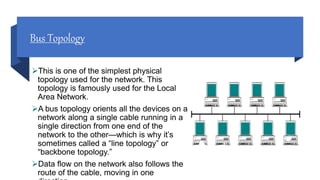
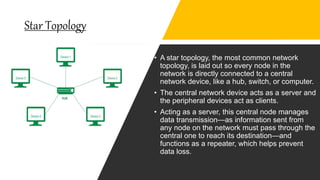
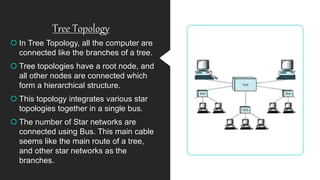
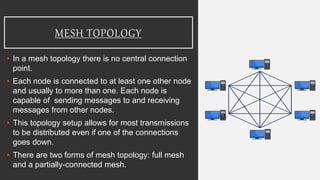
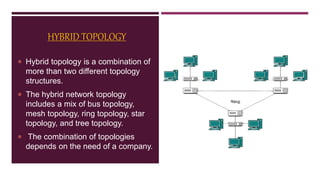
Network topology refers to how devices are arranged in relation to each other on a network. There are two types of topology: physical and logical. Common network topologies include bus, ring, star, tree, mesh, and hybrid. Each has advantages and disadvantages depending on factors like cost, speed, reliability, and ease of expansion. A hybrid topology combines elements of different topologies to meet an organization's specific needs.