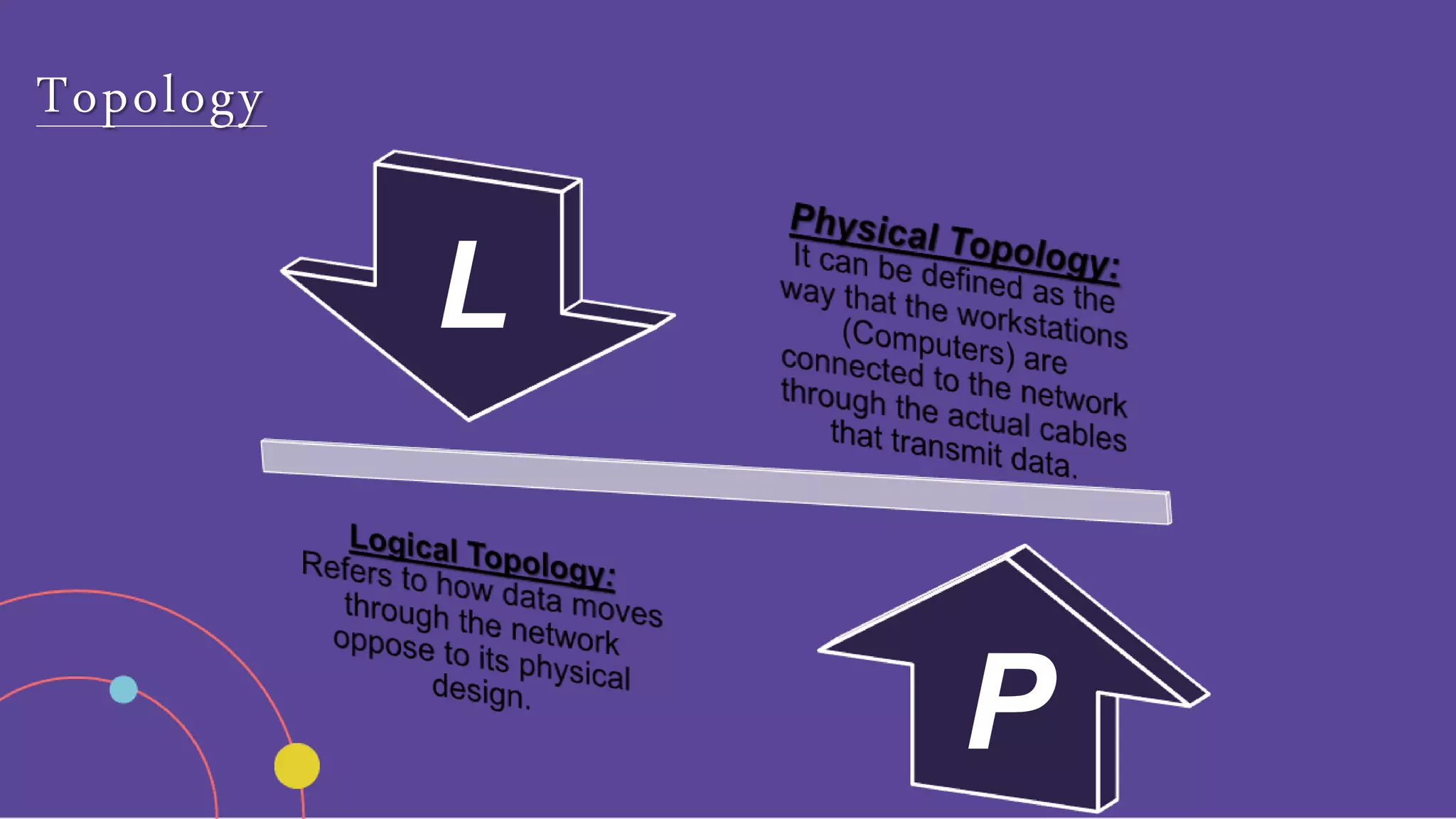
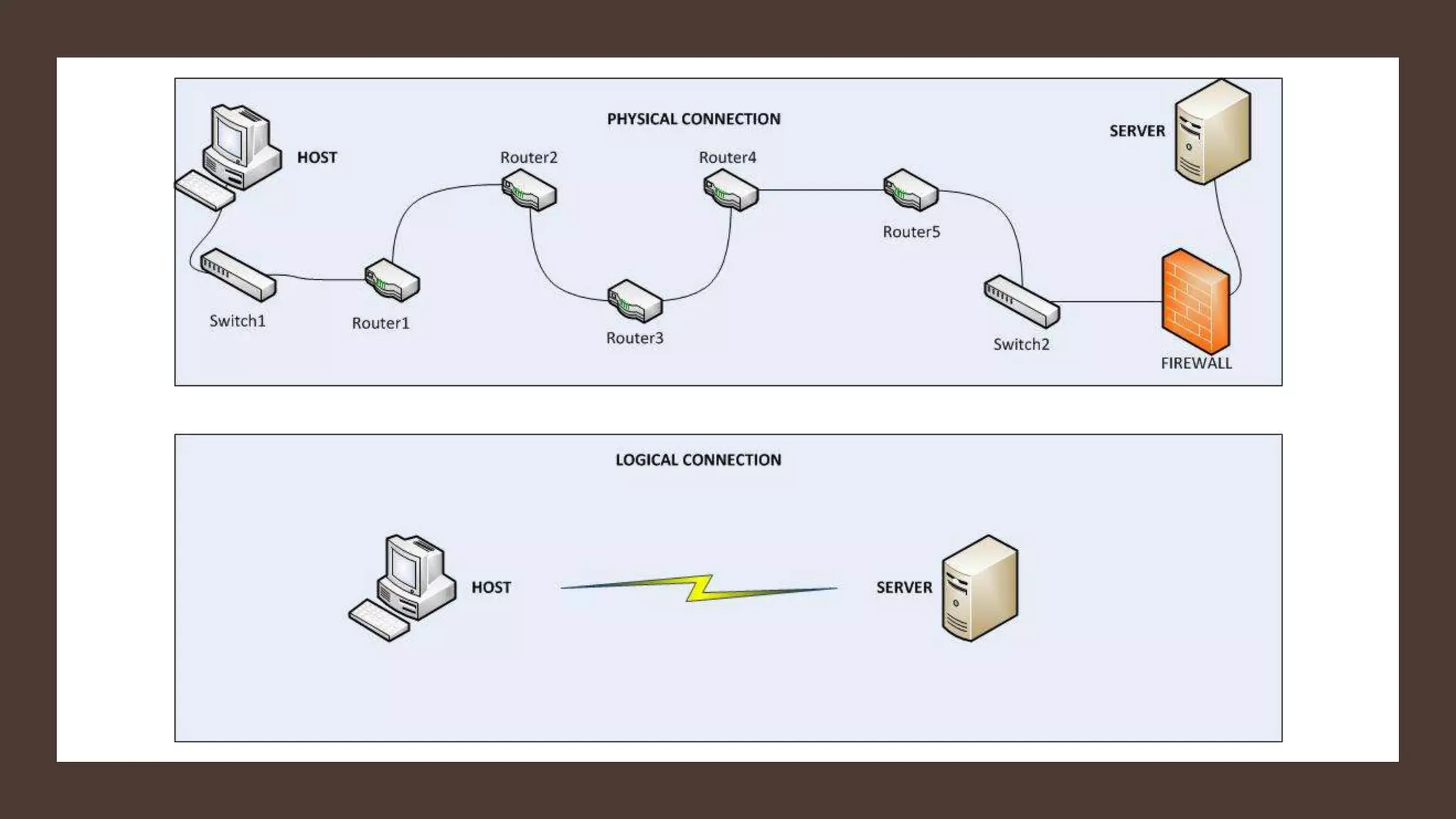
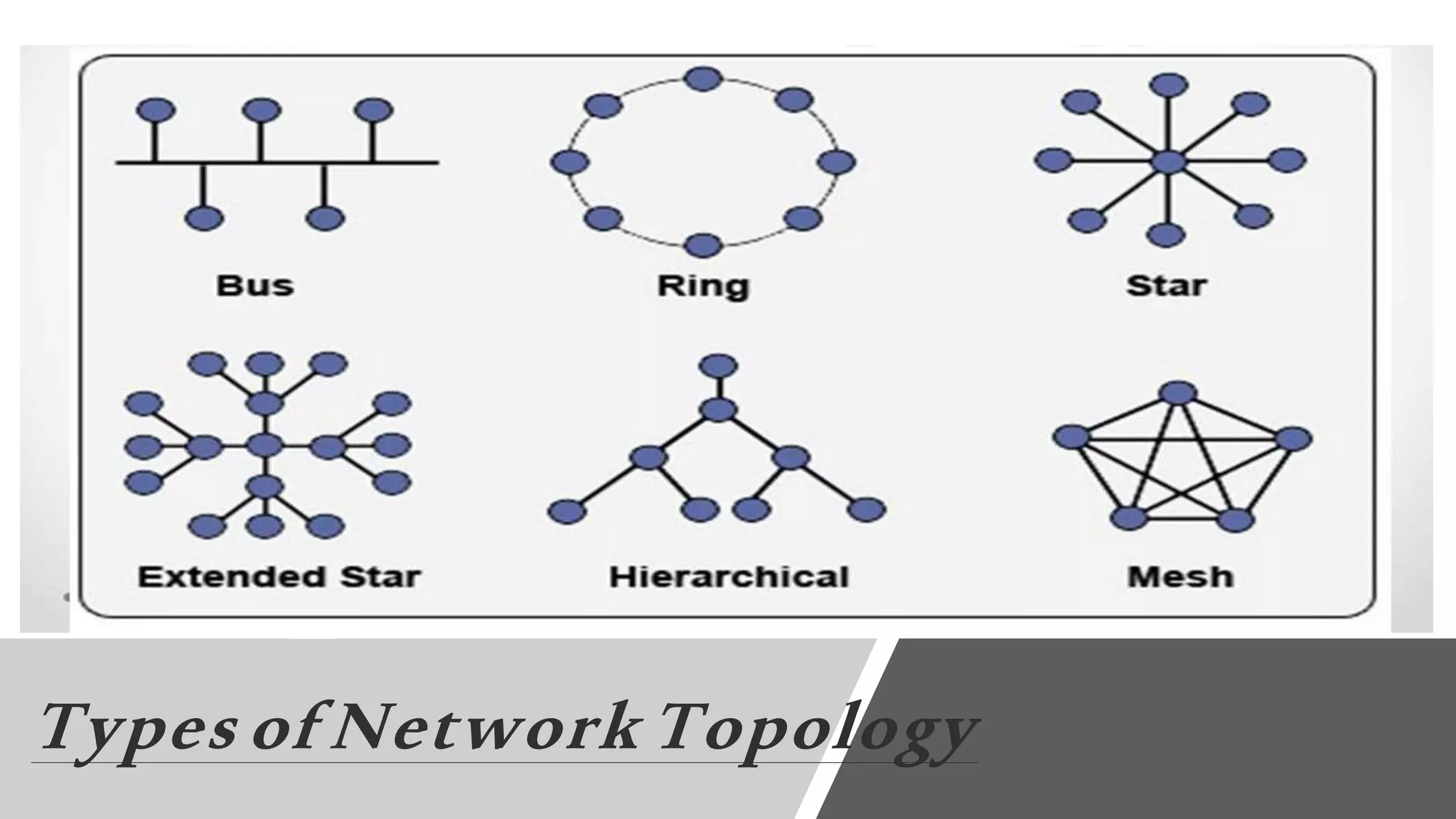
