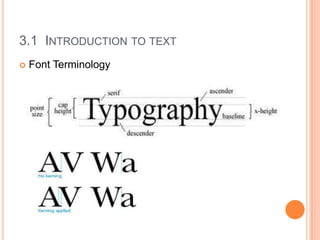
The document discusses text and fonts. It defines text as a human readable sequence of characters that form words to explain or describe subjects and contexts. Fonts are sets of printable text characters in a specific style and size, also called typefaces. Fonts are classified based on proportion, serifs, shape, weight, and new technological creations. Common font proportions are monospaced and proportional. Software like MS Word and PowerPoint as well as Adobe products can be used to create and edit text.