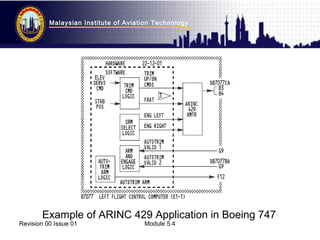
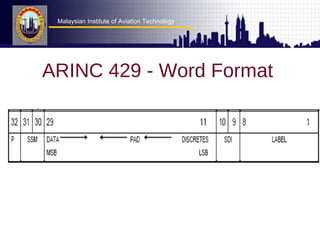
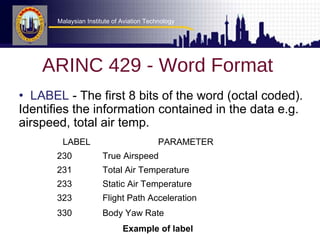
This document discusses data buses used in aircraft systems. It focuses on ARINC specifications for digital data transfer between avionics components. ARINC 429 defines how avionic equipment communicates through a point-to-point data bus using a 32-bit word format. The format includes fields for labels, source/destination identification, data, status information, and parity. ARINC 629 is a newer bidirectional standard used in Boeing 777 that allows periodic or aperiodic transmission at 2 Mbps.