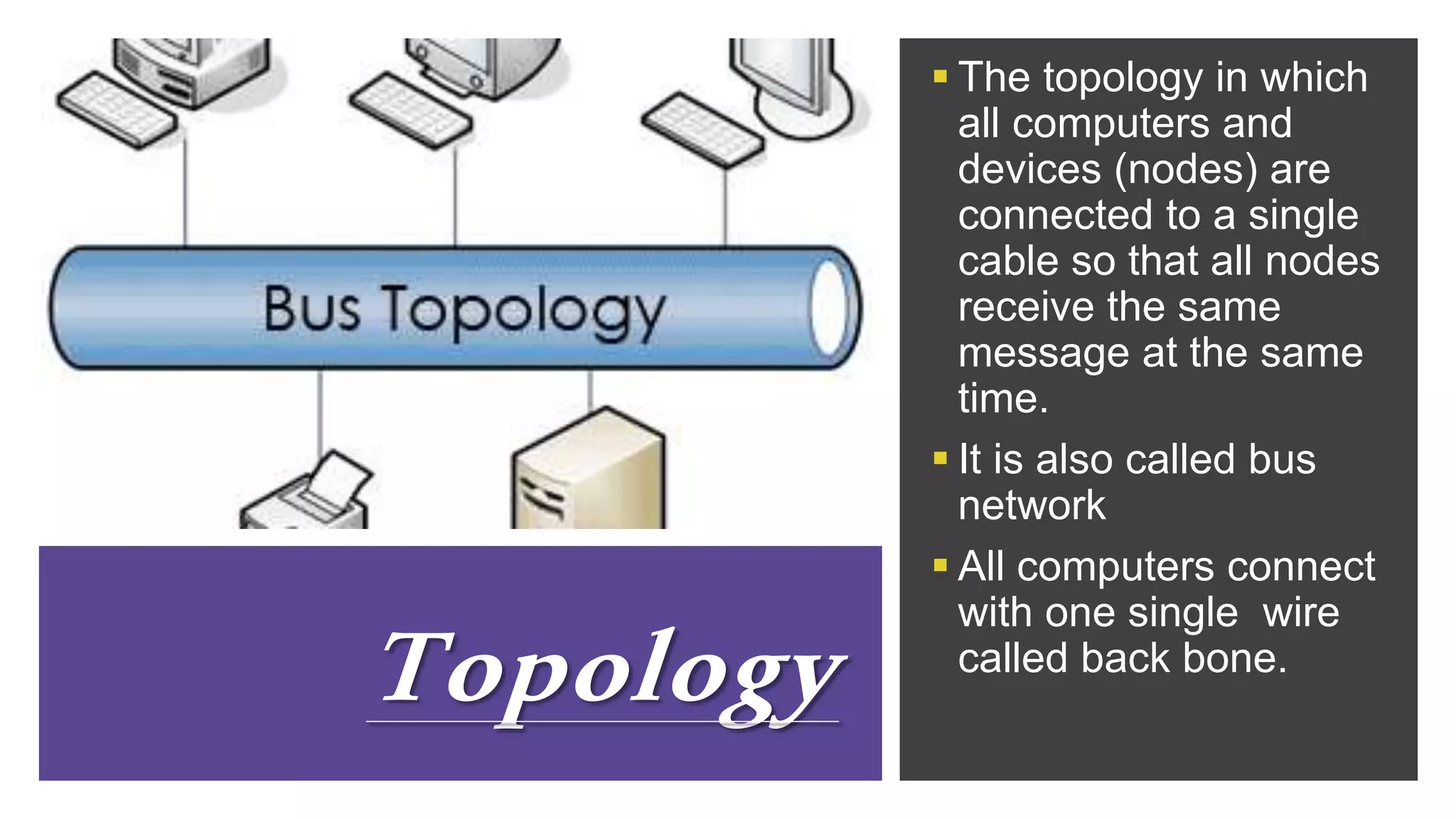
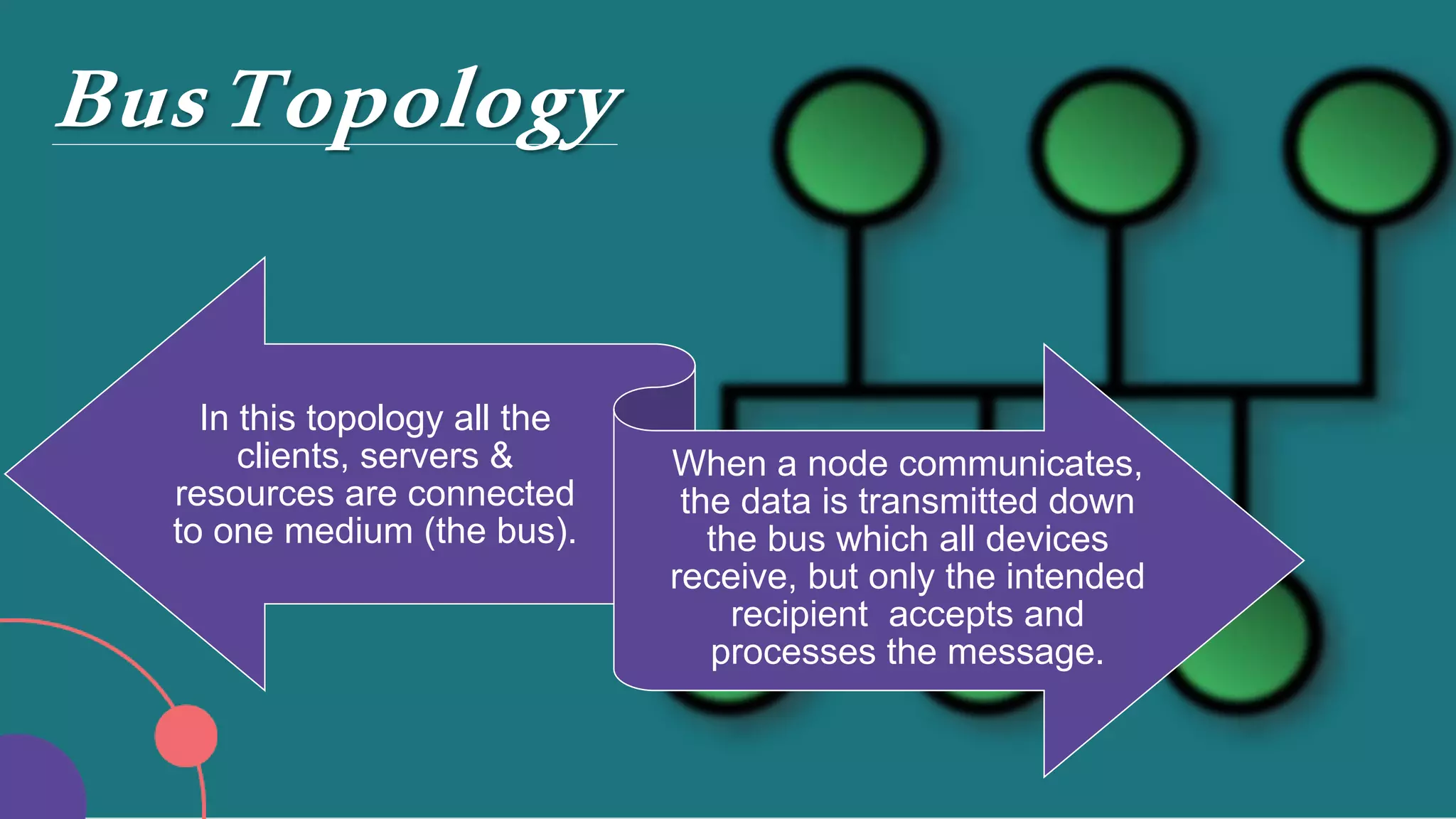
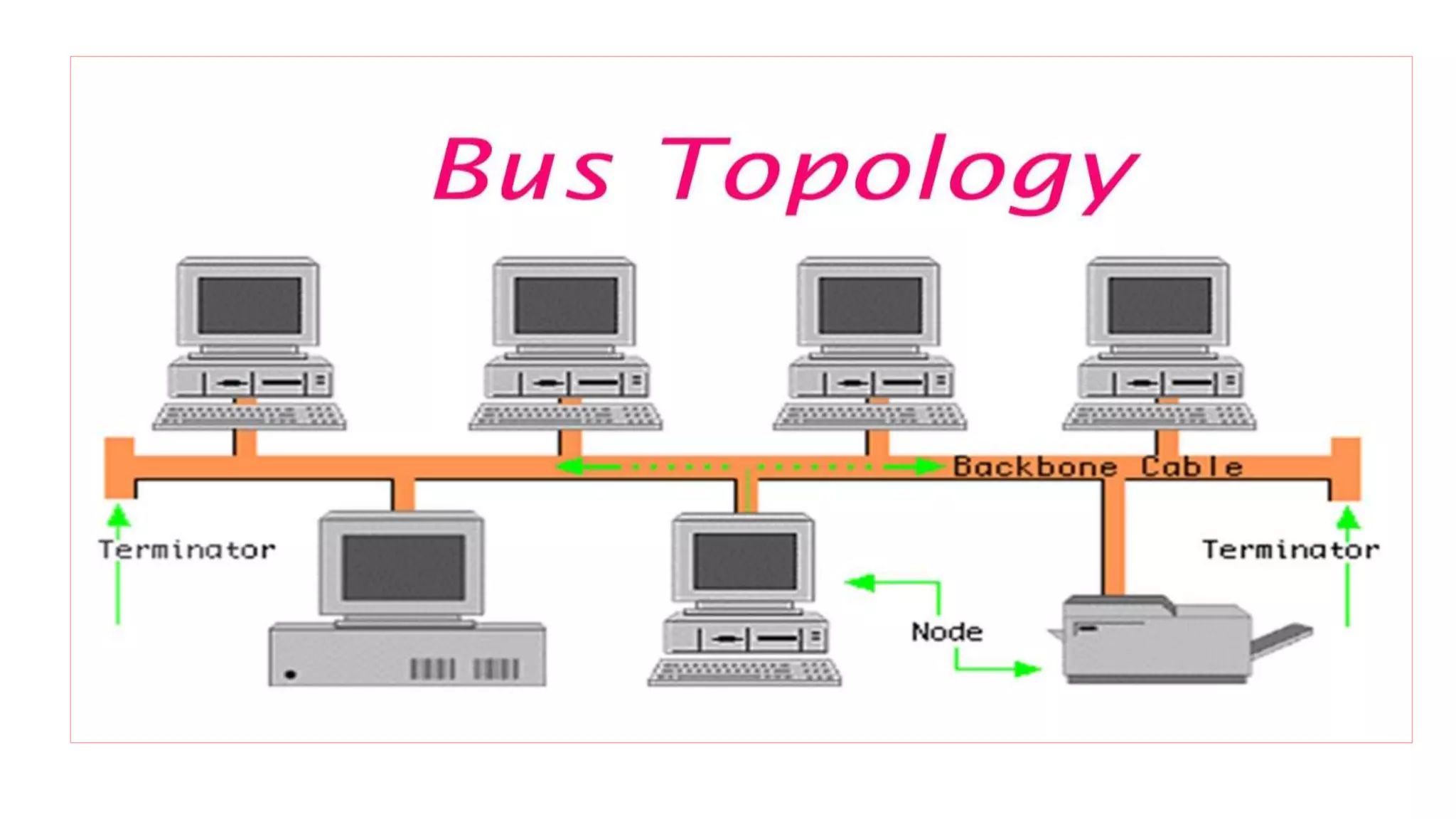
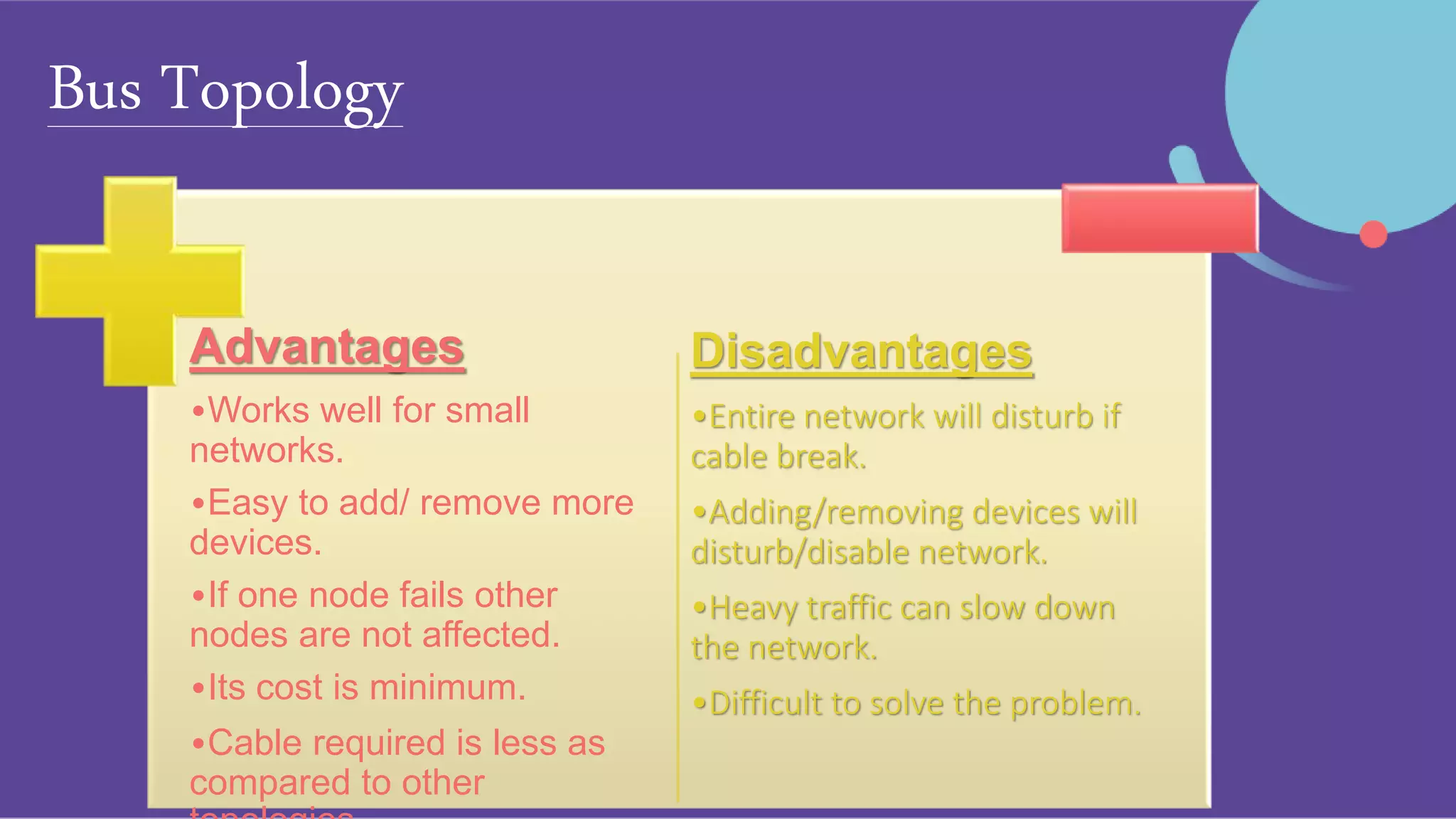
