Tonsillectomy is the surgical removal of the palatine tonsils. It is indicated for recurrent throat infections, tonsillitis causing medical issues, or enlarged tonsils obstructing breathing.
Pre-operative assessment involves evaluating the patient's medical history, examining the throat, and in some cases checking coagulation or doing a sleep study. Certain conditions like bleeding disorders or Down syndrome require special pre-operative management.
The surgery involves using various techniques like dissection and snare to separate the tonsils from surrounding tissue and remove them. Post-operative care focuses on pain management, diet, hygiene and watching for potential complications like bleeding or infection. Newer techniques aim to reduce morbidity through less invasive procedures


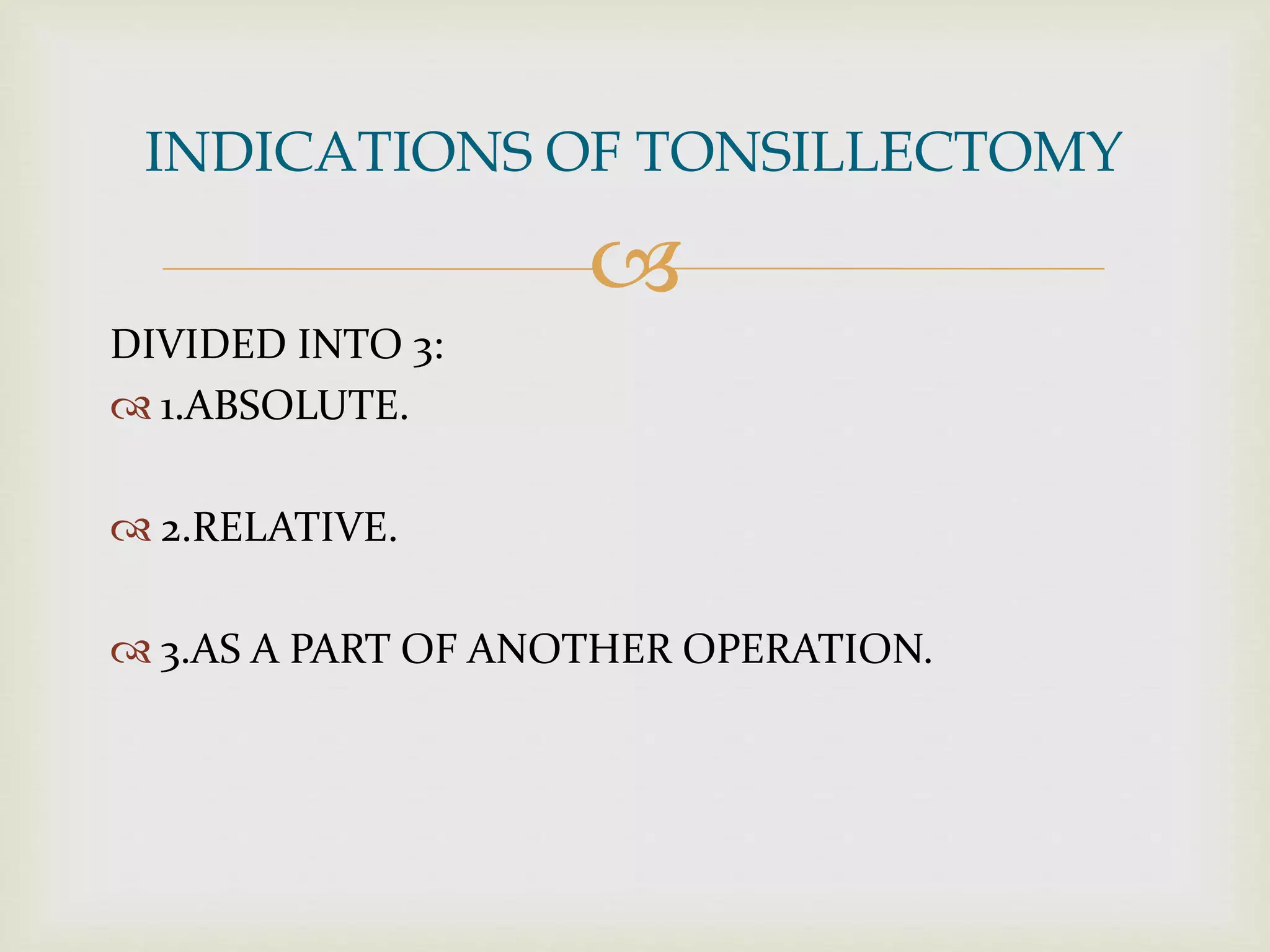


















![
Other Tests
Antibodies for streptolysin-O (ASLO) have been
studied as possible indicators for tonsillectomy. [2]
These antibodies are correlated with previous
infection with group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus
(GABHS)..
When the diagnosis of recurrent GABHS is
questioned, high ASLO titers can shed light on the
patient's history.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tspro-180506185240/75/Tonsillectomy-22-2048.jpg)





















