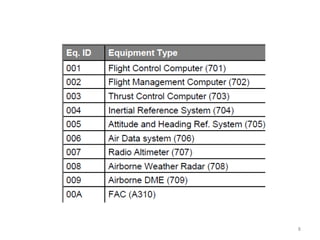
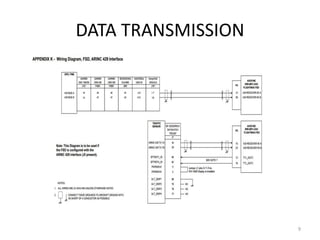
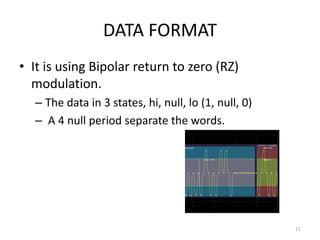
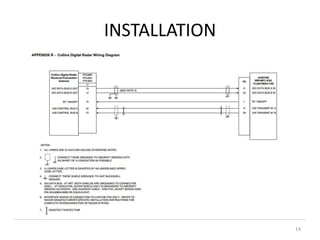
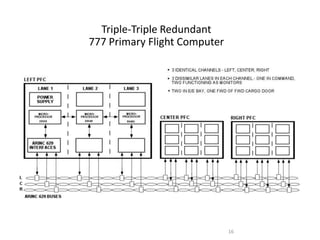
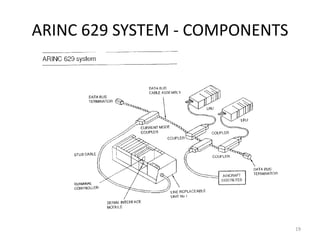
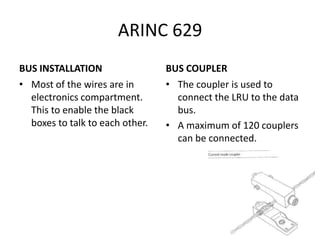
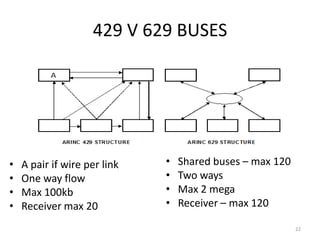
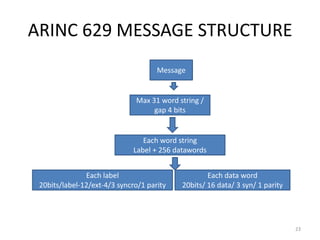
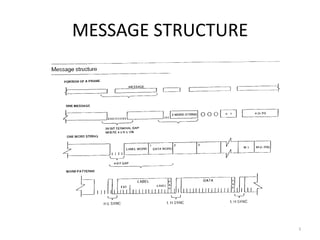
The document discusses data hierarchy and the structure of data buses, including concepts of bits, bytes, words, fields, and records. It specifically details the ARINC 429 and ARINC 629 data buses used in avionics, highlighting their specifications, data transmission characteristics, and message structures. The ARINC 429 operates on a 32-bit serial bus with one-way data flow, while ARINC 629 can handle multiple terminals and supports higher data rates.