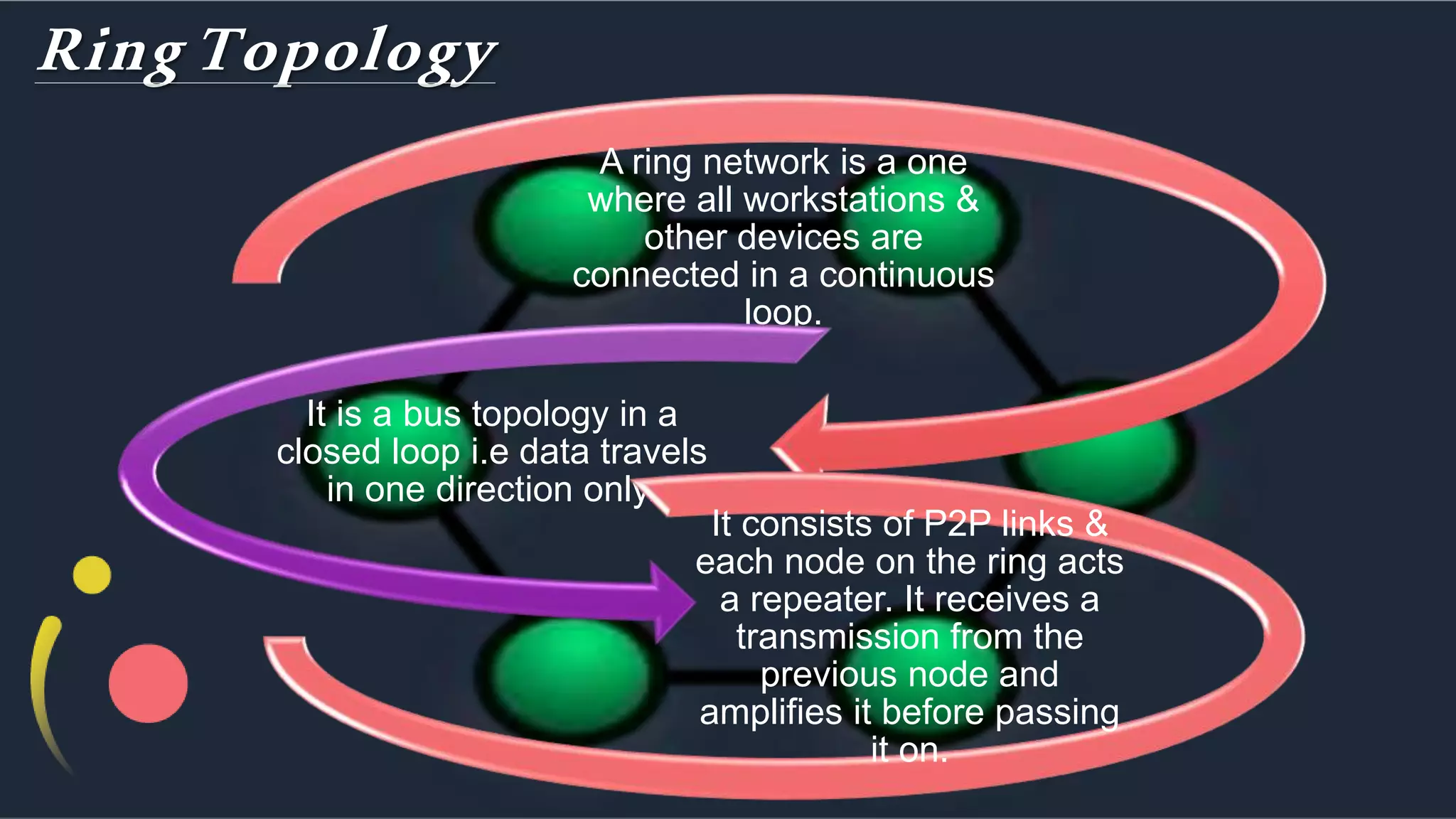
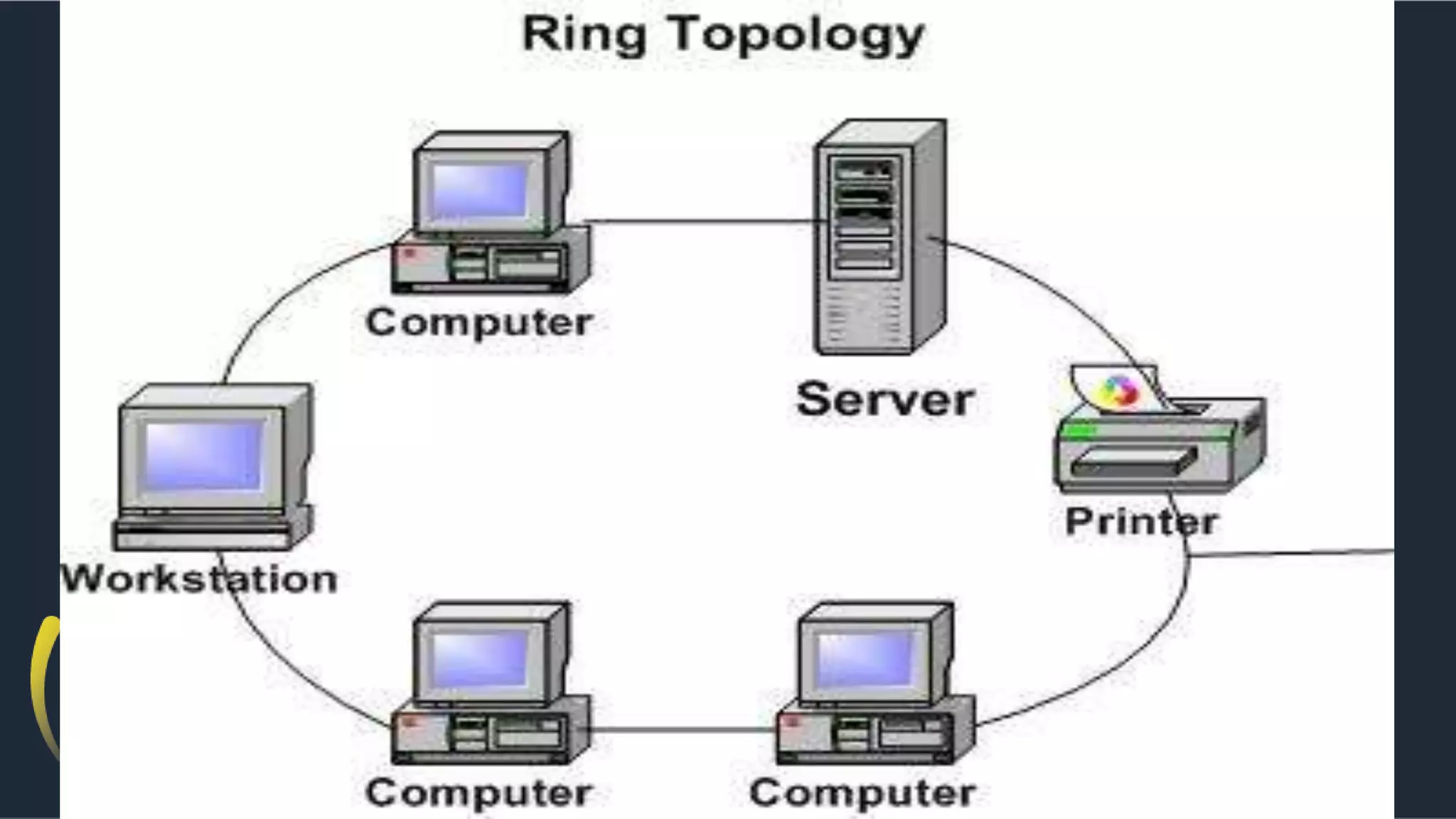
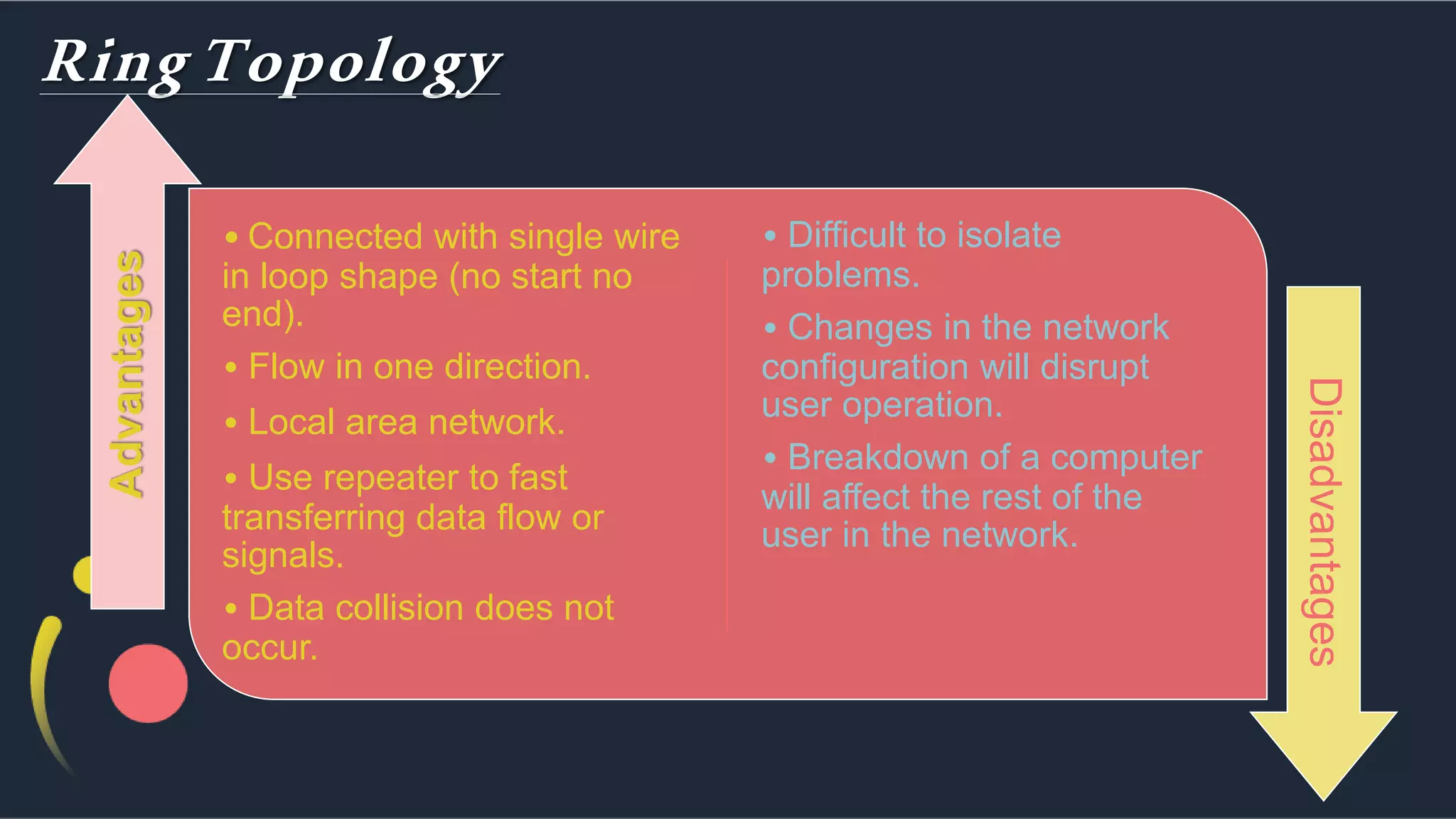
