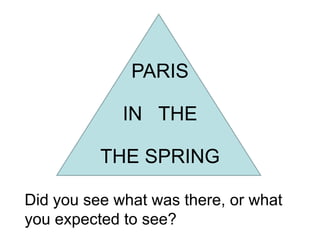
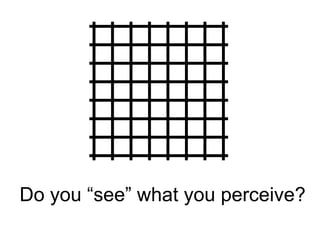
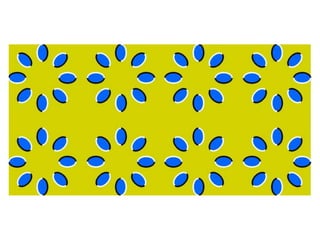
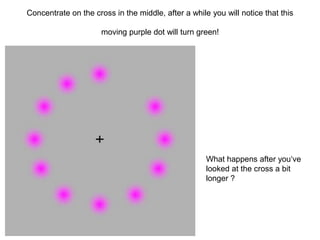
This document discusses issues with relying on sense perception as a way of knowing. It provides examples of how we may fail to see something that is there or see something that is not there. Images shown may lead us to see what we expect rather than what is actually there. Moving images and sounds can also be problematic in similar ways. Our perceptions are subject to the limitations of our sensory systems and psychological effects, so what we experience may not accurately represent the external world. In summary, sense perception has limitations and is not always a reliable way of knowing.