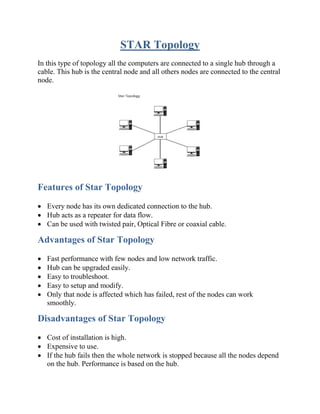
The document discusses different network topologies including physical and logical topologies. It defines network topology as how nodes in a network are connected and how they communicate. It then describes various common topologies - bus, ring, star, tree, mesh, and hybrid - covering their features, advantages, and disadvantages. Key factors to consider when choosing a topology are the number of cables and ports needed, cable length, cable type, cost, reliability, and security.