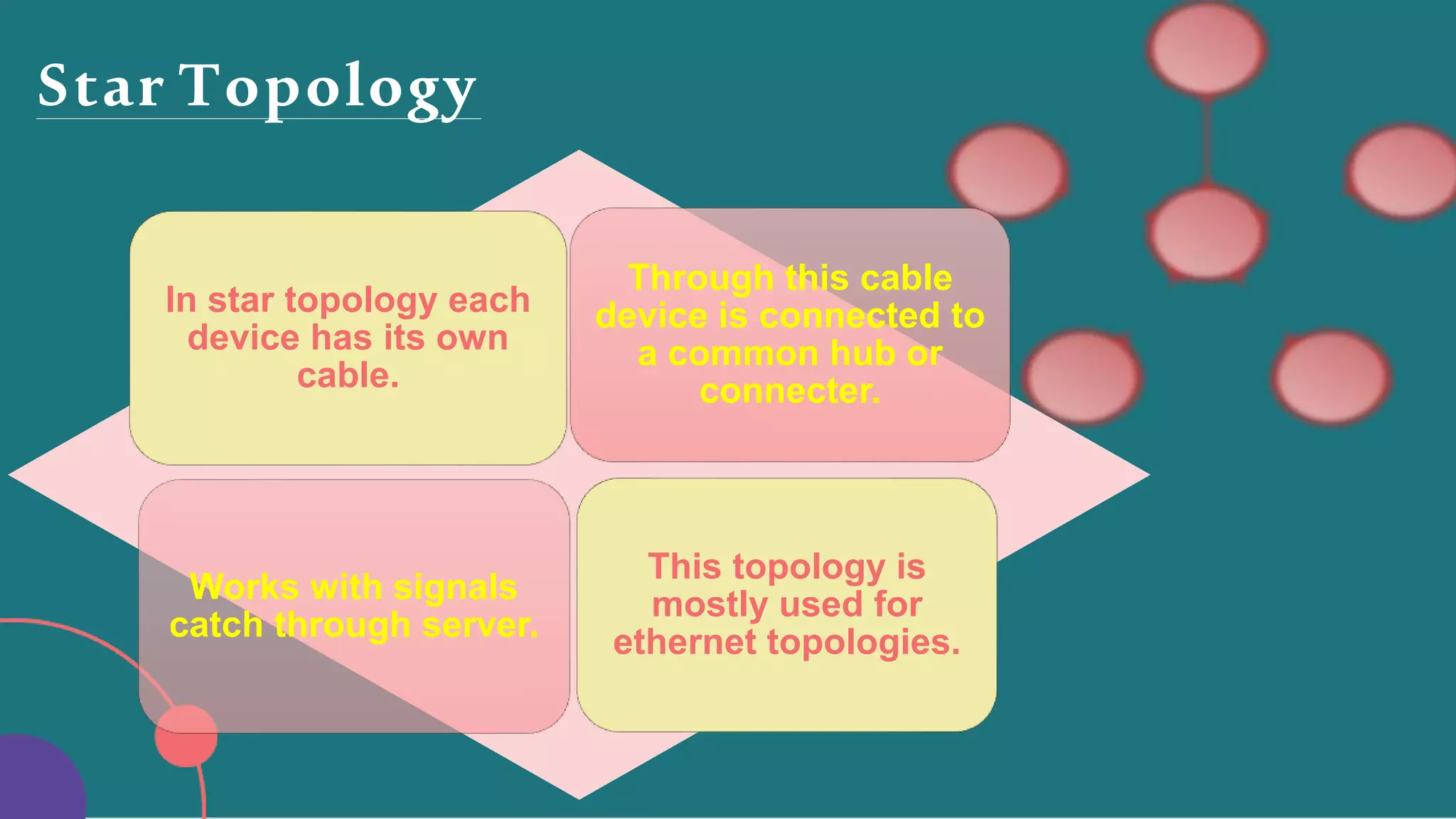
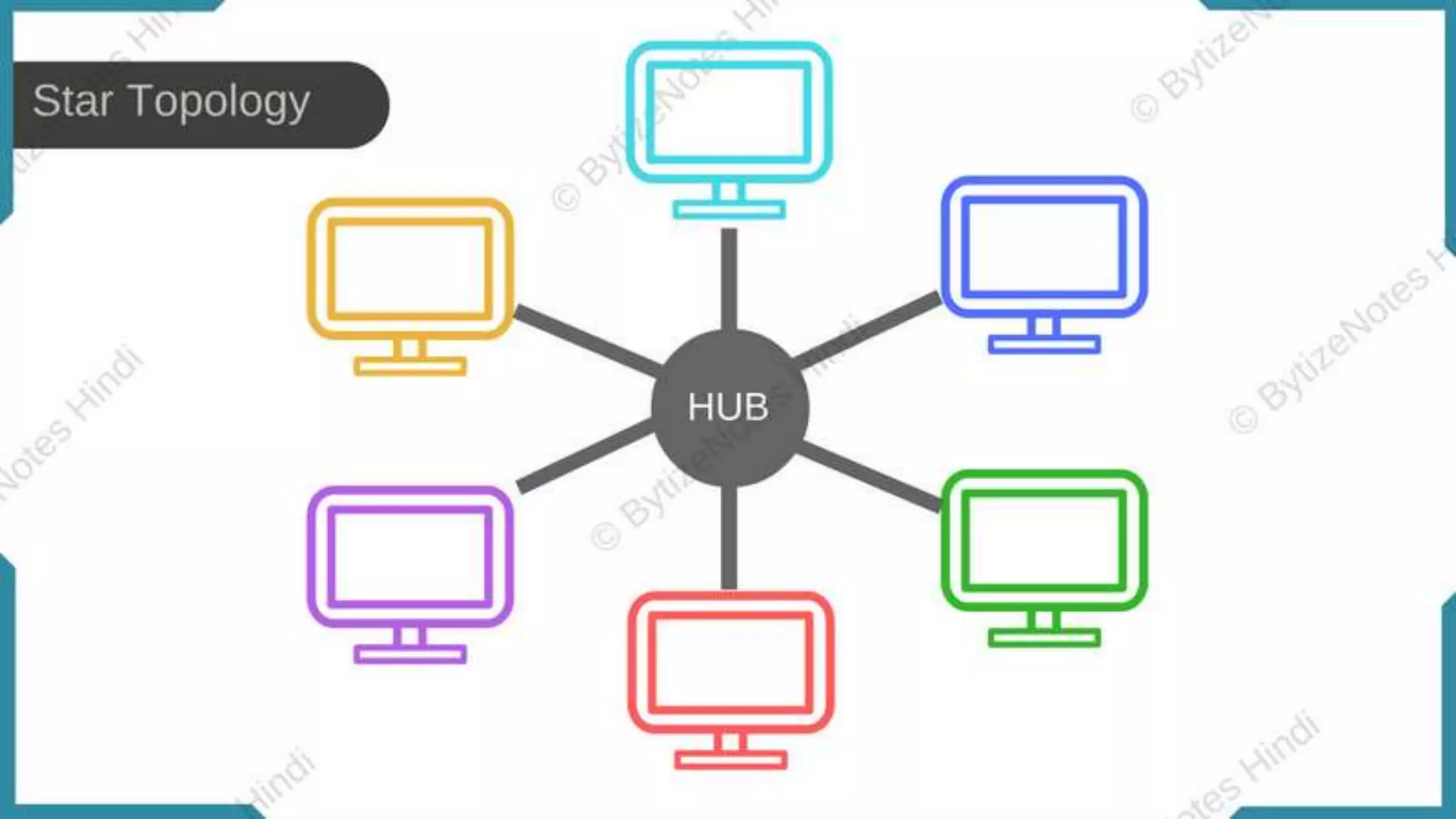
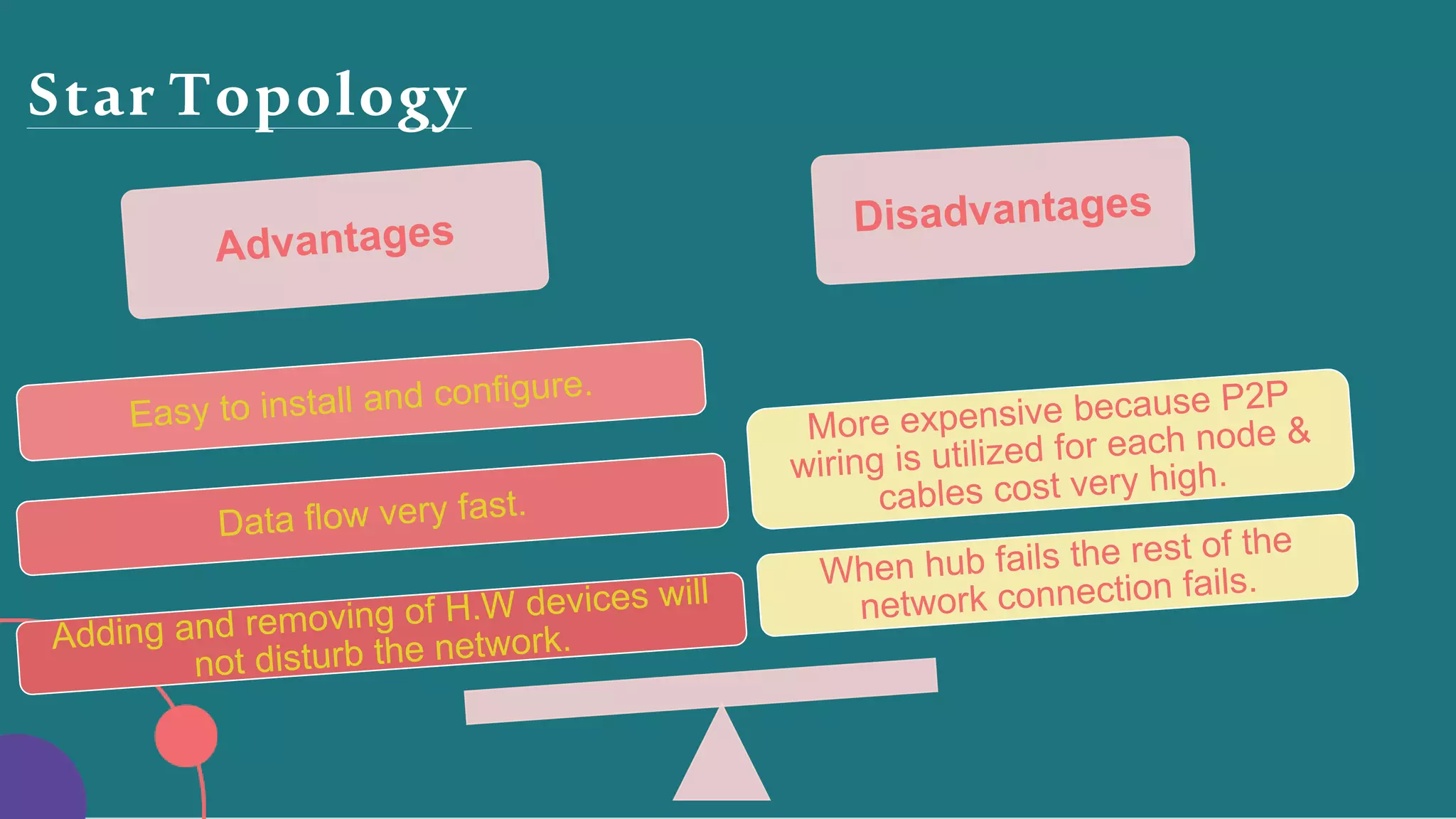
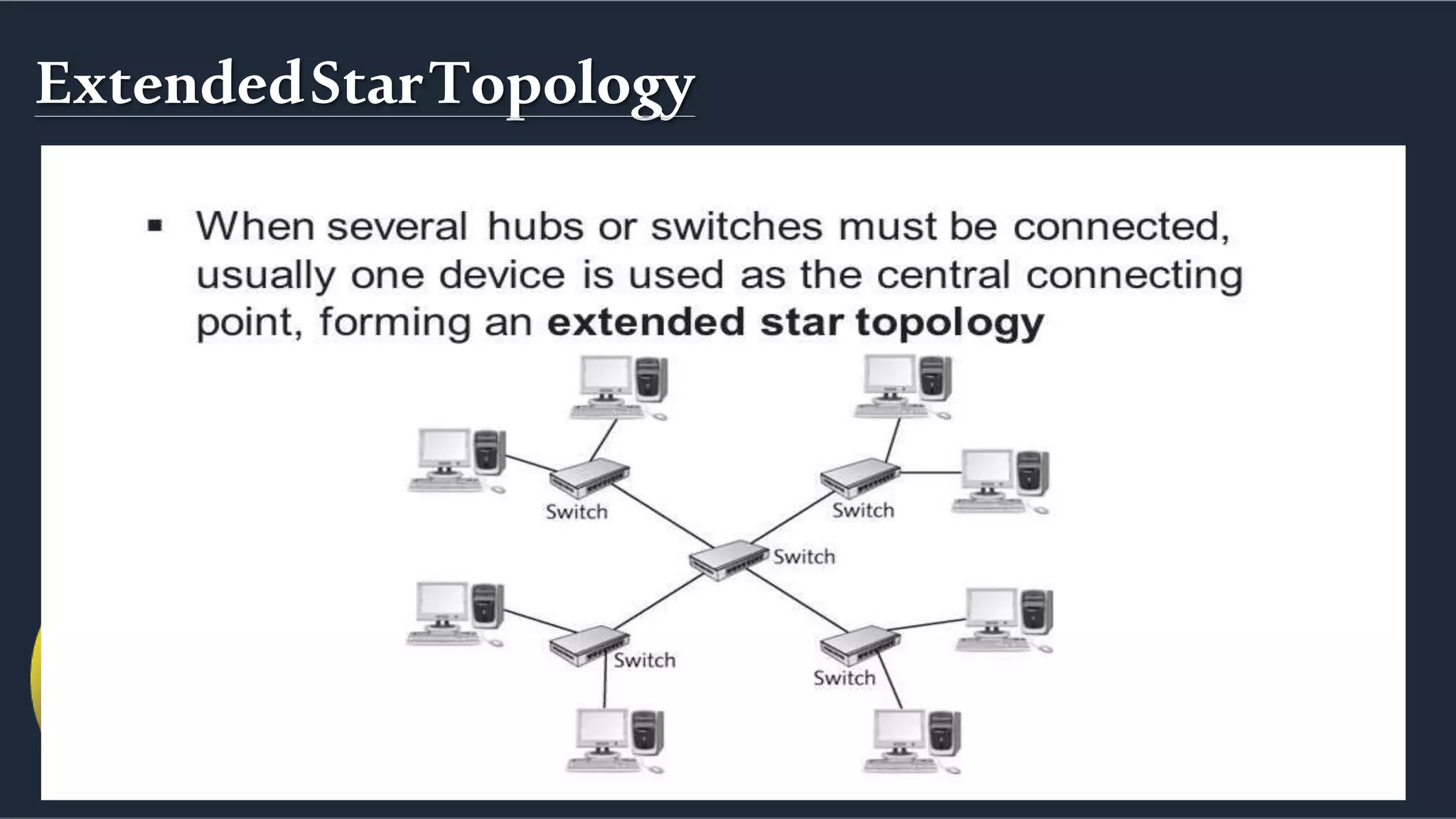
