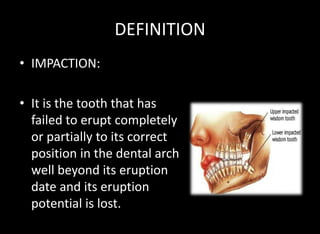
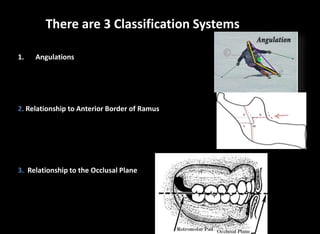
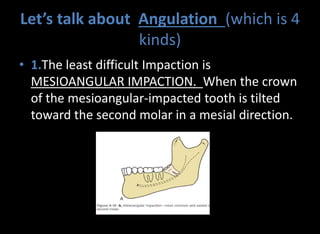
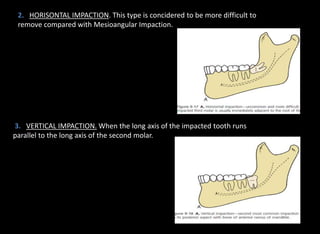
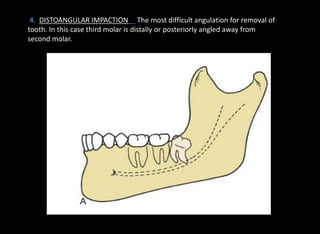
Tooth impaction occurs when a tooth fails to fully erupt into the dental arch by its expected eruption date. Commonly impacted teeth include third molars, maxillary canines, and premolars. Causes of impaction include local obstructions, lack of space, and systemic factors like hormonal disorders or hereditary conditions. There are three classification systems for impacted teeth based on their angulation, relationship to the anterior border of the ramus, and relationship to the occlusal plane. Mesioangular and horizontal impactions of third molars are most common and can require surgical removal.