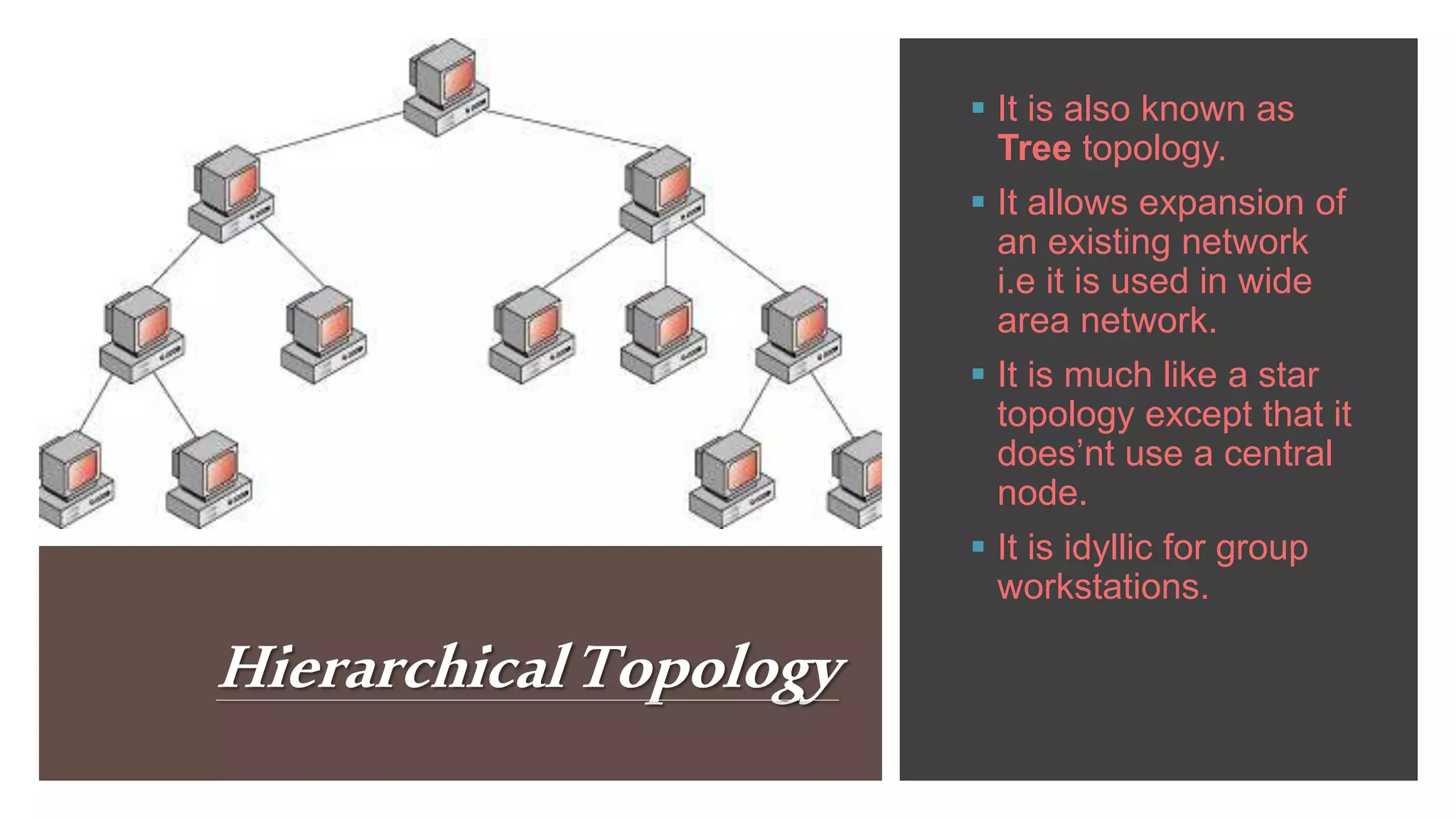
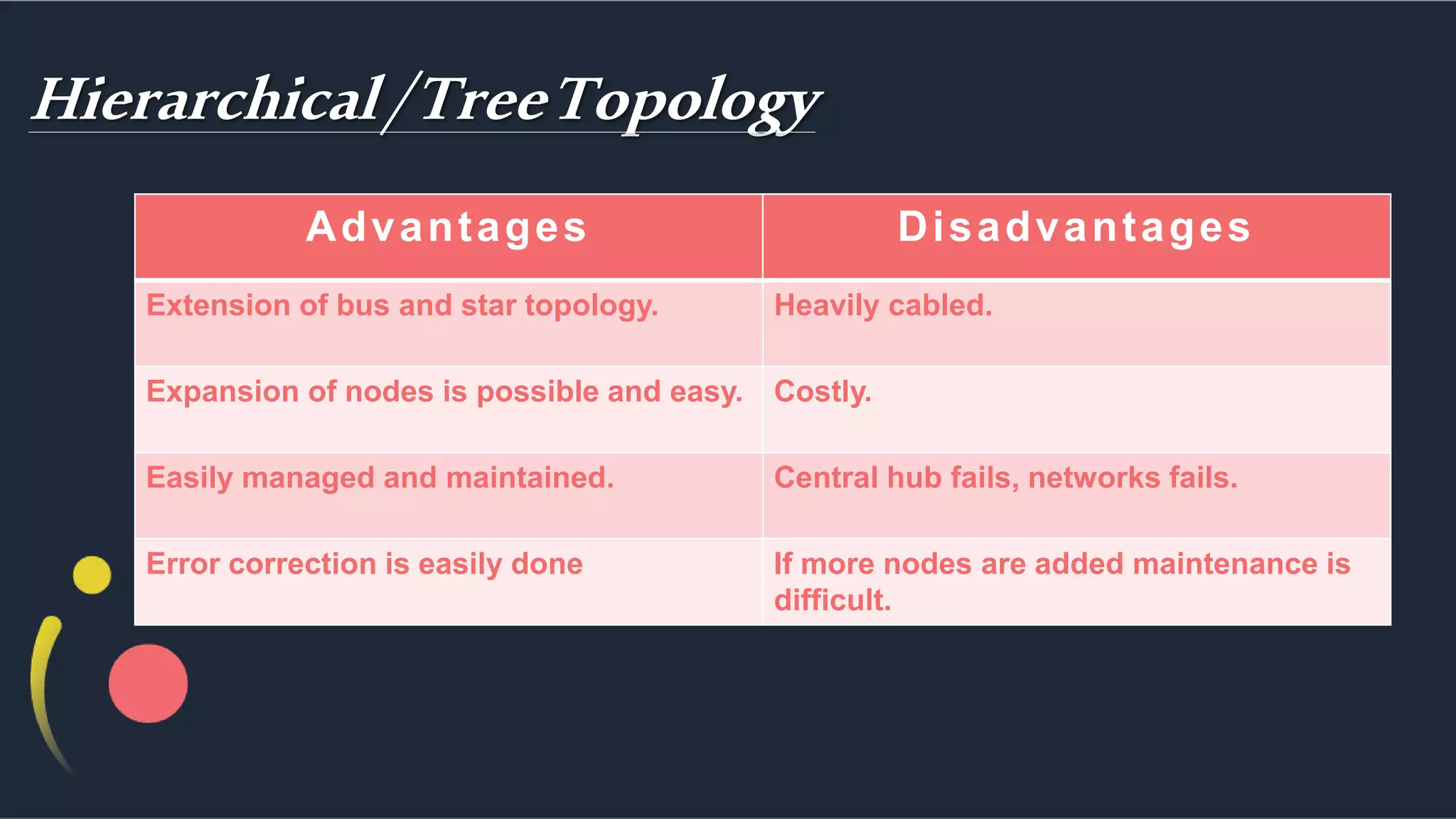
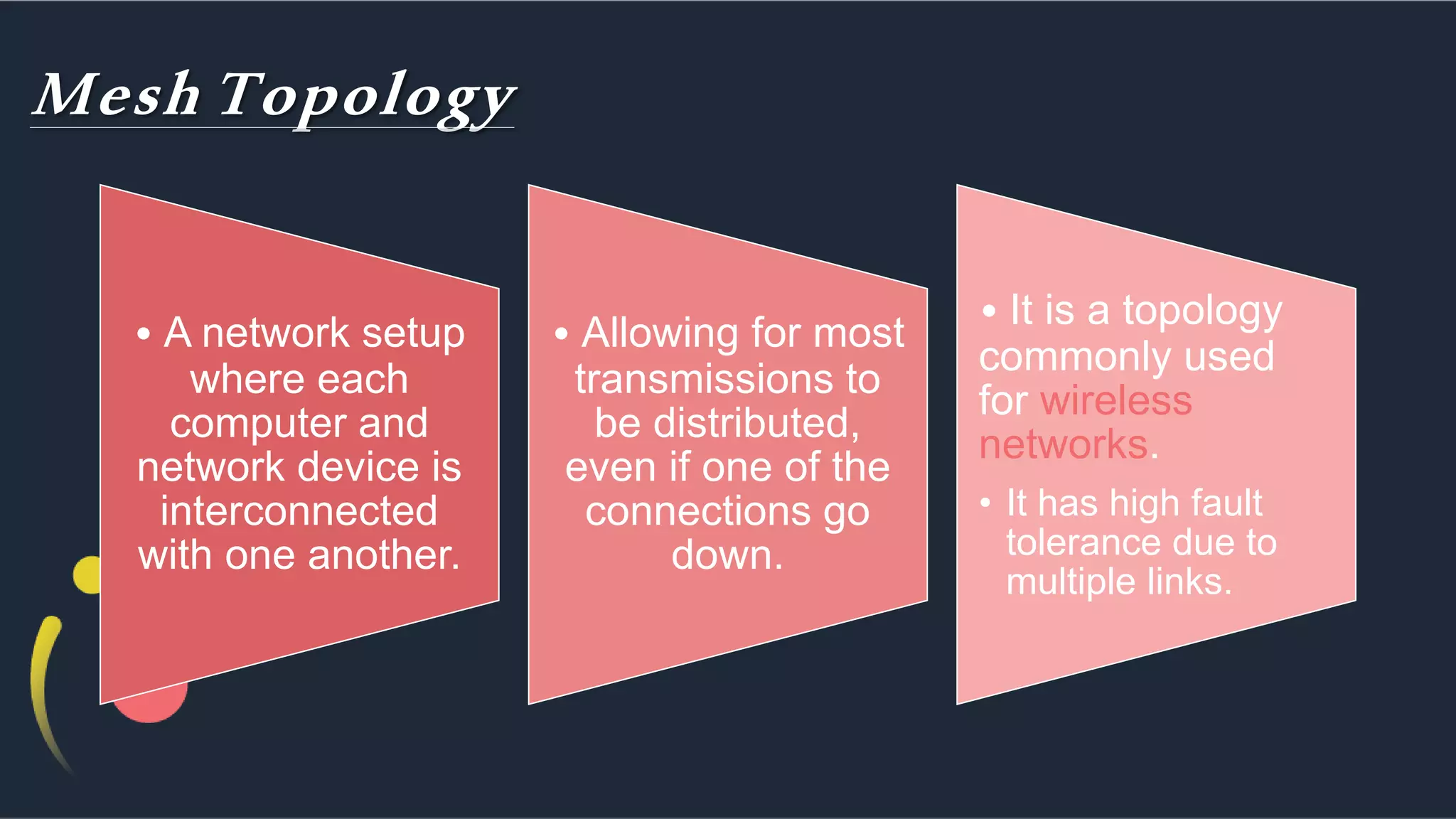
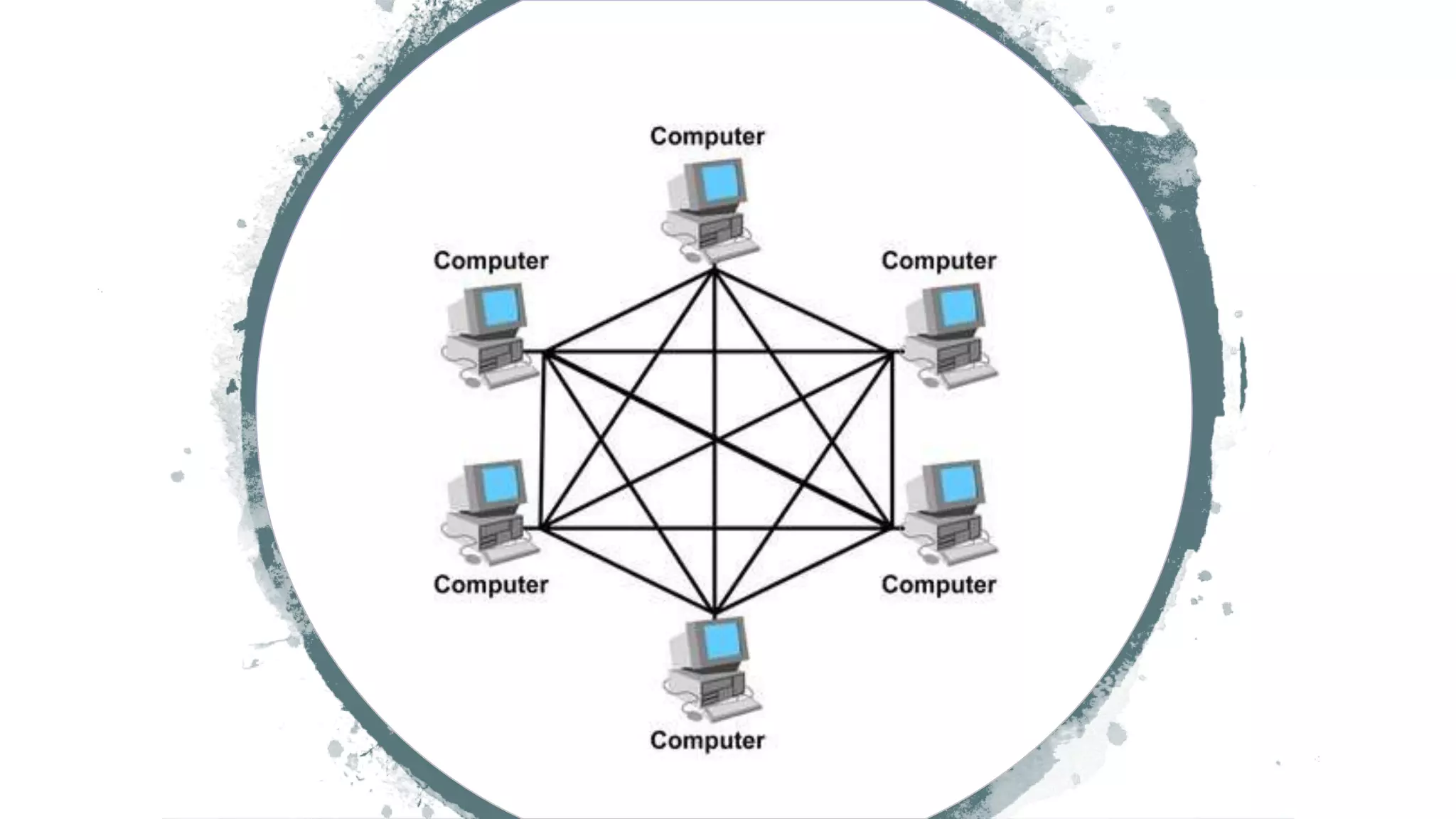
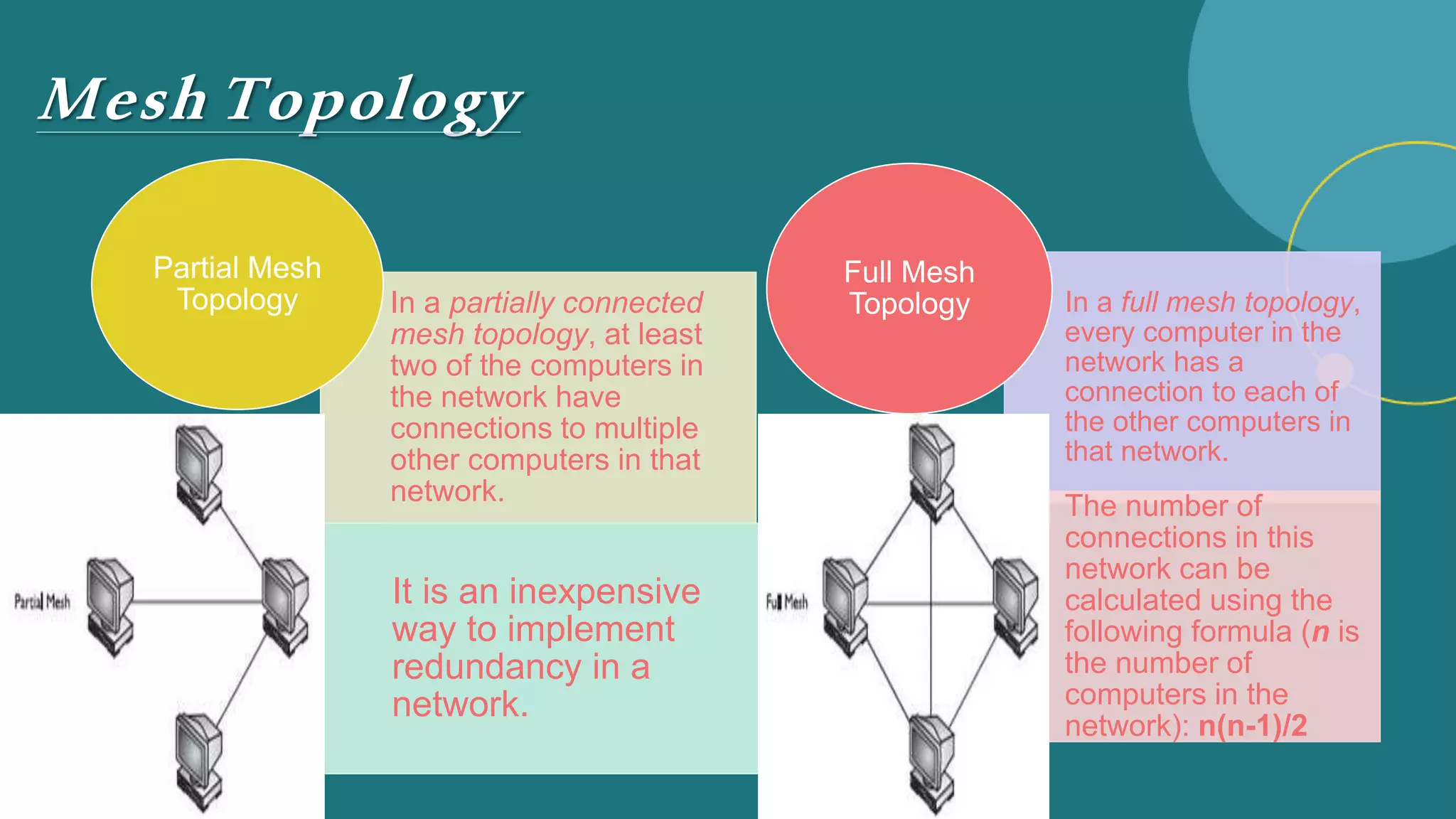
The document discusses different network topologies including bus, ring, star, hierarchical/tree, and mesh. It defines topology as the layout and organization of connected devices in a network and how information is exchanged. It provides details on each topology type, describing their structure and characteristics, and listing their advantages and disadvantages.